CORRECTION OF LAST REVISION ASSIGNMENT
Integrated pest management is the use of two or more methods of pest control in combating a particular pest affecting a farm. E.g the use of both cultural and chemical methods of pest control on a farm at the same time.
DATE : 11TH AUGUST , 2020.
Hello students and how are you all doing? I hope you are all fine? Today’s revision is on crop pests, however,if you are not too familiar with this topic then your note and textbook on this subject matter should be contacted for more information.
REVISION LESSON
By the end of today’s lesson, you should be able to :
- Define crop pest ;
- State the economic importance of crop pests;
- Classify crop pests;
- State the methods of controlling crop pests;
TOPIC: CROP PESTS.
A crop pest can be defined as any living organism which can cause damage to crop plants either on the field or in the store. E.g Rat , yam bettle , giant rat , grasshopper, weevil etc.
ECONOMIC IMPORTANCE (EFFECTS) OF CROP PESTS.
- Reduction in farmer’s income.
- They reduce the quality of farm produce.
- They predispose crops to secondary attacks by diseases.
- They reduce the viability of stored produce.
- They increase the cost of production in the cause of controlling them.
Now let us go into classification. You will recall that crop pests are classified thus:
CLASSIFICATION OF CROP PESTS.
Crop pests can be classified into two :
Based on location as :
- Field pests;
- Store or storage pests.
FIELD PESTS , i.e , pests that attack crop plants on the field or on the farmland. E.g grasshopper , cotton stainer , aphid, cane rat , white fly, mealy bug, monkey , stem borer etc.
STORE (STORED PRODUCE OR STORAGE ) PESTS , i.e , pests that attack and destroy crops in the store. E.g weevil , rat , yam beetle, groundnut beetle , kolanut beetle etc.
Based on morphology as :
- Insect pests ;
- Non-insect pests .
INSECT PESTS : These are strictly insects that cause damage to crops either on the field or in the store. E.g grasshopper , locust , weevil , aphid etc.Insect pests, again, can be classified into three based on mode of feeding as :
- BITING AND CHEWING INSECTS , i.e , insect pests whose mouth parts are modified into strong mandibles and maxillae for biting and chewing plant parts. E.g grasshopper , locust ,termite , army worm , beetle , caterpillar etc.
- PIERCING AND SUCKING INSECTS , i.e , insect pests whose mouth parts are modified into proboscis for piercing and sucking out sap(plant juice ) when inserted into the tissues of crop plants. E.g cotton stainer , aphid , mealy bug , capsid etc.
- BORING INSECTS ,i.e , insect pests capable of boring into plant parts and destroying the tissues. E.g rice weevil , bean beetle , maize weevil etc.
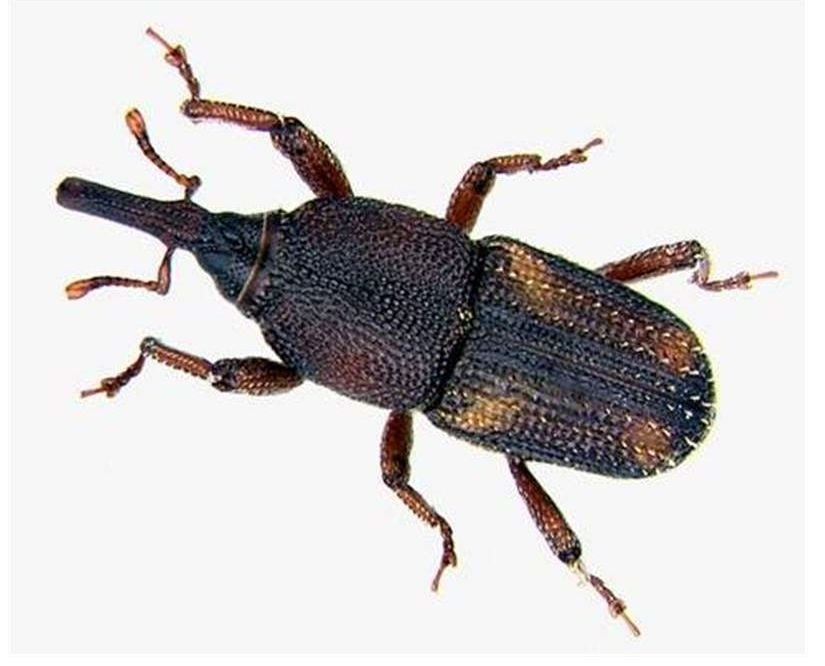

RICE WEEVIL- A BORING INSECT.
NON-INSECT PESTS : These are organisms other than insects that cause damage to crops e.g rodents , birds , monkeys , nematodes , man etc.
METHODS OF PEST CONTROL.
Crop pests can be controlled and prevented through the following methods Physical (mechanical) method , i.e , the elimination of crop pests through physical means such as :
Hand picking;
Use of traps;
Use of scare crows;
Flooding;
Manipulation of temperature and humidity during storage.
Cultural method , i.e , application of suitable farm or agronomic practices such as :
Good farm sanitation;
Crop rotation;
Land fallowing;
Ploughing and harrowing to expose larvae of pests to the soil surface;
Timely planting and harvesting;
Regular weeding;
Use of resistant varieties.
Biological method , i.e, the use of parasites , predators and other natural enemies of crop pests. E.g use of cat to control rodents in storage facilities and lady beetle to control white fly in cassava farm.

LADY BEETLE – A NATURAL OR BIOLOGICAL PRADATOR OF WHITE FLY.
Chemical method ,i.e , the use of chemicals known as pesticides to control different pests in the form of stomach poison , contact poison , systemic chemicals and fumigants. Pesticides include insecticides , avicides , nematicides ,rodenticides etc.
Quarantine ,i.e , preventive measures aimed at discouraging the entering of infected plant materials with pests into a country.
I hope you have learned a few things from today’s lesson. Answer the assignment questions below and submit your answers using the form below it after supplying your name , class and E-mail address. Thank you and stay safe.
ASSIGNMENT
- What is integrated pest management (IPM) ?
CORRECTION OF LAST REVISION ASSIGNMENT.
FARM ANIMALS USED FOR SPORTING ACTIVITIES.
- Horse
- Sheep
- Domestic fowl
- Dog.
FOUR STOMACH COMPARTMENTS OF RUMINANTS.
- Rumen
- Reticulum
- Omasum
- Abomasums.
DATE : 4TH AUGUST , 2020.
Hello students and how are you all doing? I hope you are all fine? Today’s revision is on classification of farm animals, however,if you are not too familiar with this topic then your note and textbook on this subject matter should be contacted for more information.
REVISION LESSON
By the end of today’s lesson, you should be able to :
- Define farm animal ;
- State the different ways farm animals are classified;
- State the factors affecting the distribution of farm animals
TOPIC: CLASSIFICATION OF FARM ANIMALS.
The animals reared on land for agricultural purposes are referred to as livestock or farm animals. E.g Cattle , pig , goat , poultry birds , rabbit ,guinea pig , sheep etc.
Farm animals may be classified based on the following :
- Size;
- Habitat;
- Mode of reproduction;
- Type of stomach;
- Purpose of rearing.
