LESSON 16
8th,Sept.2020
Hello students, warm greetings to you and hope you are doing great.
TOPIC: QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS CONTINUES
When little of a given substances is heated in an ignition tube or in a small hard test-tube until no further change is observed ,gases usually evolved from such substances .These gases are being identified by:
[1]Noting their colours .
[11]Noting their odours
[111]Inserting in the gas ,a burning splint.
[iv]Testing the gas with a moist red and moist blue litmus paper to know if the gas is acidic or basic.
With the knowledge of identification of gasnues,fill in the spaces[1-30] in the table below as an assignment using the form provided under the table,after suppling your name,class and Email.
| GAS | COLOUR | ODOUR | ACTION WITH SPLINT | ACTION WITH LITMUS PAPER |
| 1 | Greenish yellow | 2 | 3 | Turns red then bleashes |
| Hydrogen Chloride[HCL] | 4 | Irritating smell | Does not burn or support combustion | 5 |
| 6 | Reddish brown | Iritating ssmell | 7 | Turns red litmus blue |
| Trioxonitrate iv] acid vapour | Pale yellow Fumes | 8 | 9 | Turns red from blue |
| Tetraoxosulphate [vi] acid | 10 | Irritating | Does not burn or support combustion | 11 |
| Sulpuhur [vi] oxide | Colourless | 12 | 13 | Turns red |
| Hydrogen Sulphide | 14 | Rotten egg | 15 | 16 |
| Ammonia | 17 | Chocking | 18 | 19 |
| Hydrogen | 20 | Odourless | 21 | Not applicable |
| oxygen | Colourless | 22 | 23 | Not applicable |
| Carbon [iv] oxide | 24 | Faint and not easily detected | 25 | 26 |
| Water vapour | 27 | 28 | 29 | Not applicable |
| Nitrogen | 30 | Odourless | Does not support combustion | Not applicable |
LESSON 15
1 SEPTEMBER 2020
Hello students, welcome to the month of September,I pray that this month will deliver good things to your life in Jesus name.Today we will look at TEST FOR GASES.It will be based on the following;ODOUR,COLOUR,REACTION WITH LITMUS,OTHER REACTIONS,INFERENCE.
- ODOUR;Smell of rotten egg
COLOUR;; colourless
REACTION WITH LITMUS; turns blue to pale red
OTHER REACTIONS; burns with blue flame depositing sulphur.turns purple KMnO4 colourless and acidified K2Cr2O7 from orange to green with a yellow deposit of sulphur in both cases.
INFERENCE; H2S
2 .ODOUR; irritating and chocking smell.
COLOUR;; colourless.
REACTION WITH LITMUS; turns blue to red.
OTHER REACTIONS; fumes in moist air.
INFERENCE; HCl
3 .ODOUR; odourless
COLOUR; colourless
REACTION WITH LITMUS; neutral
OTHER REACTIONS; does not burn or support combustion
INFERENCE; water vapour
4. ODOUR; irritating and chocking smell
COLOUR; reddish brown
REACTION WITH LITMUS;turns blue to red
OTHER REACTIONS;turns starch iodide paper blue-black
INFERENCE; NO2
5. ODOUR; pungent smell
COLOUR;colourless
REACTION WITH LITMUS;turns moist red to blue
OTHER REACTIONS; forms dense white fumes with conc.HCl
INFERENCE; NH3
6. ODOUR; sweet sickly
COLOUR; colourless
REACTION WITH LITMUS; neutral
OTHER REACTIONS;rekindles brightly glowing splint and extingquishes a feeble one
INFERENCE; NO
7.ODOUR; odourless
COLOUR;colourless
REACTION WITH LITMUS;turns blue to red
OTHER REACTIONS;turns purple KMnO4 to colourless and aciudified K2Cr2O7 from orange to green without a yellow deposit of sulphur in either case.
INFERENCE;SO2
ASSIGNMENT
Write the following gases under the following headings……
Odour,Colour,Reaction with litmus,Other reactions,Inference.
1.O2 2.H2 3.Cl2 4.CO2
.
