Hello Dear Students, Happy New Month.
Week 7. Lesson 2
Date: 1/7/20
Exercises
- State two ways by which hair infection can be prevented.
- (a) List four snacks.
(b) List three items that can be used to pack snacks and drinks. - (a) Explain the term Home Economics.
(b) Enumerate the three (3) main areas of Home Economics that are taught in your state.
(c) Mention three (3) subject Home Economics drew knowledge from. - (a) Explain the meaning of family resources.
(b) Enumerate five (5) types of Human resources.
(c) Define possessions. - (a) State four (4) conditions that are necessary for child development.
(b) List two (2) materials and tools for making a round cap.
Week 7. Lesson 1
Date: 29/6/20
Correction for the last Exercises
- B
- A
- A
- D
- B
- D
- D
- D
- B
- B
- C
- B
- D
- D
- A
- C
- A
- D
- C
- A
- B
- D
- D
- C
- B
- A
- B
- B
- C
- A
Exercises.
Week 6. Lesson 2
Date: 24/6/20
Correction to the last exercises
- Hair follicle
- Sand
- Fly
- Iris
- Sorting
- Puberty
- Vacuum cleaner
- White
- Three
- Cotton bud
- Epidemics
- Entertainment
- Three
- Vitamin C
- Niece
Exercises:
- Adolescent boys and girls are usually very active, so their meals should be rich in…. giving foods.
A. active B. energy C. protein D. vitamins
- Uche had running stomach because she ate food that was….
A. contaminated. B. hygienic. C. properly cooked. D. steamed. - Wash every fruit properly before consuming it to avoid food….
A. contamination. B. digestion C. good health. D. hygiene. - Measurers or scale of quality, quantity and method of goal attainment are referred to as….
A. ends. B. goals. C. objectives. D. standards. - Decision making occurs when there are ….to choose from.
A. less than one situation B. more than one situation
C. one action D. up to one situation - One disadvantage of using drafted pattern is….
A. any body can draft a suitable pattern. B. can be adapted to any type of style.
C. does not require special skill to draft. D. it is expensive. - Forming a personal routine for keeping yourself clean, neat, and attractive is referred to as good…
A. bath. B. growth. C. grooming. D. hygiene - The two sets of teeth human beings grow are the …. and ….teeth.
A. children and adult B. first second C. foster and permanent D. milk and permanent - For healthy teeth we need….
A. chloride. B. fluoride. C. nutried. D. nutrient. - Which of the food nutrient supply the body with heat and energy?
A. Carbohydrates and calcium B. Carbohydrates and fats
C. Minerals and fats D. Oils and vitamins - That which helps digestion and bowel movement is
A. Minerals B. Proteins C. Roughage D. Starch - Family needs are classified into two:
A. Primary and immediate B. Primary and secondary
C. Primary and tertiary D. Secondary and immediate - Human resource is classified into….
A. five B. four C. three D. two - Which of the following is not a human resources?
A. Attitude B. Energy C. Knowledge D. Money
15. An indigenous cosmetic that smoothens the skin when applied is called
A. Camwood B. Lali C. Nzu D. Tangere
- Cloths should not be store damp or in a damp place in other to prevent the close from been
attacked by
A. Ant B. Moths C. Mildew D, Rat - One of the tools is not used for taking body measurements.
A. French curve B. Paper C. Pencil D. String - The signs of HIV/AIDS include the following except..
A. diarrhea. B. rashes on the body. C. weight loss. D. vomiting. - HIV/AIDS is mainly contracted through…
A. eating together with an infected person. B. handshake.
C. sex with infected person. D. touching the infected person. - A protective cloth that covers the front part of our clothes and uses ties around the waist is….
A. apron. B. batik C. fringe mat. D. napkin. - Which area of Home economics teaches a child about knitting and crocheting….
A. child development. B. clothing and textile.
C. family living. D. home management. - The basic sewing stitches are grouped into….
A. back and running stitches. B. embroidery.
C. permanent and back. D. permanent and temporary. - Which of the following is not a consequences of self-medication?
A. Complication B. Drug abuse C. Drug misuse D. Good nutrition - The basic pattern drafted to the exact size of the body is called a….