CLASSIFICATION BASED ON SIZE : Under this classification , there are :
- Large animals , i.e , tall and fat animals . e.g cattle , sheep , goat , horse , camel.
- Small animals ,i.e , small body size animals . e.g , poultry , rabbit , cat fish ,guinea pig .
CLASSIFICATION BASED ON HABITAT : Under this grouping , there are :
- Land (Terrestrial) animals , i.e , animals living on land. E.g Pig ,goat , rabbit .
- Aquatic (Water) animals ,i.e , animals living in water. E.g Tilapia , cray fish ,catfish , prawn , shrimp.
CLASSIFICATION BASED ON MODE OF REPRODUCTION : Under this ,livestock are either ;
- Mammals , i.e , animals that can give birth to their young ones alive and produce milk from the mammary glands(breast) to feed their young ones. E.g Sheep , goat , cattle, rabbit.
- Non-mammals , i.e , farm animals that lay eggs and do not feed their young ones with milk from mammary glands. E.g ,Poultry birds , catfish, prawn.
CLASSIFICATION BASED ON TYPE OF STOMACH : Under this classification ,there are :
- Ruminant (Polygastric) animals ,i.e , livestock which possess four stomach compartments (or complex stomach). E.g Cattle , sheep , goat ,camel , house , donkey. They ruminate oe chew the cud.
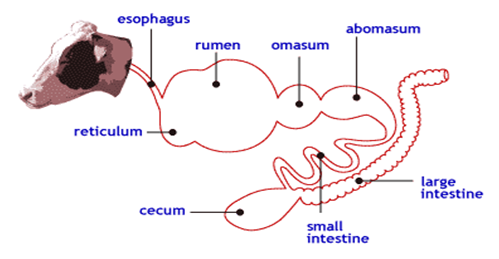
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OF A RUMINANT.
- Non-ruminant(Monogastric) animals , i.e ,farm animals which possess one simple stomach. E.g Poultry birds , rabbit , guinea pig , pig.
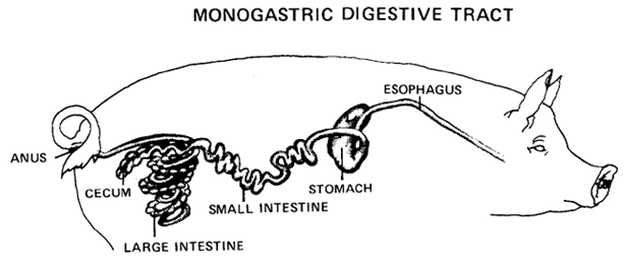
CLASSIFICATION BASED ON PURPOSE : Under this ,farm animals are classified for the reason they are kept as follows :
- Milk producing animals . e.g , Cattle , sheep , goat.
- Egg producing animals , e.g , Duck , turkey , domestic fowl , goose.
- Wool producing animals , e.g , Sheep, rabbit.
- Meat producing animals , e.g ,Cattle , sheep , goat , pig.
- Feather producing animls , e.g , domestic fowl , duck , turkey.
Now, let us look at the ecological distribution of farm animals as well as some of the problems facing livestock industry in Nigeria , thus ,
ECOLOGICAL DISTRIBUTION OF FARM ANIMALS.
Ecological distribution of farm animals refers to the geographical spread of farm animals across the vegetation in Nigeria.
FACTORS AFFECTING THE DISTRIBUTION OF FARM ANIMALS IN NIGERIA.
- CLIMATIC FACTORS , e.g rainfall , temperature , sunlight , wind etc.
- DISEASES , e.g trypanosomiasis , heat stress etc.
- RELIGION AND CULTURE , e.g pig population is low in the north but high in the south.
- SOCIO-ECONOMIC STATUS ,e.g the Fulanis attached importance to the number of heads of cattle in their possession.
- AVAILABILITY OF FOOD ,e.g , large expanse of grassland abundance of cereal crops favour rearing of ruminants in the north.
PROBLEMS FACING LIVESTOCK INDUSTRY IN NIGERIA.
- Poor management . e.g poor housing and water supply.
- Inadequate quality and quantity of food for farm animals.
- Diseases and pests .e.g .coccidiosis , tse-tse fly.
- Unfavourable climatic conditions.
- Inadequate record keeping.
I hope you have learned a few things from today’s lesson. Answer the assignment questions below and submit your answers using the form below it after supplying your name , class and E-mail address. Thank you and stay safe.
ASSIGNMENT
- Mention four(4) farm animals used for sporting activities?
- Mention the four(4) stomach compartments of ruminants?
CORRECTION OF LAST REVISION ASSIGNMENT.
KOLANUT.
- It is used major traditional rites or ceremonies. E.g marriage .
- It is used in the production of beverages.
RUBBER LATEX.
- Used in the production of tyres .
- Used in the production of plastic materials.
TIMBER.
- For building houses.
- For making paper and pencil.
EGG.
- It is a source of protein in human food.
- Egg shell is used in the production of animal feed.
DATE : 28TH JULY , 2020.
Hello students and how are you all doing? I hope you are all fine? Today’s revision is on levels of agricultural production, however,if you are not too familiar with this topic then your note and textbook on this subject matter should be contacted for more information.
REVISION LESSON
By the end of today’s lesson, you should be able to :
- Define subsistence and commercial farming as levels of agriculture ;
- State the characteristics of subsistence and commercial agriculture;
- State the differences between subsistence and commercial farming.
TOPIC: LEVELS OF AGRICULTURAL PRODUCTION.
Agriculture or farming in its various forms could be practiced at two levels . These are :
- Subsistence agriculture;
- Commercial agriculture.
SUBSISTENCE AGRICULTURE: This is a type or kind of agriculture whereby the farmer farms on a small piece of farmland for himself and his family’s consumption without any intention to sell the surplus produced.
COMMERCIAL AGRICULTURE: This is the kind or type of farming in which the farmer farms on a large area of land with the primary objective to sell his produce.
Now, let us look at the peculiar features of subsistence and commercial farming.
CHARACTERISTICS OF SUBSISTENCE AGRICULTURE
- Use of simple farm tools.
- Produce is for family consumption only.
- There is low capital investment.
- Family labour is used and are usually unskilled.
- Small and fragmented farmland is usually used.
- Farm records are rarely kept.
- There is low farm input and output.
- There is no specialization as mixed cropping is usually practiced.
CHARACTERISTICS OF COMMERCIAL AGRICULTURE
- Complex farm machines are usually used.
- Produce is mainly or principally for sale.
- There is high capital investment involved.
- Paid workers are used and are usually skilled.
- Large expanse of land is usually used.
- Farm records are properly kept.
- There is high farm input and output .
- There is specialization as monocropping is usually practiced.