LESSON 14
25th,August 2020
TOPIC; QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS
A very good morning to you all and hope you are working hard,especially those of you registed for GCE exams.Today, we will look at the above topic whivh is also called SALT ANALYSIS.It talks about the stuff a chemical compound is made up of i.e the ions present in a given compounds.Basically there are two types of ions present in a sample -ANION and CATION.
Qualitative ananlysis questions shall be based on tests for gases like O2,CO2,NH3,SO2,H2S, and NO2 and tests for acid radicals[anions] like NO3-,Cl-,SO32-,and CO32-
and also metallic radicals[cations]like Ca2+,Cu2+,Pb2+,Fe2+,Fe3+,NH4+,Zn2+ and Al3+.Test for unsaturation,functional groups like OH,COOH,etc from organic compounds.Also test for sugar,starch,protiens,fats and oils.
PRELIMINARY TESTS
This involves observation of the salts for physical properties.
1.COLOUR
Some substances have characteristics colurs which can give a useful guide to their identification,as shown below.
COLOUR OF SOLUTION SUBSTANCE. INFERENCE.
Pale green Iron[ii] or anhydrous copper[ii]salt.
Yellow Hydrated Iron[iii]
Blue Hydrated copper[ii]
Bright green Hytrated Nickel[ii]
Black colour Oxide or Sulphide
White or colourless Salt of Ca,Pb,Na,Zn,Al, or NH3
Note that;A colourless salt that smells of ammonia may contain an ammonium salt.
2. FLAME TESTS
This gives a quick preliminary test for metallic radicals.
OBSERVATION OF FLAME COLOUR. INFERENCE
Persistent yellow/Golden yellow Sodium
Lilac Potassium
Bluish-green Copper
Apple green Barium
Crimson-red Strontium
Brick-red Calcium
Green flashes Zinc
Yellow sparks Iron
Bluish Lead
The colour of the flame is an indication of the metallic ion present.
3. ACTION OF HEAT ON DRY SOLID
When the solid sample is heated,thermal decomposition can occur.This may lead to evolution of a gas or gases.The type of gas can lead to identification of the acid radical e.g trioxocarbonate[iv] can decompose thermally to produce carbon[iv]oxide.
ASSIGHMENT
In a tabular form,indicate odour,colour,reaction with litmus,other reactions for the following gases;H2S,HCL,NO2,NH3,NO,SO2,O2,H2,Cl2,CO2.
LESSON 13
11th,August 2020.
Topic: Preparation and collection of gases
Good morning everyone ,hope your weekend was good. Today we will look at the above topic, before then ,make sure you check the corrections to previous lessons .God bless you.
In the preparation of gasses, various method are employed and it depends on two major factors.
[i]Vapour density of the gas.
[ii]Solubility of the gas in water.
Gases which are lighter than air[less dense air]are collected by upward delivery of gas also known as
Downward displacement of air .Gases in this category are :Hydrogen[H] and ammonia[NH 3].
On the other hand ,gases which are denser[heavier] than air are collected by downward delivery of gas[upward displacement of air].Examples are HCL,NO2,CO2,SO2,C l2,H2S, SO3.
However ,gases with vapour densites close to that of air[vapour density of air is 14.4],these gases can
Neither displace air upward nor downward. Such gases are collected over water ,if their solubilitiies in
Water are negligible, that is slightly soluble or insoluble in water. Examples of gases in this category
Are O2, N2O, NO, CO, N2 and PH3.
Assignment:
- List gases that can be collected by upward delivery of gases.
LESSON 12
TOPIC;Revision on Nitrogen and its compound
4th,august 2020
Good morning students,hope your weekend was fine.If you have questions to ask,please feel free to do so.Today,we will look at past questions that cuts across the above topic and some ss1 topics as a way of rounding off.Make sure you attempt the questions.
Objectives
1NaNO3 decomposes on heating to give……
[a]O2.[b]No2. [c]N2O3[d]NO.[e]N2O5.
2.A solvent for gold and platinum is…
[a]Chloroform.[b]Methanol.[c]Ethanol.[d]Aqua regia.[e]Water
3.The oxidation state of nitrogen in N2O5 is
[a]+1.[b]+2.[c]+5.[d]+3.[e]+4
4.The formula for nitrogen[iv]oxide is
[a]N2O.[b]NO.[c]N2.[d]NO2[e]N2O5
5.The formation of dense white fumes of NH4Cl when in contact with concentrated hydrochloric acid gas is a test for.