A. style. B. fashion. C. block. D. vogue. - The following are rights of consumer except the right to….
A. be heard. B. be informed.
C. choose between alternative. D. destroy new p rod u ct. - The first immunization given to a baby is….
A. B.G.G B. D.T.P C. Measles D. Polio vaccine - A good storage facility should be….
A. cool, clean and crowded. B. dry, cool and clean.
C. moist, warm and clean. D. leaky, cracked and soiled.
28. Which of the following is NOT an importance of Home Economics?A. It aims at improving family life. B. It prevent people from developing their ability. C. It reduces poverty in the society. D. It helps to promote the health of citizens. 29.A career in Home Economics that deals with planning and decoration of home etc. is called . A. advertising. B. hotel management. C. interior decoration D. surrounding decoration. 30.Pick out the items not needed in making cosmetics. A. Acid B. Mixing spoon. C. Petroleum jelly D. Pomade container
Week 6 lesson 1
Date: 22/6/20
Correction to the last lesson
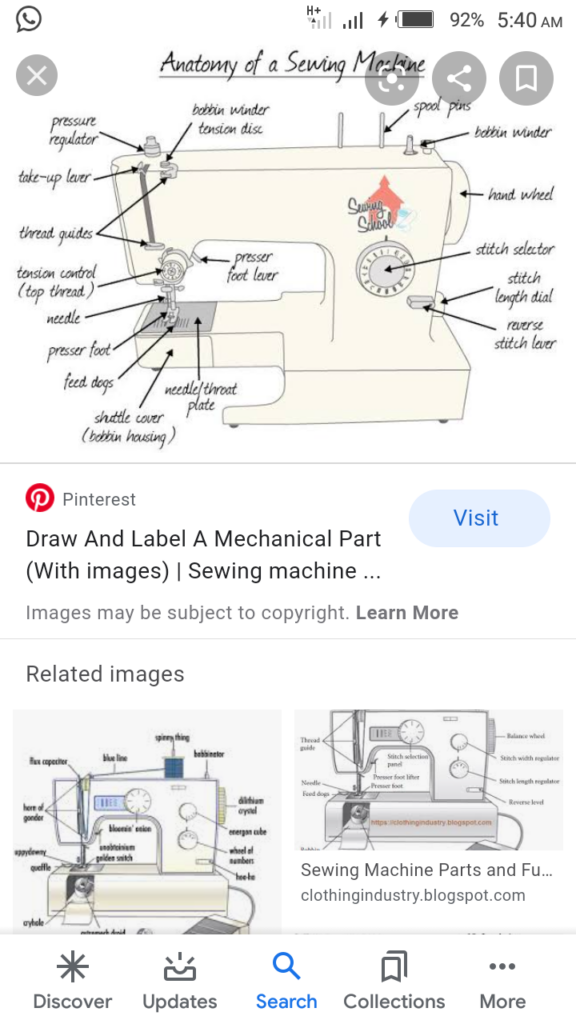
- Types of sewing machine
Hand wheel or Hand sewing machine
Electric sewing machine
Treadle sewing machine
2. Parts of sewing machine
*Stitch Regulator: it is used to determine the length of the stitch that is used, suitable for various types of materials.
*Shuttle or Bobbin case: it holds the threaded bobbin in position.
*Needle Clamp: it is a place where needle is fixed.
*Bobbin Winder: it is used to hold the Bobbin into place, to wind the thread into the Bobbin by loosening the motion screw.
*Presser Foot: this is a detachable part for holding fabrics in place while sewing.
*Spool Pin: this is located on top of the sewing machine and is used to hold the sewing thread in position.
3.
- 4. Factors to consider when choosing a sewing machine
- Buy durable sewing machine
- Buy one that serves your purpose
- Buy one whose spare parts are available.
- Buy one that is simple and easy to operate
- Buy within your purchasing power
- 5. Ways of caring for a sewing machine
*cover your sewing machine when not in use.
*service the machine regularly
*oil the movable joints of the machine
*read instructional manual booklet and understand it to enable you take good care of it
*have a permanent center in the home or shop to prevent carrying it all about to make it durable.
Exercises
- What is the name given to the narrow tube in the skin in which hair grows?.
- Glass is manufactured mainly from ——–.
- Dysentery can easily be spread by ——-.
- The coloured part of the eye is the ——-.
- The first step in laundry process is ——-.
- A fourteen year old girl is regarded as having reached the age of ———.
- What is suitable for cleaning rugs?.