A LARGE SCALE CROP PRODUCTION FARM
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN SUBSISTENCE AND COMMERCIAL AGRICULTURE.
| SUBSISTENCE FARMING | COMMERCIAL FARMING | |
| 1. | Cost of production is low. | Cost of production is high. |
| 2. | Yield is low. | Yield is high. |
| 3. | Simple storage facilities are used. E.g crib ,rhombus ,barn etc. | Modern storage facilities are used. E.g silo , cold room etc. |
| 4. | It is mostly practiced by poor farmers. | It is mostly practiced by rich farmers. |
| 5. | Crop production depends solely on natural rainfall. | Crop production may depend on irrigation. |
| 6. | Local varieties of crops are cultivated. | Improved varieties of crops are usually grown. |
| 7. | No environmental pollution. | Farming activities can lead to environmental pollution. E.g exhaust from farm machines, fertilizer usage etc. |
| 8. | Agrochemicals are rarely used. | Agrochemicals are heavily used. E.g fertilizers , pesticides etc. |
| 9. | Simple housing facilities are used for rearing animals. | Improved housing facilities are used for rearing farm animals. |
| 10. | Unskilled family labour is used. | Skilled hired or paid labour is used. |
I hope you have learned a few things from today’s lesson. Answer the assignment questions below and submit your answers using the form below it after supplying your name , class and E-mail address. Thank you and stay safe.
ASSIGNMENT
State two(2) uses each of the following agricultural produce:
- kolanut;
- rubber latex;
- timber;
- egg.
CORRECTION OF LAST REVISION ASSIGNMENT.
BENEFITS OF PRACTICING BOTH CROP AND LIVESTOCK ON THE SAME PIECE OF LAND.
- Animal manure can be used to improve soil fertility.
- Crop residue can be fed to livestock.
ADVANTAGE AND DISADVANTAGE OF PRACTICING SHIFTING CULTIVATION AS A FARMING SYSTEM.
| ADVANTAGE | DISADVANTAGE |
| It ensures a supply of food without the use of fertilizers and pesticides. | It cannot be practiced where there is scarcity of land. |
DATE : 21ST JULY , 2020.
Hello students and how are you all doing? I hope you are all fine? Today’s revision is on forms and branches of agriculture , however,if you are not too familiar with this topic then your note and textbook on this subject matter should be contacted for more information.
REVISION LESSON
By the end of today’s lesson, you should be able to :
- Identify the various forms of agriculture:
- Mention the different branches of agriculture;
TOPIC: FORMS AND BRANCHES OF AGRICULTURE.
There are different forms in which agriculture can be practiced. The main forms of agriculture are:
- Crop farming;
- Livestock farming.
CROP FARMING : This involves the principles and practices of crop production. Some of the various agricultural practices used in crop farming include:
- Shifting cultivation ;
- Mono-cropping;
- Mixed cropping.
SHIFTING CULTIVATION : This is the system of farming whereby the farmer abandons his unproductive land for a productive one , with the intention of not returning to the poor or unproductive land again.
MONO-CROPPING : This is the practice of growing only one type of crop on a piece of land.
MIXED CROPPING : This involves the growing of two or more crops on the same piece of land at the same time. There are two types of mixed cropping ; namely ;
(i) inter-planting, i.e , where the crop planted first is harvested first.e.g Yam inter-planted with maize.
(ii) inter-cropping, i.e , where the crop planted first is harvested later. E.g Maize inter-cropped with cassava.
LIVESTOCK FARMING : This involves only the rearing of farm animals(livestock) by the farmer. Types of livestock farming include :
- Pastoral farming;
- Bee keeping;
- Snail farming;
- Poultry farming;
- Pig farming;
- Rabbit farming.
BRANCHES OF AGRICULTURE.
The branches of agriculture include the following:
- Crop science;
- Soil science;
- Animal science;
- Horticulture;
- Forestry;
- Fishery;
- Agricultural extension;
- Agricultural engineering;
- Agricultural economics;
- Veterinary medicine.
I hope you have learned a few things from today’s revision lesson. Answer the assignment questions below and submit your answers using the form below it after supplying your name , class and E-mail address. Thank you and stay safe.
ASSIGNMENT.
- State two(2) benefits of practicing both crop and livestock farming on the same piece of land by a farmer ?
- State one(1) advantage and one(1) disadvantage of practicing shifting cultivation as a farming system ?
CORRECTION OF LAST REVISION ASSIGNMENT.
OCCUPATION DERIVED FROM AGRICULTURAL ACTIVITIES.
Crop pathology;
Fish farming;
Horticulture;
Snail farming;
Veterinary medicine.
FEATURES OF ERAS OF AGRICULTURAL REVOLUTION .
PALEOLITHIC ERA :
Hunting , fishing and fruits gathering were the main agricultural practice.
Human population was very small.
MESOLITHIC ERA:
Clubs and dogs were used for hunting wild animals.
Hunting , fishing and wild fruits gathering were man’s predominant occupation.
NEOLITHIC ERA :
Cultivation of crops and domestication of animals by man began in this era.
The spread of different crops and animals to different parts of the world from their places of origin was witnessed by man.
DATE : 14TH JULY , 2020.
Hello students, How are you all doing? I hope you are all fine? Today’s revision is on meaning ,importance and origin of farming , however,if you are not too familiar with this topic then your note and textbook on this subject matter should be contacted for more information.
REVISION LESSON
By the end of today’s lesson, you should be able to :
- Define agriculture:
- State some importance of agriculture;
- Describe the origin of agriculture in man’s history.
TOPIC: MEANING AND IMPORTANCE OF AGRICULTURE.
The term “ agriculture “ derived from the two Latin words “Ager “ meaning “ Field or Land “ and “Cultura “ meaning “ Cultivation “ means more than just land cultivation. It is indeed the sum total of all activities concerned with the production of crops and rearing of farm animals and their products for the use of human beings.
Agriculture , therefore , can be defined as the cultivation of crops and the rearing of farm animals for man use.
IMPORTANCE OF AGRICULTURE
- Provision of food.
- Provision of shelter.
- Provision of raw materials for industries.
- Income for farmers.
- Provision of foreign exchange.
- Rural development.
- Provision of employment.
ORIGIN OF AGRICULTURE
The history of agriculture is as old as man. The three eras of agricultural revolution, historically , are
- the paleolithic era (Old stone age).
- the mesolithic era (middle or medieval age).
- the neolithic era (new stone age).
THE PALEOLITHIC ERA : In this period , the dominant agricultural practices were hunting , fishing and gathering of wild leaves , fruits , roots , snails and insects. Human population was very small and people lived in caves.
THE MESOLITHIC ERA: In this era , man was still a food gatherer living by hunting , fishing and collecting fruits and other edible plants. Clubs and dogs were used in hunting of game , i.e , wild animals.
THE NEOLITHIC ERA: This is era when man started a settled life , and began the cultivation of crops and the domestication of animals. At this time , the population has started increasing. Wooden farm tools were replaced with metals for tilling the land. Shifting cultivation was the main system of farming . Other cropping and farming systems such as crop rotation , continuous cropping , ley farming , pastoral farming and zero tillage were adopted.
This era marked the first step to human civilization as different crops and animals spread to other parts of the world from their origin by early missionaries , explorers and traders.
CROPS AND THEIR PLACES OF ORIGIN.
| CROP | PLACE OF ORIGIN | |
| 1. | Maize | Central America |
| 2. | Cassava | Brazil |
| 3. | Cocoa | Mexico |
| 4. | Yam | India |
| 5. | Oil palm | Africa |
| 6. | Kola | Africa |
| 7. | Cowpea | West Africa |
| 8. | Onion | Asia |
| 9. | Coffee | Ethiopia |
| 10. | Guinea corn | India |
I hope you have learned a few things from today’s revision lesson. Answer the assignment questions below and submit your answers using the form below it after supplying your name , class and E-mail address. Thank you and stay safe.