[a]HCl.[b]NH3.[c]H2.[d]Cl2.[e]H2S
Essay
1[a] State the method of collecting gases which are denser than air.[b]Name two gases that can be used to perform the fountain experiment in the laboratory.State the physical property which makes them suitable for the the experiment.
2[a]Give one example of naturally –occuring acids.[b] state three differences between electrovalent compounds and covalent compounds.
3[a]What is meant by the term acid salt?Give one example.[b]State the reason why an all-glass apparatus must be used for the laboratory preparation of concentrated trioxonitrate [v] acid.
4[a]Three elements A,B and C have atomic numbers 8,11 and 12 respectively.[i]Write the formula of the compound formed by the chemical combination of A and B.[ii]State which of the three elements belong [s] to the s-block of the periodic table.Give reasons for your answer.[b]List the component elements of bleaching powder.
CORRECTION TO LESSON 11
1[a]This is a test for the trioxnitrate [v].A solution of trioxonitrate[v],e.g KNO3,mixed with freshly prepared solution of iron[ii]tetraoxosuylphate[vi] is placed in a test tube.Concentrated H2SO4 acid is then added to the solution through the side of the test tube.This moves to the bottom of the tube producing two layers in the test tube.A brown ring will be formed at the boundry of the two layers due to the formation of FeSO4.NO which is brown in colour.
[b]KNO3 is used in the manufacture of gun powder.
[ii]NaNO3 is used as a fertilizer and in the production of HNO3 acid.
[iii]NH4NO3 is used as a fertilizer.
[c][i]NaOH +HNO3—–àNaNO3 +H2O
[ii]CaCO3 +2HNO3 —-àCa[NO3]2 +H2O +CO2
[iii]P +5HNO3——àH3PO4 + H2O +5NO2
[iv]H2S +2HNO3 —–àS +2H2O +2NO2
[v]4Zn +10HNO3 ——à4Zn[NO3]2 +3H2O +NH4NO3.
CORRECTION TO LESSON 12
OBJECTIVES
1.A 2.D 3.C 4.D 5.B
ESSAY
1[a]Downward delivery of gas/upward displacement of air..
[b]HCL and NH3.They are used to perfume the fountain experiment because they are highly soluble in water..
2[a]examples are Ethanoic acid,amino acid,Lactic acid, Citric acid,Fatty acid, Ascorbic acid e.t.c.
[b]Differences between electrovalent and covalent compounds.
| Elctrovalent compounds [1]Are soluble in water [2]Contain aggregates of charged ions. [3]Have a high melting and boiling points. [4]Conduct electricity [5]Are hard and brittle.. | Covalent compounds Are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents. Contain only molecules. Have a low melting and boiling Do not conduct electricity.. Are gases,liquids or solids which vaporize easily. |
3[a]Acid salt contains replaceable hydrogen ions and has acidic properties.Acid salts result when there is an insufficient supply of metallic ions in the acid.e.g NaHCO3 e.t.c.
[b]The reason is that the Glass is not attacked by trioxonitrate[v]acid vapour but it attacks cork or rubber.
4[a]The formula of the compound by the chemical combination of A and B are[i]B2A [ii]BandC belong to S-block of the periodic table because their valency electrons are filled in S-subenergy level.
[b]Calcium,Oxygen and Chlorine.
LESSON 11.
28th,July 2020.
TOPIC:TRIOXONITRATE {V} SALTS
Hello students, a warm greeting to you all and hope your weekend was good.I really appreciate those of you that are punctual to class,keep it up.The corrections for previous lessons must be checked and understood by you.God bless you all.Today,we will discuss HNO3 salts.
HNO3 salts are normal salts of trioxonitrate [v] acid.
Preparation
[a] Neutralization of trioxonitrate[v] acid.
NaOH +HNO3 ——>NaNO3 +H2O
[b]Action of trioxonitrate[v]acid on metals,metallic oxides or trioxocarbonates[iv].
[i]Mg +HNO3 —->Mg[NO3]2 +H2.
[ii]CaO +2HNO3 ——->Ca[NO3}2 +H2O.