- Dandruff can be seen as ——flakes on the scalp.
- The ear is divided into —– parts.
- What is best used for cleaning the ear?.
- Epidermis is the ——- of the skin
- The act of receiving people and making them feel happy is called ——.
- Food items are divided into —– groups.
- The nutrient content of fruits is Vitamin —-.
- Your sister’s or brother’s daughter is your—–
Week 5 lesson 2
Date: 17/6/20
Exercises
- List 3 types of sewing machine
- Explain 5 parts of sewing machine.
- Draw and label a sewing machine
- Explain 5 factors to consider when choosing a sewing machine.
- Explain 5 ways of taking care of a sewing machine.
Week 5 lesson 1
Date 15/6/20
Marriage.
A boy-girl relationship should be a healthy one. Both should share common interest.
Problems associated with unhealthy boy-girl relationship include : HIV/AIDS, teenage pregnancy, unhealthy sexual relationship, general disease, etc.
Courtship is a period which lasts between the initiation of a relationship and marriage. The intending couple become close and get to know each other better.
Marriage is a Union between a man and a woman as husband and wife.
The different types of marriages in Nigeria are, traditional, court, Christian and Islamic.
Factors to consider when choosing a partner include : love, age, character, health, compatibility, background etc.
The disadvantages of early marriage include lack of love, communication gap, complications during child birth, etc.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy occurs when the spermatozoan from the man fertilizes the ovum or egg in the fallopian tube.
A normal pregnancy lasts for nine months.
Pregnancy is marked by signs and symptoms like, enlargement of the abdomen, menstruation cessation, etc.
A pregnant woman is expected to attend antenatal clinic
A pregnant woman is expected to attend postnatal clinic
Baby’s layette is the set of clothes required by a new born baby.
Week 4 lesson 2
Date: 10/6/20
Exercises
- Briefly explain “family crisis”
- State three causes of conflicts in the family
- List five fundamental human rights in Nigeria
- State any three uses of food in the body
- List three sources each of the following (i) carbohydrates (ii) fats and oils (iii) proteins (iv) vitamins
- List five deficiency diseases
- list three methods of food preservation
- List three methods of food storage
- List three methods of cooking foods
- List five laundry agents
WEEK 4 LESSON 1
DATE: 8/6/20
Hello my lovely students. You are welcome back to this on line class. I hope you are writing down all notes, class work, assignments and corrections into your school notes, if not, do so because every work will be checked and marked on resumption. Thanks.
Correction to last Lesson
1. What are textiles?
Textiles are types of cloth made by weaving and knitting
2. Example of textiles.
i. Textiles from animals – Wool, silk
ii. Textiles from plants; cotton, linen
iii. Chemical fibre; Nylon, Terylene, rayon
3. Fibre: this is a material like cloth or rope made from a mass of natural or artificial threads e.g. nylon.
Yarn: these are threads which are obtained by twisting several fibres together.
Warp: these are threads that run horizontally or length wise on fabrics
Weft: these are threads that run across the warp threads.
Selvedge: this the edge that is made on a piece of cloth which stops the edge from coming out
4. Reasons for studying Textiles
(i) for an individual to have to have basic knowledge of the various type of cloth and their properties
(ii) To be able to identify the various fabrics and their origin
(iii) To know their various uses because they are suitable for many purposes.
(iv) To make people become a wiser consumer.
(v) To enlighten individuals how to launder each variety in the right way
5. Importance of textiles to Man.
i. to prevent nakedness
ii. To protect the body against germs and diseases
iii. To make the body beautiful
iv. To keep the body warm
v. to protect the body against bad weather
6. Uses of textiles
i. it is used to produced household linen
ii. They are used for production of medical linen, mask, assorted bandages, overall etc.
iii. It is used for making tents, belts, rugs, carpets.
iv. They can be converted to swimming wears, sport wears.