ASSIGNMENT
1. List five(5) occupations derived from agricultural activities ?
2. State two(2) features each of the following eras of agricultural revolution:
a. Paleolithic era;
b. Mesolithic era;
c. Neolithic era.
CORRECTION OF LAST REVISION ASSIGNMENT.
- FARM ANIMALS USED FOR PROTECTION AND COMPANIONSHIP.
a. Cat;
b.Dod;
c. Parrot;
d,Goose;
e. Ostrich
POULTRY BIRDS USED BY MAN FOR GUARD
a.Ostrich;
b. Goose;
c. Parrot.
DATE: 7TH OF JULY ,2020.
Hello students, How are you all doing? I hope you are all fine? Today’s revision is on forms of farm animals , however,if you are not too familiar with this topic then your note and textbook on this subject matter should be contacted for more information.
REVISION LESSON
By the end of today’s lesson, you should be able to :
- Define farm animal;
- Mention some benefits derived from farm animals ;
- List and describe the various forms of farm animals.
TOPIC: FORMS OF FARM ANIMALS.
Farm animals are those animals which have been domesticated by man for economic and social benefits. e.g Cattle , sheep , goat ,rabbit , pig , catfish ,duck ,turkey ,guinea pig etc.
BENEFITS DERIVED FROM FARM ANIMALS
- They are used as food by man.
- Some are used for security and protection.
- Some are used for sport.
- Some are used as pets.
- Some are used for work and means of transportation by man.
- They are used as sources of raw materials.
- Source of organic manure.
Farm animals come in various forms. These include :
- Work animals;
- Poultry birds;
- Guard animals;
- Dairy animals;
- Aquatic animals;
- Pets.
WORK ANIMALS: These are farm animals produced to serve as source of labour on the farm.They possess great strength , ability to move in rugged areas , quiet temperament and submission to discipline. They are also referred to as drought animals. They are usually used for pulling tillage implements like plough , harrow , ridger during land preparation. E.g Strong and healthy bulls , horses , donkeys , camels etc
POULTRY BIRDS: These are all birds that have been domesticated by man for their meat , feather , manure and egg. Examples of poultry birds are domestic fowl , duck , turkey , guinea fowl , goose , pigeon etc.

DOMESTIC FOWLS AND THEIR EGGS.
GUARD ANIMALS: These are animals used by man to protect his properties against thieves and other pests. E.g Dog , cat , goose , parrot.
DAIRY ANIMALS:These are farm animals kept or reared to produce milk rather than for their meat. E.g Cattle , sheep , goat etc.
AQUATIC ANIMALS:These are animals which live in water such as river , lake and man-made ponds. E.g Cat fish , tilapia , carp ,prawn , lobster etc.
PETS :These are animals kept and cared for at home by man to keep his company, i.e , for companionship. E.g Cat , dog ,parrot ,rabbit etc.
I hope you have learned a few things from today’s lesson. Answer the assignment questions below and submit your answers using the form below it after supplying your name , class and E-mail address. Thank you and stay safe.
ASSIGNMENT
- Mention five(5) farm animals used for both protection and companionship ?
- List three (3) poultry birds used by man for guard?
CORRECTION OF LAST REVISION ASSIGNMENT.
- CROPS CLASSIFIED AS BOTH OIL AND PULSE CROP
a. Groundnut;
b. Soyabean;
c. Benniseed.
CROPS GROUPED AS BOTH FRUIT AND VEGETABLE CROP.
a. Garden egg;
b. Cucumber
DATE: 30TH OF JUNE , 2020.
Hello students, is nice reaching out to you once again.How are you all doing? I hope you are all safe as I pray that God should continue to protect us in this trying moment.
Today’s revision lesson is going to be as interesting as the previous one . So today we shall be looking at – Classification of Crops.
CLASSIFICATION OF CROPS
Now, do you still remember this topic ? Let’s remind ourselves once again that:
A crop is a plant cultivated by man for his use. Crops can be classified into different groups based on the following:
- Forms or morphology,
- Life span or life cycle,
- Uses,
- Nutrients.
CLASSIFICATION OF CROPS BASED ON FORMS
Under this classification, agricultural crops can be classified into two groups based on the number of cotyledon or seed leaf . These are:
- monocotyledonous plants;
- dicotyledonous plants.
MONOCOTYLEDONOUS PLANTS: These are crops whose seeds have one cotyledon or seed leaf . e.g Maize , rice , wheat ,sorghum ,millet ,sugarcane etc.
DICOTYLEDONOUS PLANTS: These are crops whose seeds have two cotyledons or seed leaves. e.g Soyabean , melon ,groundnut , cowpea etc.
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN MONOCOTYLEDONOUS AND DICOTYLEDONOUS PLANTS.
| MONOCOT | DICOT | |
| 1 | Presence of one seed leaf. | Presence of two seed leaves. |
| 2 | The leaves have parallel veins ,i.e parallel venation. | The leaves have net veins , i.e , net venation. |
| 3 | Leaves are attached to stem directly without a stalk or petiole. | Leaves are attached to the stem through the stalk or petiole. |
| 4 | They do not have branches. | They have branches. |
| 5 | The plants have hypogeal germination. | The plants have epigeal germination. |
| 6 | The leaves are narrow and slender. | The leaves broad. |
| 7 | Flowers are in three or multiples of three. | The number of flower is four or multiples of four. |
CHARACTERISTICS OF MONOCOTYLEDONOUS PLANTS
- They have one seed leaf or cotyledon.
- They possess fibrous root system.
- They do not have branches.
- They exhibit hypogeal germination.
- They possess parallel venation.
CHARACTERISTICS OF DICOTYLEDONOUS PLANTS
- They have two seed leaves or cotyledons.
- They possess tap root system.
- They have branches.
- They exhibit epigeal germination.
- They have net venation.
CLASSIFICATION OF CROPS BASED ON LIFE SPAN OR LIFE CYCLE
Under this classification, crops can be classified as :
- Annual crops ,i.e, crops that complete their vegetative and reproductive stages (life span) within one year.e.g Rice ,Yam etc.
- Biennial crops ,i.e , crops that complete their vegetative and reproductive stages within two years. e.g Plantain ,Onion , Cabbage etc.
- Perennial crops ,i.e, crops that complete their vegetative and reproductive stages (life cycle ) after two years .e.g ,Mango , Oilpalm ,Rubber ,Citrus etc .
- Ephemeral crops ,i.e., crops that grow three or more times in a year. e.g Okra , Water leaf etc.
CLASSIFICATION OF CROPS BASED ON USES
In this classification ,crops are grouped based on what they use them for into the following :
- Cereal crops e.g Maize ,rice , millet , wheat, barley etc;
- Legume (Pulse ) crops e.g Melon ,cowpea , groundnut , soyabean etc;
- Root and tuber crops e.g Yam , cassava , sweet potato ,cocoyam etc ;
- Fiber crops e.g Cotton ,jute ,sisal etc;
- Vegetable crops e.g Indian spinach ,lettuce okra tomato etc ;
- Beverage crops e.g Cocoa ,coffee , kola etc ;
- Fruit crops e.g Guava, mango ,apple etc ;
- Oil crops e.g Coconut , groundnut ,melon , oilpalm ;
- Latex crops e.g Rubber .