[iii]CaCO3 +2HNO3——->Ca[NO3]2 +H2O +CO2.
Chemical properties.
All trioxonitrate[v] salts are soluble in water and they have the following properties.
[a] Action of heat
They decompose on heationg to varing products.
[i]2NaNO3[white] —–>2NaNO2[yellow] +O2
[ii]2Pb[NO3]2[white] —->2PbO[pale yellow] +O2 +4NO2[brown]
[iii]2Cu[NO3][Greenish-blue] —–>2CuO[black] +O2 +4NO2 [brown]
[iv]2AgNO3[colourless] —->2Ag[white] +O2 +2NO2 [brown]
All with the exception of sodium trioxonitrate[v] decompose to give the oxides,oxygen and brown fumes of nitrogen[iv]oxide.NaNO3 decomposes to give NaNO2 and Oxygen,while AgNO3 in addition to O2 and NO2 gives metallic silver [Ag].
[b]They produce nitrogen[iv]oxide when heated with copper and tetraoxosulphate[vi] acid.This the confirmatory test for trioxonitrate[v].
H2SO4 +NO3––>HNO3 +HSO4–
Cu +4HNO3 —>Cu[NO3]2 +2NO2 +2H2O.
[c]On heating NH4NO3,dinitrogen[i]oxide is produced .
NH4NO3—>N2O +2H2O.
[d]BROWN RING TEST
This is a test for the trioxonitrates[v].A solution of trioxonitrate[v],e.g KNO3,mixed with freshly prepared solution of iron[ii]tetraoxosulphate[vi] is placed in a test tube.
Concentrated tetraoxosulphate[vi]acid is then added to the solution through the side of the test tube.This moves to the bottom of the tube producing two layers in the test tube .A brown ring will be formed at the boundry of the two layers due to the formation of FeSO4.NO which is brown in colour.
Equations of the reactions
KNO3 +H2SO4—>KHSO4 +HNO3
6FeSO4 +2HNO3 +3H2SO4——->3Fe2[SO4]3 +4H2O +2NO.
In the above equation, NO which is liberated then reacts with FeSO4 to give FeSO4.NO which is brown in colour.
FeSO4 +NO—–>FeSO4.NO.
USES OF TRIOXONITRATES {V}
[a]Potassium trioxonitrate[v] is used in the manufacture of gun powder.
[b]Sodium trioxonitrate[v] is used as a fertilizer and in the production of trioxonitrate[v]acid.
[c]Ammonium trioxonitrate[v] is used as a fertilizer.
Classwork
[1a]Explain the brown ring test.
[b]list three uses of trioxonitrates[v]
[c] With the equations only, show the reactions of trioxonitrate[v] with the following;
[i]NaOH [ii]CaCO3 [iii]P [iv]H2S [v]Zn
CORRECTION TO LESSON 10
1[a]Industrial preparation of trioxonitrate[v]acid.
4NO3 +5O2——>4NO +6H2O
2NO +O2—–>2NO2
4NO2 +O2 +2H2O——>4HNO3
[b][i]The acid reacts with MgO to give Magnesium trioxonitrate [v] salt and water.
[ii]CO2 gas,2H2O and 4NO2 are produced.
[iii]Iron[ii]tetraoxosulphate[vi] is oxidised to Iron[iii]tetraoxosulphate [vi] while nitrogen[ii]oxide is liberated.This gas reacts with of air to form NO2.
The acid decomposes on heating to give nitrogen[iv]oxide.
[c]Any 3
[i]It is fuming,colourless liquid with a chocking smell.
[b]It is soluble in water and forms a constant boiling mixture with water at 121oC.
[c]It has a specific gravity of 1.5.
It turns blue litmus red.
[e] The acid is highly corrosive and it readily destroys organic matter.
CORRECTION TO LESSON 9
[1]Nitrogen[iv] oxide is prepared in the laboratory by the decomposition of lead[ii]trioxonitrate[v] on heating
2Pb[NO3]2——>2PbO +4NO2+O2
PROPERTIES
_Itis a reddish brown gas.
_Itis poisonous with a pungent and irritating smell.
_It is denser than air.
_It is readily soluble in water.
_It turns blue litmus papre to red.
_It dissolves in water to form a mixture.