V. it can be used for making family and personal cloths.
7. Properties of wool:
i. it is warm and a bad conductor of heat
ii. It does not crease
iii. It is inflammable.
iv. It is water repellent because it contains natural oil.
v. it cannot easily fray
2. Silk:
i. it is the strongest of all natural fibres
ii. it is beautiful, smooth and shinning.
iii. it smells like burning feathers when burnt
iv. it does not absorb moisture
v. it is the one of the most expensive fibers
3. Cotton: i. it dyes easily
ii. it is not easily attacked by moth
iii. it crease easily.
iv. it can averagely absorb moisture
v. it can shrink
4. Linen: i. it has no elasticity
ii. it is strong when wet
it is inflammable
iv. it is strong and durable
v. it does not easily shrink
5. Terylene:
i. it is strong
ii. it is durable
iii. it is difficult to dye
iv. it does not absorb moisture
v. it can be easily dry cleaned
TOPIC: KITCHEN EQUIPMENT AND UTENSILS
Factors to consider in choosing food preparation equipment are
i. money available
ii. Specific use of the equipment
iii. Size of the family
iv. Durability of the equipment
- Two different types of kitchen equipment are large and small equipment or utensils
- The equipment in our homes are made from different raw materials like aluminum, iron, stainless steel, silver, copper etc.
FOOD PURCHASING
Food purchasing is the art of buying foods.
Risk factors encountered during buying practices include
- Adulteration of food products
- Fraudulent practices of sellers
- Poor handling practices
- Buying food from unsafe sources
- Hoarding of products by sellers.
Factors to consider when purchasing foods are
- Money at hand
- Family income
- Size of the family members
- Food in season
- Bilk purchase of foods
Wise buying is the art of buying intelligently in order to get value for your money.
Week 3 Lesson 2
Date: 3/6/20
Correction for the last lesson
Factors to consider when buying foods
1.money available to the family will determine the quantity and quality of foods to be bought
2. Buy food in season because they are cheaper and of good quality.
3. Buy in bulk and share
4.perishable foods is best purchased in the morning if it is bought in an open market
5. To avoid wastage, buy foods based on the size of the family.
6. Ensure good storage facilities to reduce food spoilage.
7. Buy non- perishable foods in bulk and store in containers with tight fitting lids.
B) Characteristics of carbohydrates
- Carbohydrates are made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
- All sugars which are also carbohydrates are sweet but they vary in sweetness.
- Sugars are soluble in water.
- Simple sugars are colorless, starch are white in color and are soluble in water.
- Starches which are also found in carbohydrates are often stored as starch grains plant cells.
- The product of carbohydrates digestion is glucose.
Exercises
1.what are textiles
2. List examples of textiles
3. Explain – fiber, yarn, warp, weft, selvedge.
4.state reasons for studying textiles.
5. List 4 importance of textiles to man.
6. Give 5 uses of textiles.
7. List 4 properties each of – wool, silk, cotton linen, terylene.
No Fields Found.Week 3 Lesson one
Date: 1/6/20
Scientific study of food nutrients
The study of the characteristics and sources of nutrients is essential to enable us to plan, purchase, prepare and serve meals properly
Nutrients differ in their physical and chemical properties
The effect of dry heat on starch produces Dextrin and the process is known as Dextrinization.
The effect of moist heat on starch produces a gel and the process is known as Gelatinization.
The effect of dry heat on sugars produces caramel and the process is known as caramelisation.
The effect of moist heat on protein is known as coagulation.
Heat melts solid fats and expands oils.
Simple tests and experiment were carried out to identity different nutrients in food stuffs. For example;
-test for starch using the iodine test turns blue- black in colour
-test for simple sugars using Fehling’s and Benedict’s tests produce an orange or brick red precipitate and a red – orange or yellow precipitate respectively.
-test for protein using Million’s and Biuret test produce a red precipitate and purple violet colour respectively.
-test for fats and oils using the grease spot and Sudan 111 test produce a translucent patch and a distinct red coloration respectively.
MEAL PLANNING
Good food contributes to the good health of the family.
Some of the factors that influence meal planning are money available, occupation, age, size, sex. Health, locality of the family members.
The meal planner should consider the different groups of the members of the family and plan meals to meet their nutritional needs, occupation and health.
A menu card guides people as to what to choose at a meal.
BUYING, PRESERVATION AND STORAGE OF FOOD
The knowledge of buying and storing food adequately helps to prevent food wastage.
Food preservation is the art of taking care of food or treating food eg. using chemicals, to prevent it from going bad easily. Preserved food last longer.
Food stuffs are classified into three namely
—Perishables
–Non perishables and
—Semi perishables.
Food can be persevered by freezing, smoking, sun drying, use of chemicals etc.