- Spice crops e.g Onion , pepper , ginger etc;
- Forage crops e.g Elephant grass , centro , guinea grass etc;
- Drug crops e.g Tobacco , kola etc
- Ornamental crops e.g Hibiscus , pride of Barbados , rose etc.
CLASSIFICATION OF CROPS BASED ON NUTRIENTS
Under this classification , crops are grouped ,based on the nutrients and substances formed in them, as follows:
- Carbohydrates, i.e , crops that supply energy and provide warmth. e.g Cassava , yam , cocoyam ,maize ,oat ,rice etc.
- Protein, i.e ,crops needed for the production of hormones , body building and replacement of worn out tissues in animals . e.g Cowpea , soyabean , groundnut.
- Fat and oil, i.e , crops that provide energy and regulate body temperature in animals. e.g Groundnut , melon ,oilpalm etc.
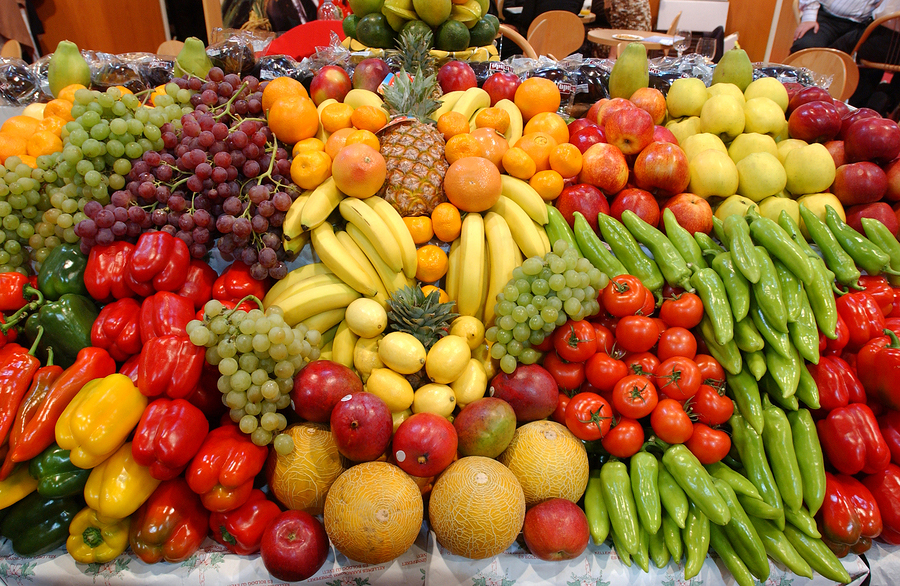

FRUITS AND VEGETABLES –SOURCES OF VITAMINS AND MINERALS .
- Vitamins, i.e , crops that help in basic body metabolism and disease resistance in man and livestock. e.g Vegetables ( Indian spinach , garden egg ) and fruits ( Mango, pineapple) .
- Minerals, i.e . crops that supply materials needed for metabolic activities within in human and farm animals.e.g Orange , pawpaw , banana, fluted pumpkin etc.
- Water i. e , crops with a lot of metabolic water required for various metabolic activities such as digestion and excretion in man and livestock . e.g Vegetables ( cucumber , Amaranthus spp. and fruits (pineapple , mango, orange)
I believe today’s revision lesson has once again reminded us of those foundational topics learned in JSS 1 class. Answer the assignment questions below and submit your answers using the form below it after supplying your name , class and E-mail address. Thank you and stay safe.
ASSIGNMENT
- Mention three(3) crops classified both as oil crop and pulses?
- List two(2) crops grouped both as vegetable and fruit crops
CORRECTION OF REVISION LESSON 3 ASSIGNMENT
- Pollination can be defined as the transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of a flower on the same plant or on another plant of the same specie by an agent.
- TYPES OF POLLINATION.
- Self pollination,
- Cross pollination,
- Artificial or man-made pollination.
DATE: 23RD OF JUNE , 2020.
Hello students, How are you all doing? I hope you are all fine? My prayer is that you will all come back to school safe in Jesus Name! Amen! Now that we are done with the remaining topics for your class. I guess we should resume back to our revision class.
Today’s revision is on crop plant forms-the basics on crop science , however,if you are not too familiar with this topic then your note and textbook on this subject matter should be contacted for more information.
REVISION LESSON : 3
By the end of today’s lesson, you should be able to :
- Define a crop plant;
- Describe the two (2) major parts of flowering plants and their functions ;
- Liist and state the parts of flowering plants as well as their functions.
TOPIC: CROP PLANT FORM.
INTRODUCTION
A plant is a living thing that posses different parts. There are so many plants found in various habitats on earth. Some possess flowers and are usually refer to as flowering plants while others grow without flowers , hence , the reason they are called non-flowering plants.
Flowering plants are made up of the following parts:
- The leaves,
- The stem,
- The root,
- The branches,
- The flower,
- The fruit etc.
Crop plants are plants grown by farmers on the farm and are mostly flowering plants.
Now let’s get started this way:
DEFINITION
A crop plant can be defined as a plant grown by the farmer to provide useful substance called crop . Any unwanted plant which grow among cultivated crops is known as a weed.
FLOWERING PLANTS.
A flowering plant is made up of two(2) major portions ; namely ;
1. The shoot system.
2.The root system.
THE SHOOT SYSTEM:This is the part or portion of the plant that grow above the soil (ground).It is made up of parts such as the stem ,leaves ,flowers, buds ,fruits , seeds and branches.
THE ROOT SYSTEM:This is the part of the plant that grows below the soil (ground).
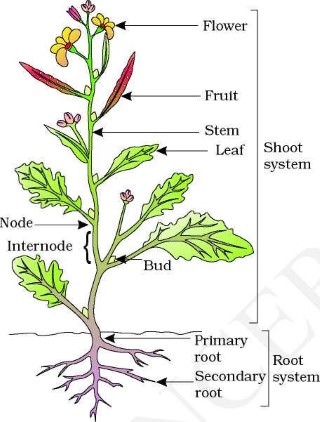
PARTS OF A FLOWERING PLANT.
FUNCTIONS OF PARTS OF PLANTS
THE STEM:
- It supports the leaves and exposes them to sunlight.
- It supports the flowers for pollination.
- It carries water and mineral salts from roots to leaves and fruits.
- Some stems serve as food storage organs . e.g Sugarcane , yam.
THE LEAVES:
- The leaves manufacture food for the plant through the process called photosynthesis.
- They give off excess water found in plant through the process called transpiration.
- Some serve as food storage organs. E.g Onion , lettuce.
THE FLOWER:
- It is the reproductive organ of the plant.
- It produces the seeds and the fruits.
THE ROOT:
- It holds plant firmly in the soil.
- It carries water and nutrients up to the stem.
- It serve as food storage organ in some plants e.g Yam ,cassava, carrot.
I hope you have learned a few things from today’s lesson. Answer the assignment questions below and submit your answers using the form below it after supplying your name , class and E-mail address. Thank you and stay safe.