2NO2[g] +H2O——>HNO2 +HNO3
_The gas also reacts with alkalis .
2KOH +2NO2—->KNO3 +KNO2 +H2O
_Nitogen[iv]oxide is reduced to nitrogen by heated copper or Iron.
2Cu +2NO2——>4CuO +N2
LESSON 10
21/07/2020
TOPIC;TRIOXONITRATE [V} ACID
This is one of the commonest mineral acids in the laboratory.When nitrogen[iv]oxide is passed into water,a mixture of trioxonitrate[v] acid and dioxonitrate[iii]acid is produced.
LABORATORY PREPARATION OF HNO3
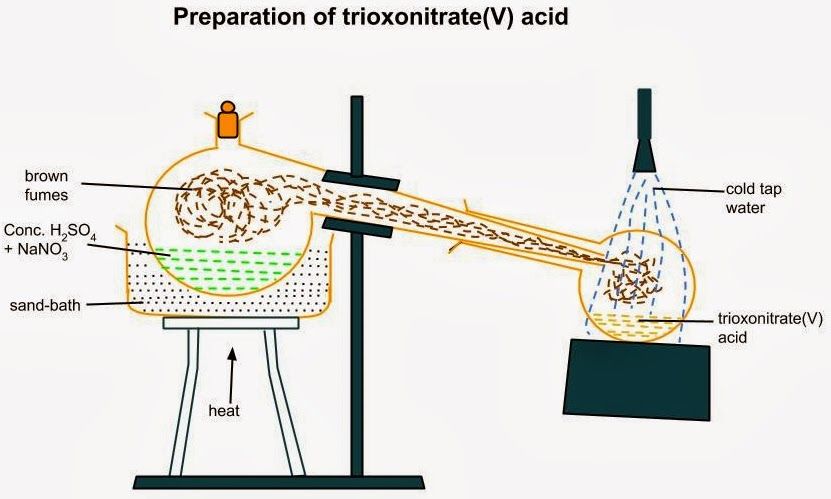
SODIUM trioxonitrate[v],10g and10cm3 of concentrated tetraoxosulphate[vi]acid are placed in a retort and the mixture is heated.The trioxonitrate[v]acid given out is cooled in a round bottomed flask surrounded by cold water.
NaNO3 +H2SO4——>NaHSO4 +HNO3
COMMERCIAL PREPARATION
Ammonia is produced by the Haber process.Purified ammonia and excess and excess air are passed over platinum guaze catalyst.The platinum gauze is heated to red hot. Ammonia is then oxidized by air to nitrogen[ii]oxide.
4 NH3 +5O2 —–>4NO +6H2O
The nitrogen [ii]oxide is cooled and combines with more air to form nitrogen[iv]oxide.
2NO +O2–>2NO2
The nitrogen [iv]oxide mixed with air is absorbed in water to form trioxonitrate[v] acid.
2H2O +4NO2 +O2–>4HNO3
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
[a]It is a forming ,colourless liquid with a chocking smell.
[b] It is soluble in water and it forms a constant boiling mixture with water at 121 degree centigrade.
[c]It has a specific gravity of 1.5.
[d]It turns blue litmus red.
[e]The acid is highly corrosive and it readily destroys organic matter.
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
[a]Trioxonitrate [v]acid is a strong acid with the usual acidic properties.
[i]NaOH +2HNO2—>NaNO3 +H2O
[ii]MgO +2HNO3—->Mg[NO3]2 +H2O
[iii]CaCO3 +2HNO3—–>Ca[NO3]2 +H2O +CO2
[iv]Mg +2HNO2—->Mg[NO3]2 +H2
[b]Trioxonitrate[v]acid is a strong oxidizing agent.
[i]C +4HNO3 —–>CO2 +2HNO3 +4NO2
[ii]P +5HNO3—–>H3PO4 +H2O + 5NO2
In the above reactions with non-metals,brown fumes of NO2 gas are produced.
[c]As a strong oxidizing agent it undergoes redox reactions with common reducing agents e.g H2S and FeSO4.
Iron [ii] tetraoxosulphate [vi] is oxidized to iron[iii]tetraoxosulphate[iv] while nitrogen[ii] oxide is liberated.This reacts with oxygen of the air to form nitrogen [iv]oxide.The acid decomposes on heating tro give nitrogen[iv]oxide.