Non perishable foods are foods that do not spoil easily, e.g. rice, millet, maize, beans, etc. they are usually stored in air tight containers to prevent attack of weevils
Perishable foods are foods that spoil easily, e.g. fresh fish, meat, etc. they are usually stored in the freezer.
Food storage containers or facilities in the home include; cupboards, shelves, cabinets, larders, tins, jars, bottles, refrigerators and freezers et c. they should be properly care for according to type.
Assignment
Mention five factors to be considered when buying foods
State five characteristics of carbohydrates.
No Fields Found.Correction for Last class work
1. A
2. A
3. C
4. D
5. C
6. C
7. B
8. A
9. B
10. C
11. D
12. C
13. D
14. D
15. D
16. B
17. A
18. A
19. C
20. A
21. A
22. D
23. B
24. D
25. B
26. C
27. B
28. A
29. D
30. C
31. D
32. A
33. A
34. NONE
35. C
36. D
37. C
38. C
39. B
40. C
41. A
42. D
43. C
44. A
45. A
46. B
47. A
48. A
49. B
50. A
51. B
52. A
53. C
54. D
55. C
56. B
57. C
58. B
59. B
60. C
Week 2 Lesson 2
Date: 27/5/2020
Revision of selected Topics
ARRANGEMENT OF FULLNESS
Arrangement of fullness is the sewing of your fabric in such a way that extra allowance is provided in your garment, e.g. Pleats, darts, tucks, gathers.
Facings are durable methods of finishing neck line faced, raw edges or cross way strip piping.
A hem is made by folding materials twice to one side of the work, making the first turn narrow.
Fastenings are those devices attached to openings, e.g. press studs, zips buttons, etc.
CARE OF FAMILY CLOTH
Clothing is any article placed on our body for protection, beautification and adornment.
Care and maintenance of the family clothing is the process of keeping clothing clean and in a good condition.
Clothing repair is the process of mending family clothing articles.
It is important to store cloth in order to save money, make it last longer, and improve the appearance of the wearer.
Clothing articles need to be stored in boxes, bags, closets, shelves, etc.
Process of storing cloth requires clean storage space, not using perfume or deodorants, realizing that damp clothes are not good for storage, removal of broaches and pins before storing, etc.
Two major types of clothing repairs are patching and Darning
Other repair in clothing maintenance include zippers, buttons and buttonholes, elastic bands
HOUSEHOLD LINENS
Household linens are articles that are used in the home to enhance domestic activities
They improve the appearance and beauty of the home
Their use depends on the purpose of each room, e.g. bed sheet for bedroom, table linen for dinning and towels for bathroom
Household linen should be durable, washable and attractive for their purposes in the home
PATTERN DRAFTING
Pattern Drafting is the act of using body measurement on a paper
Pattern Drafting is an act of adapting or altering basic block to fashion style.
Fashion designing is the art of applying designs and aesthetics or natural beauty to clothing and accessories.
Fashion Designers design cloth that are functional and give aesthetic value to the customer
Tools needed for pattern drafting are pencils, rulers, tape measure, brown paper etc.
Equipment needed for pattern drafting are working tables, chairs, stools, ironing boards, etc.