ASSIGNMENT
- Define the term pollination in flowering plants?
- Mention the three(3) types of pollination in flowering plants?
CORRECTION OF LESSON 3 ASSIGNMENT.
AGRICULTURAL PRODUCE NOT EXPORTED FROM NIGERIA
- Mango.
- Garden egg.
- Sweet potato.
- Tomato.
AGRICULTURAL PROFESSIONALS INVOLVED IN EXPORT PROMOTION
- Agronomist.
- Crop pathologist.
- Veterinary doctor.
- Agricultural Economist.
PROBLEMS MILITATING AGAINST EXPORT PROMOTION IN NIGERIA.
- Poor quality of most export produce.
- Poor access to funds needed by local exporters.
16TH OF JUNE 2020
Hello students, is nice reaching out to you once again.How are you all doing? I hope you are all safe as I pray that God should continue to protect us in this trying moment.
Today’s lesson is going to be as interesting as the previous .This is probably one of the most interesting topics in Agricultural Science. So today I share my view on the topic—Export Promotion In Agriculture.
The idea behind today’s lesson is to show you how the government of Nigeria encourages the sales of Nigerian agricultural produce in other countries as well as the importance of export promotion to the Nigerian economy.
LESSON : 3
By the end of today’s lesson, you should be able to :
- Explain the meaning of export promotion;
- State the importance of export promotion ; and
- Identify some important export commodities in Nigeria.
TOPIC: EXPORT PROMOTION IN AGRICULTURE.
INTRODUCTION
Export of agricultural produce in our country cannot be underestimated. This predates pre-colonial era and trade liberalization policies were hinged on this. A commodity that is transported from one country to another for the purpose of trade is called an export or export produce e.g cocoa ,cotton ,hides and skins etc . A person or a country who sells goods or services in a foreign market is known as an exporter.
To promote the development and the diversification of the Nigerian export trade, the Nigerian Export Promotion Council (N.E.P.C.) was established through Decree No 26 of 1976. This was later amended by the council to Decree No .18 of 1986 and later to Decree No . 41 of 1988.
Now let us look at what export promotion is:
MEANING OF EXPORT PROMOTION.
Export promotion is the effort of the government in encouraging the farmers or firms to produce agricultural produce (goods) for export through agricultural and trade policies. It is an incentive program designed to attract more farmers or firms into exporting.
The government agricultural and trade policies include :
(a). creation of awareness in the need for farmers to produce export crops.
(b). giving grants or loans to farmers for export produce production.
(c). encouraging commercial banks to give loans to farmers of export produce.
IMPORTANCE (BENEFITS) OF EXPORT PROMOTION.
- It exposes farmers to international market and competitions.
- It promotes infrastructural development through the income generated from tax. e.g roads ,schools ,airports etc.
- It improves the standard of living of farmers.
- It serves as additional market outlet for farmers to earn income.
- Export promotion helps to generate employment as the volume of export produce increase leads to jobs for people involved. e.g processing , packaging , loading and off-loading.
- It helps in the exhibition of export produce which attract foreign investors through international trade fairs.
- It helps to develop local industries and technologies as some export produce are also used as raw materials locally.
- Farmers and government earn foreign currencies through the sales of produce to other countries. e .g Dollas , Euros , Pound sterlings , Yens etc.
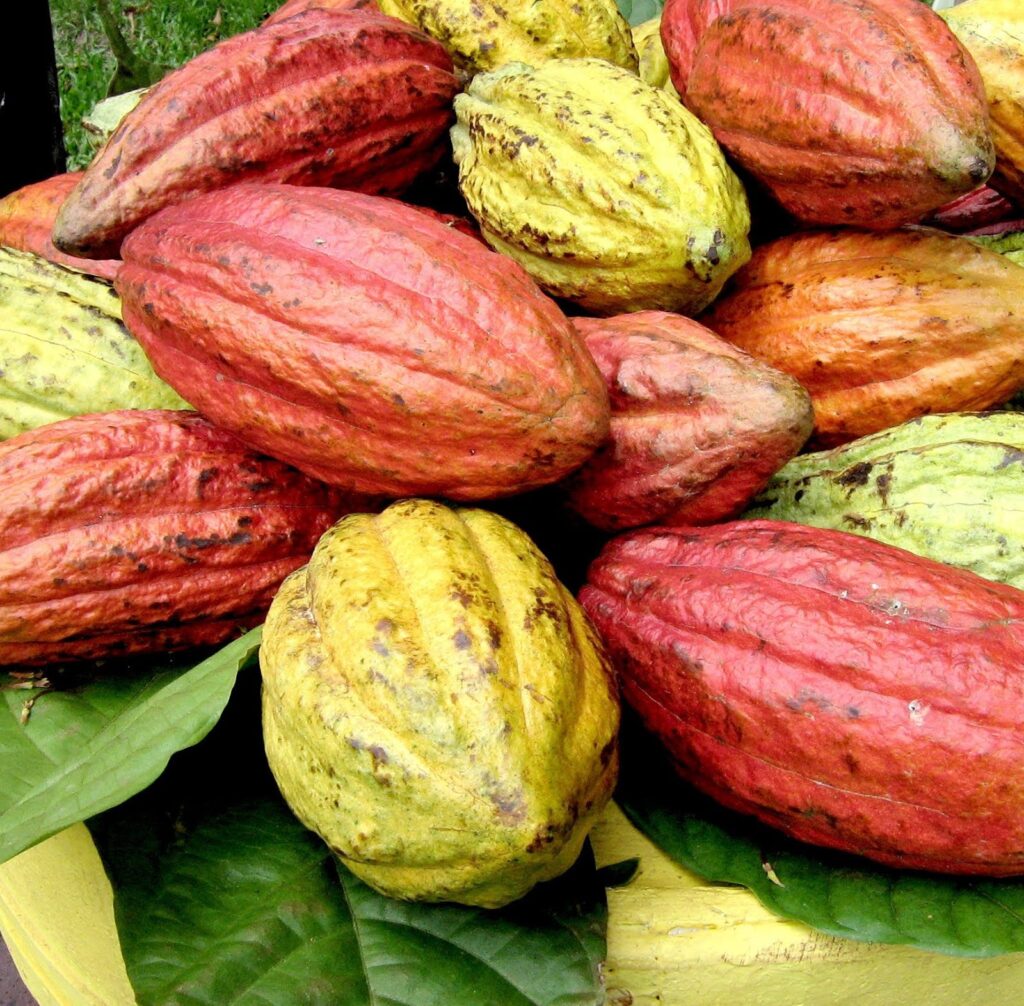

COCOA – AN IMPORTANT FARM EXPORT PRODUCE FROM NIGERIA.
SOME EXPORT AGRICULTURAL PRODUCE IN NIGERIA.
(a). Cassava.
(b).Groundnut.
(c).Palm kernel.
(d).Cocoa.
(e).Gum Arabic.
(f).Soya bean.
(g).Rubber latex.
(h).Hides and skins.
(i).Kolanut.
(j).Coffee.
(k).Cashew nut.
(l).Yam.
(m).Cotton.
(n).Ginger.
(o).Timber.
(p).Sesame seed.
(q).Sorghum.