[d]Nitration of benzene[C6H6];This is the introduction of NO2+[nitronium ion] into the benzene ring .The reaction takes place in the presence of concentrated tetraoxosulphate[vi]acid
C6H6 +HNO3 —>C6H5NO2 +H2O
USES
Trioxonitrate [v] acid is used
[a]In the manufacture of compounds which serve as fertilizer and dyes.
[b]In the manufacture of explosives e.g dynamite,cordite,trinitrotoluene and picric acid
.[c]As an oxidizing agent in the production of nylon and terylene.
[d]As a nitrating agent.
Questions
1[a]With chemical equations describe the industrial preparation of trioxonitrate[v] acid.
[b] What are the effects of the acid on the following?
[i]MgO [ii]C [iii]FeSO4 [iv]C6H6
[c]List three physical properties of HNO3acid.
LESSON 9
14/07/2020
Hello students,how are you today?Pls always check the corrections to previous lessons and note areas of amends.God bless you in Jesus name.Today we shall discuss another type of oxides known as Nitrogen[iv]oxide.
NITROGEN [IV] OXIDE[NO2]
The oxidation number of Nitrogen in the compound is +4.
LABORATORY PREPARATION OF NITROGEN[IV] OXIDE
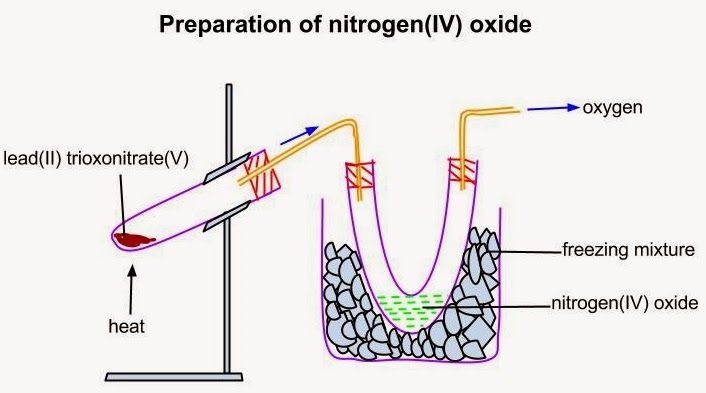
NO2 is prepared in the laboratory by the decomposition of Lead[ii]trioxonitrate[v] on heating.
2Pb[NO2][s]—–>2PbO[s]+4NO2[g]+O2
The nitrogen [iv] oxide becomes liquefied in the U-tube as a green liquid[yellow if pure]while the oxygen escapes from the U-tube as a gas..
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
[a]It is a reddish brown gas.
[b]It is poisonous with a pungent and irritating smell.
[c]It condenses at 22oC to give a yellow liquid.
[d]It is readly soluble in water to give an acidic solution.
[e]It turns moist blue litmus paper red.
[f]It is denser than air.
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
[a]It dissolves in water to form a mixture of dioxonitrate[iii] and trioxonitrate[v] acids.It is therefore a mixed anhydride.
2NO2[g]+H2O[l]——>HNO2[aq]+HNOaq
[b]The gas also reacts with alkalis to yield a corresponding mixture of dioxonitrate[v]salts.
2KOH[aq]+2NO2[g]—–>KNO3[aq]+KNO2[aq]+H2O
[c]Nitrogen[iv]Oxide is reduced to Nitrogen by heated copper or Iron.
4Cu[s]+2NO2[g]—->4CuO[s]+N2
ASSIGNMENT
1.Describe the laboratory preparation and properties of nitrogen[iv]oxide.Show the chemical equation of the reaction with all the necessary conditions
CORRECTION TO LESSON 8
1a Laboratory preparation of NO.
NO can be prepared by the action of dilute trioxonitrate[v] acid on copper turnings.
3Cu[s]+8HNO3[aq]—–>3Cu[NO3]2[aq]+4H2O[i]+2NO[g].
Nitrogen[ii]oxide forms brown on exposure to oxygen of the air.