Week 2 Lesson One
Date: 25/5/2020
Classwork
1. All the items that we wear with our clothes are called (a) accessories (b) jewellery (c) shoes (d) hats
2. Your brothers and sisters are your (a) siblings (b) relations (c) aunties (d) nephews
3. Which of the following is not a flooring covering (a) carpet (b) rug (c) wood (c) mat
4. Which of the following is not a natural fibre (a) cotton (b) silk (c) wool (d) lines
5. man made fibre is also known as ……….. (a) Natural (b) animal (c) synthetic (d) vegetable
6. Which of these fabrics is most suitable for school uniform (a) nylon (b) silk (c) cotton (d) wool
7. A person who creates new styles of clothes is called a fashion ………. (a) Model (b) designer (c) decorator (d) caterer
8. Which of the following is not a sign of pregnancy (a) vomiting (b) nausea (c) breast enlargement (d) cessation of menstruation
9. The complete set of clothes required by a newborn baby is called (a) clothing (b) layette (c) fabric (d) cloths
10. Conflict resolution methods include all of these except (a) dialogue (b) mediation (c) family changes (d) listening
11. Conflict can be stressful and damaging to ………….. (a) Parent (b) friends(c) brothers (d) relationship
12. Conflict in a family is a situation where family members are ………… (a) feeding themselves (b) involved in sharing of food (c) involve in a serious disagreement (d) having a party
13. What is a seam (a) A good seam on the material (b) a beautiful seam on a cloth (c) a good stitch on a material (d) A method of sewing two or more pieces of material together
14.The most expensive among the natural fibres is …………….. (a) cotton (b) wool (c) rayon (d) silk
15. …………. are used by babies while we use napkin on tables (a) napkins (b) nappies (c) nakins (d) nappies
16. In manufacturing processes of all fabrics the last process is ………………… (a) Ironing (b) Dyeing (c) ginning (d) boiling
17. Linen fibre burns with the smell of ……….. (a) Burning paper (b) burnt hair (c) burnt cotton (d) burnt plastic
18. An instrument for protecting the middle finger when sewing is called (a) thimble (b) scissors (c) thread (d) needle
19. Materials which are made from …………… absorb moisture easily (a) nylon (b) rayon (c) cotton (d) wood
20. Which of the following creases badly (a) Linen (b) silk (c) wool (d) nylon
21. The tiny hair-like strands used for making fabrics are (a) fibres (b) textiles (c) fabrics (d) clothes
22. A treadle machine is operated with (a) motor (b) hand (c) electric motor (d) foot
23. The parts of the sewing machine that raises and lowers the needle is (a) presser foot (b) balance wheel (c) head (d) bobbin
24. One of the following may not influence meal planning (a) age (b) health (c) money (d) season
25. Which of the following will not eat the flesh of animals and fish (a) vegetarian (b) strict vegetation (c) Lacto-vegetarians (d) the aged
26. A strict vegetarian will not eat any (a) food (b) vegetable protein (c) animal food (d) carrot
27. Lactating mothers are …………….. feeding their babies (a) bottle- (b) breast- (c) over- (d) always
28. Which of the following require increased intake of energy foods (a) manual workers (b) sedentary workers (c) clerks (d) Directors
29. Meals for children should be cooked by easily ……………. Method (a) accepted (b) manipulated (c) consumed (d) digested
30 The elements that make up carbohydrates are the following except (a) carbon (b) oxygen (c) sulphur (d) hydrogen
31. With Million’s test egg-white gives a …………………. Precipitate (a) yellow (b) white (c) green (d) pink
32. Proteins, e.g. white of egg will ………….. in moist heat (a) coagulate (b) spread (c) enlarge (d) decrease
33. With the bluret’s test, protein gives …………… colour. (a) Purple (b) white (c) green (d) pink
34. Proteins are made up of the following except (a) hydrogen (b) carbon (c) nitrogen (d) oxygen
35. A brown honey-like substance formed when sugar is heated is known as ………… (a) Honey (b) liquid sugar (c) caramel (d) brown sugar1. Conflict resolution methods include all of these except (a) dialogue (b) mediation (c) family changes (d) listening
36. Conflict can be stressful and damaging to ………….. (a) Parent (b) friends(c) brothers (d) relationship
37. Conflict in a family is a situation where family members are ………… (a) feeding themselves (b) involved in sharing of food (c) involve in a serious disagreement (d) having a party
38. Which of the following best explain family values (a) family values are social living (b) family values depend upon each other for many things (c) family values are those things that family have or do because they are useful or popular (d) each family has family values
39. Which of the following is not a factor influencing family values and family lifestyles (a) income (b) peace (c) size of the family (d) likes and dislikes
40. Which of these best explains lifestyles (a) life style is the importance a family places on things (b) Life style is the proper planning and management of family resources (c) life style is the way in which a family lives and works (d) life style is the way of life of the wealthy people
41. Which of the following is not one of the rights of the child (a) Every child shall be held in slavery (b) Every child is born free and equal in dignity and right (c) No child shall be subjected to torture or to cruel treatment (d) All children have the right to security