(r).Tobacco.
I hope this lesson has shed some light on export promotion in agriculture. You can always come back to this lesson if you need a refresher on this topic. You may need to demonstrate your level of comprehension of this topic for me by answering the assignment questions below and submit your answers using the form below it after supplying your name , class and E-mail address. Thank you and stay safe.
ASSIGNMENT:
- Mention four (4) agricultural produce that cannot be exported from Nigeria?
- Mention four(4) agricultural professionals involved in export promotion in Nigeria?
- State two(2) problems militating against export promotion in Nigeria?
CORRECTION OF LESSON 2 ASSIGNMENT.
ADVANTAGES OF USING COMPUTER FOR RECORD KEEPING
- It reduces errors.
- It corrects errors.
- It stores and analyze data.
DISADVANTAGES OF USING COMPUTER IN FARMING.
- Unauthorized person may gain access to information stored.
- Computer problems may arise.
9th OF JUNE, 2020
Hello students, glad to know you are there. In today’s lesson I am going to show you how computer aids farm work and agriculture in general . Hopefully , after this lesson , you will have a better understanding of the enormous benefits of computer in agriculture.
LESSON : 2
By the end of today’s lesson, you should be able to :
- Define computer;
- Mention some of the benefits of computer in farming ; and
- Mention branches of agriculture where computer is appreciated.
TOPIC: COMPUTER AIDED AGRICULTURE.
INTRODUCTION
A computer can be defined as an electronic device used in recording , processing and storing some important or vital information .In farming business ,computer helps to accept input data ,process it and provide result needed for the purpose of auditing and decision making.
Computerized systems quickly and accurately sort and report a great deal of information. Once the information is posted in the computer software reports and analysis can be created ,changed and printed.
BENEFITS OF COMPUTER IN AGRICULTURE.
(a). Computer can be used for analyzing the feed or ration given to farm animals, i.e , feed composition and formulation by feed millers.
(b). It is used for keeping farm records easily ,i.e ,computerized record keeping will reduce and correct errors on the farm.
(c ). It is used in fertilizer application calculation , i.e , in remote sensing to determing soil nutrient status and fertilizer usage.
(d). It can be used for regulating farmland irrigation ,i.e , the application of water to the soil artificially.
(e).It is also used to determine when to market farm produce , i.e , farm produce marketing.
(f). For dispensing drugs to livestock , i.e , automated vaccination in commercial poultry farms.
(g).It can also be used to determine the best crop to produce for maximum profit , i.e , useful tool to determine how best to combine scarce resources by farm managers and avoid wastage.
(h).The information generated can be transported through the internet to any part of the world.
(i).Computer is faster and less stressful in keeping farm records than manual method.
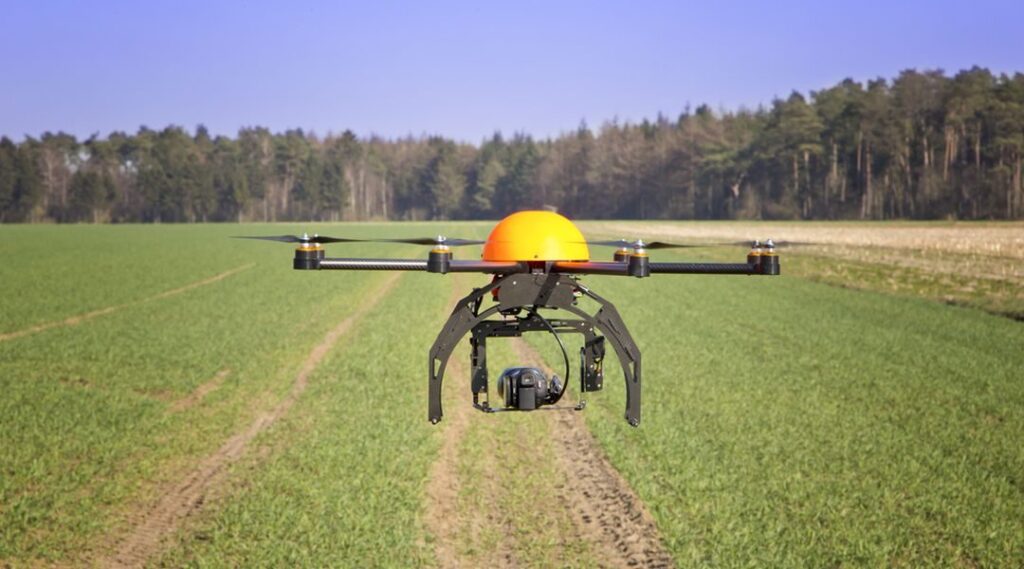

AN AGRICULTURAL DRONE FOR INCREASED FOOD PRODUCTION.
BRANCHES OF AGRICULTURE AIDED BY COMPUTER
- Animal Husbandry;
- Fishery;
- Soil Classification;
- Animal Nutrition;
- Soil Fertility Management;
- Veterinary Medicine;
- Agricultural Economics;
- Forestry;
- Agricultural Engineering
- Crop Production.
I hope you have learned a few things from today’s lesson. Answer the assignment questions below and submit your answers using the form below it after supplying your name , class and E-mail address. Thank you and stay safe.
ASSIGNMENT
- Mention three(3) advantages of using computer for keeping farm records over manual system ?
- State two(2) disadvantages of using computer in farming?
CORRECTION OF LESSON 1 ASSIGNMENT .
- (a). Unstable government policies.
- (b).Illiteracy amongst rural farmers.
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN A JOBBER AND A BROKER
| S/NO | JOBBER | BROKER |
| 1. | Does not deal with the general public directly. | Deals with the general public directly. |
| 2. | Specializes in certain group of securities. | Deals in all types of securities. |
Hello students, is nice reaching out to you once again.How are you all doing? Today’s lesson is going to be a tutorial on stock exchange and agriculture . But before that I am going to take you guys on a ride through the remaining topics in JSS 3 scheme of work as listed in the table below :
2019/2020 SESSION SCHEME OF WORK FOR JSS3
| DATE | LESSON | TOPIC |
| 2/6/2020 | 1 | STOCK EXCHANGE IN AGRICULTURE. |
| 9/6/2020 | 2 | COMPUTER AIDED AGRICULTURE. |
| 16/6/2020 | 3 | EXPORT PROMOTION IN AGRICULTURE. |
LESSON : 1
By the end of today’s lesson, you should be able to :
- State the meaning of stock exchange or capital market;
- mention the two types of markets in the stock exchange;
- mention the people involved in stock exchange activities; and
- state the importance (benefits) of stock exchange in agriculture.
TOPIC: AGRICULTURE IN STOCK EXCHANGE.
INTRODUCTION
The Nigeria Stock Exchange in L agos State, like other stock exchanges across the globe, was established in 1960 to undertake transactions in securities of private companies as well as government bonds for investors both within and outside the country.
Now, what is stock exchange?
Stock exchange or stock capital market can be defined as an organized market where government and companies’ securities such as shares or stocks ,bonds ,options ,future,commodities and debentures are traded or regularly transacted.
It provides a place for buyers and sellers of security instruments such as stock(shares) ,bonds and other securities to transact business.
A share can be defined as the smallest unit of capital issued or offered for sale by companies participating in the stock exchange while a bundle of shares is refered to as a stock.e.g We refer fingers of plantain or banana harvested the same time as a bunch of plantain or a bunch of banana.
The person who owns a share or shares of listed or quoted companies by purchase or by transfer in the stock market is known as a share holder or a stock holder.
TYPES OF MARKETS IN STOCK EXCHANGE.
The stock exchange market can be grouped into two. These are :
- Primary market;
- Secondary market.
PRIMARY MARKET: This is a place where newly offered or issued securities are traded.
SECONDARY MARKET: This is a place where securities which have been issued previously or before are traded.

PEOPLE INVOLVED IN STOCK EXCHANGE.
- BROKERS (STOCK BROKERS): These are professionals involved in buying or selling of securities on behalf of their clients , i.e, buyers or sellers from the public. The stock broker collects a commission or fee known as brokerage.
- JOBBERS: These are members of the stock exchange who act like wholesalers of securities in the market.They are also buyers and sellers of shares.
- INVESTORS: These are people or institutions that buy stock or shares for the sake of investment.They buy and hold securities in order to grow their money for regular income from their capital.
- SPECULATORS: These are people who buy shares not because of the regular income but because of the profit they will make from the fluctuation in prices of shares.Those who buy when share prices are low with the intention of selling at a higher price are called the bulls while those who sell shares in anticipation of price fall are called the bears.
- AUTHORISED CLERKS:These are clerks permitted or authorized by the stock exchange to transact business on behalf of their member-employers.
- UNAUTHORISED CLERKS: These are non registered members of the stock exchange who do minor and routine clerical work for jobbers and stock brokers. They cannot carry out business on the floor of the stock exchange apart from just assisting their employers.

SOME STOCK MARKET TERMINOLOGIES.
Now let us look at the benefits of stock exchange to the agricultural sector of the Nigerian economy
IMPORTANCE OF STOCK EXCHANGE IN AGRICULTURE.
- The stock exchange encourages investment in agriculture as profit could be made in form of dividends ,bonuses etc.
- It promotes profit maximization when farmers or agro-based industries performed maximally.
- It encourages contract farming as agreement between farmers and large agro-allied companies are reached to supply high quality farm produce e.g leather ,fruits ,cotton etc.
- It provides capital through buying and selling of shares to grow and develop farming ,thus, improving the standard of living of farmers and investors.
- The prices listed on the stock exchange can be used as yardstick for measuring performance of a farming business.
- The stock exchange serves as a medium for disseminating information to farmers , industrialists and investors.
- Investment in the share prices can serve as an indicator of the state of national economy.
- Increase in investment in agriculture through stock exchange will ensure food security.
I hope you have learned a few things from today’s lesson. You may need to demonstrate your level of comprehension of this topic for me by answering the assignment questions below and submit your answers using the form below it after supplying your name , class and E-mail address. Thank you and stay safe.
ASSIGNMENT:
1.State two problems militating against the agricultural sector in the Nigerian Stock Exchange?
2.State two differences between a jobber and a broker in any stock exchange market?
No Fields Found.
CORRECTION OF LESSON 2 ASSIGNMENT.
(1) Problems of agricultural marketing
- Inadequate transportation system.
- Inadequate market infrastructure.
- Perishability of produce.
- Problem of middle-men.
- Inadequate processing and storage facilities.
(2) Advantages of retailers
- They make produce readily available to consumers.
- They provide jobs for many people.
REVISION LESSON 2
Hello students, it’s nice reaching out to you once again. How are you all doing? I hope you are all safe as I pray that God should continue to protect us in this trying moment.
Today’s revision lesson is going to be as interesting as the previous revision. This is probably one of the most interesting topics in Agricultural Science. So, today I share my view on the topic—Marketing of Agricultural Produce.
MARKETING OF AGRICULTURAL PRODUCE
What is agricultural marketing?
Agricultural marketing are the activities involved in the flow of goods and services from the producers(farmers) to the final consumers. Marketing of farm produce is yet to be completed until produce gets to you and I for consumption. e.g Eggs ,milk ,vegetables etc.
Now, do you still remember some of the benefits of agricultural marketing?
IMPORTANCE OF AGRICULTURAL MARKETING
>It enables the producer to know the taste of the consumers.
>It creates employment opportunities for many people e.g Fish mongers.
>It helps to make products available throughout the year.
>It helps in price determination.
>It helps in the provision of infrastructure. e.g Electricity, roads , airports.etc.
For these farm produce to get to us, there are pathways to follow.Can you recall some?
CHANNELS OF AGRICULTURAL MARKETING.
Marketing channels refer to all linkages or pathways through which farm produce pass before they get to the final consumers. These channels are also refer to as agents of agricultural marketing.These include:
- Retailers;
- Middlemen;
- Wholesalers;
- Producers;
- Commodity boards;
- Co –operative societies. Now let us look at the stages or processes these farm produce pass before consumption:

Now let us look at the stages or processes these farm produce pass before consumption:
STAGES OF AGRICULTURAL MARKETING.
- Farm level processing : This involves local processing of farm produce immediately after harvesting in readiness for sale.
- Grading or Sorting: This is the grouping of farm produce into various weights and sizes for easy handling.
- Packaging:This involves loading of produce into various packs in readiness for storage.
- Warehousing: This is the storage of produce before sale or export.
- Transportation : This refers to the movement of farm produce from warehouse to the market.
- Advertisement: This involves the process of marketing produce to create awareness through radio, television, newspapers, internet etc.
- Merchandizing: This is the exportation of farm produce through the ports to other countries.
- Assemblage: This is the re-gathering and the repacking of produce from different sources in readiness for final consumption.You can always come back to this lesson if you need a refresher on this topic.You may need to demonstrate your level of comprehension of this topic for me by answering the assignment questions below and submit your answers using the form below it after supplying your name , class and E-mail address:
ASSIGNMENT:
1.State five problems militating against agricultural marketing in Nigeria?
2.Mention two advantages of retailer as an agent of agricultural marketing?
No Fields Found.CORRECTION OF LESSON ONE ASSIGNMENT
- (a) Cardboard box (b) Wooden box OR plastic OR sack OR basket.
- (a) Jute bags are strong and durable. (b) They can permit air circulation freely.
REVISION LESSON 1
Hello students, how are you doing? Let`s do the revision on :
TOPIC: Packaging Criteria For Agricultural Produce.
What is packaging?
Packaging is the technology of enclosing and protecting agricultural produce for distribution ,storage and use.
Aims Of Produce Packaging.
>To preserve the quality of produce.
>To prevent or reduce food spoilage.
>For easy transportation.
Materials used for produce packaging.
1 Cardboard boxes.
2 Drums or barrels
3 Trays
4 Jute bag
5 Polythene

Factors to Consider in Produce Packaging.
>Bulkiness.
>Nature of produce.
>Distance to market.
Criteria for selecting packaging materials.
– Convenience.
-Attractiveness.
-Availability.
ASSIGNMENT:
1 ) Mention two packaging materials for transporting banana?
2) State two reasons why jute bags are used for the transportation of mangoes in O yo State?
Use the form below to complete your submission. write your answers in the answer box below:
No Fields Found.