42. Human right violation includes all these except (a) holding someone in slavery (b) subjecting someone to arbitrary arrest, detention or exile (c) tempering with someone’s right to freedom of opinion (d) the right of equal access to public service
43.Which of the following is not a type of food nutrient (a) Carbohydrate (b) Protein (c) Legumes (d) fat and oil
44. Nutrients are …………. (a) Chemical materials in foods (b) liquid substance (c) protective foods (d) edible substances
45. Protein is ……………. (a) body-building food (b) essential food (c) incomplete foods (d) complete foods
46. Which of the following is not affected by family crisis (a) family relationship (b) family cycle (c) family goals (d) family values
47. The following are types of family crisis except …………. (a) good education (b) cultism (c) bereavement (d) accident
48. The following are the nutrients in the food we eat except (a) balanced diet (b) vitamin (c) protein (d) fats and oil
49. For the welfare of the family, conflicts are best (a) overlooked (b) resolved (c) buried (d) ignored
50. The struggle between two or more people who disagree is called (a) conflict (b) crisis (c) problem (d) challenge
51. Conflict in families can arise from any of the following (a) situations, personality, unity (b) situations, personality; power struggles (c) personality situations, affection (d) personality, power struggles, and love
52. A situation that marks a turning-point, when things cease to go on as usual in a family is called (a) crisis (b) conflict (c) debate (d) right
53. Surplus carbohydrates in the body is stored as (a) starch (b) acid (c) fat (d) glucose
54. Which of the following is a deficiency disease (a) malaria (b) fever (c) AIDS (d) Kwashiorkor
55. …………… is important for body tissues and fluids (a) fats (b) maize (c) Water (d) bread
56. …………… are for protecting the body from diseases (a) starch (b) vitamins (c) carbohydrate (d) oils
57. Which of the following is a body builder (a) Yam (b) fat (c) beans (d) oil
58. Cooking food in hot oil is (a) boiling (b) frying (c) stewing (d) oiling24. ……….. are small animals which infest the hair (a) hair lice (b) flies (c) rashes (d) insects
59. ……………. results when the body is given a blow with sufficient force. (a) cuts (b) bruises (c) injuries (d) stings
60. Which of the following is important for balance (a) skin (b) nose (c) ear (d) tongue
No Fields Found.Week 1 Lesson Two
Date: 20/5/2020
Subject: Home Economics
Class: JS 3
Classes of fibres
There are two main classes of fibres. They are natural and man-made fibres or synthetic fibres.
- Natural fibres are obtained from plant and animals sources. Examples of plant fibres are:
- Linen origin: Stem of the flax plant
- Cotton origin: Cotton balls of the cotton plant.
- There are two types of man-made and synthetic fibres. They are:
- Cellulose based fibres, e.g. viscose, rayon and acetate
- Non-cellulose based or synthetic fibres, e.g. nylon and polyester
Properties are the special qualities that each fiber possesses. Knowledge of these properties enables us to put the fabrics to their proper use and care.
Care of different fabrics
Types of care given to fabrics are determined by the type of fabric finish. Fabric finishes are special treatments given to fabrics by manufacturers to improve their qualities, e.g. embossed, crease resistant, etc.
All the processes that dirty clothes undergo in order to become clean is known as laundering.
The laundering tips on the different fabrics when followed will help you greatly in caring properly for your personal clothing’s and household linen.
Basic Elements of design
The clothes we wear are made up of different colours
There are three types of colours: primary, secondary and tertiary colours.
Tertiary colours are derived by mixing secondary and primary colours
Figure types
Figure type is the way an individual is built.
Some of the normal figure types are:
- The tall and slim-slender figure.
- The short and slim-petite figure
- The tall and fat-huge figure
- The short and fat-stout figure
Assignment
- With the aid of a flow chart, classify fabrics into types.
- List three fabrics and gives two uses each.
Week 1 Lesson One
Hello students, hope you are keeping safe. The Lord will see us through this period. I want to welcome you to this online class. I would love you to get an exercise book for your jottings.
Revision Questions
1.List four fabrics and give two uses of each
Wool fabrics e.g Tweed, flannel, blankets
Silk fabrics e.g tafetta, satin, chiffon
Viscose rayon e.g bandages, air craft tyres
2.What are fabric finishes
fabric finishes are special treatments given to fabrics by the manufacturer in order to improve their quality.
3.State five guidelines for choosing 1. Lines, 2. Colours. 3. Patterns
Light, bright and attractive colours should be worn for ceremonies because these colours express happy moods
White colours could be worn by people of any complexion or figure type
Patterns with horizontal strips tend to add width and reduce height
Neat and small patterns are suitable for children’s dresses
If you are tall and slim, go for bold patterns
No Fields Found.