2NO[g]+O2[g]—–>2NO2
[b]Chemical properties of NO
[i]NO reacts with burning phosphorus or magnesium to form nitrogen and oxides of phosphorous or magnesium
[ii]It reacts with a cold solution of Iron [ii]tetraoxosulphate[vi] in dilute tetraoxosulphate[vi] acid to give a dark brown solution.
LESSON 8
07/07/2020
Hello students,how are you doing?Make sure you participate in all the lessons and copy the notes.Also check the corrections before proceeding to the next lesson.Today we shall continue with Oxides of Nitrogen.
NITOGEN {II} OXIDE[NO]
The oxidation number of nitrogen in the compound is +2.
LABORATORY PREPARATION OF NO
It is prepared by the actiuon of dilute trioxonitrate[v] acid on copper turnings.
3Cu[s] +8HNO3[aq]—–>3Cu[NO3]2[aq]+4H2O[l] +2NO[g]
Nitrogen[ii]oxide forms brown fumes of nitrogen[iv]oxide on exposure of the air.
2NO[g]+O2[g]—–>2NO2[g]
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
[a]It is a colourless and poisonous gas.
[b] It is almost insoluble in water.
[c]It is slightly denser than air.
[d]The gas is neutral to litmus.
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
[a] NO reacts with a cold solution of Iron[ii]tetraoxosulphate[vi] in a dilute tetraoxosulphate [vi] acid to give a dark brown solution.
[b]It also reacts with burning phosphurus or magnesium to form nitrogen and oxides of phosphurus or magnesium.
P4[s]+10NO[g]—–>P4O10[s]+5N2[g]
2Mg[s]+2NO[g]—–>2MgO[s]+N2[g]
ASSIGNMENT
1a Explain the laboratory preparation of NO
b.List two chemical properties of NO
CORRECTION TO LESSON 7
1[a]Oxides of nitrogen are
N2O,NO,N2O3NO2N2O5
[b]It is prepared by heating powdered mixture of sodium trioxonitrate[v] and ammonium chloride.
[c]Uses
It is used as a mild anaesthetic for minor surgical operations.
30/06/2020 lesson 7
Hello students,warm greetings to you.All corrections for previous lessons should be checked before proceeding to lesson 7.God bless you.For today’s lesson,we shall start with oxides of nitrogen.
OXIDES OF NITROGEN
Nitrogen has many oxides as shown below…….
Nitrgen[i]oxide[N2O]
Nitrogen[ii]oxide[NO]
Nitrogen[iii]oxide[N2O3]
Nitrogen[iv]oxide
Nitrogen[v]oxide
NITROGEN [I}OXIDE OR DINITROGEN[I]OXIDE[N2O]
The oxidation number of nitrogen in N2O ism +1.It is often referred to as laughing gas
PREPARATION OF DINITROGEN[i]OXIDE
It is prepared by heating powdered mixture of sodium trioxonitrate[v] and ammoniumChloride
NaNO3[s] +NH4Cl –>NH4NO3 +NaCl
The ammonium trioxonitrate [v] decomposes to give dinitrogen[i]oxide and water.
NH4NO3—->2H2O +N2O
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF N2O
[a]It is a colourless gas with a sweet sickly smell.
[b]It is neutr4al to litmus.
[c]It rekindles a strong glowing splint.
[d]It is fairly soluble in cold water.
[e]It is insoluble in hot water.
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
It supports combustion,this is due to the decomposition of dinitrogen[i]oxide into nitrogen and oxygen.It is this liberated oxygen that supports combustion.
2N2O–>2N2 +O2
[a]S+2N2O–>SO2 +2N2
[b]Mg +N2O –>MgO +N2
Heated copper reduces dinitrogen[i]oxide to nitrogen.
Cu +N2O—->N2 +CuO
TEST FOR DINITROGEN[i]OXIDE
Like oxygen, it rekindles a very hot glowing splint.
USES
It is used as a mild anaesthetic for minor surgical operations.
ASSIGNMENT
[1]List five oxides of Nitrogen
[b]Describe the laboratory preparation of dinitrogen[i]oxide
[c] List uses of dinitrogen[i]oxide
CORRECTION TO LESSON 6
[1]On commercial scale,ammonia is produced by the Haber process.Hydrogen from water gas and Nitrogen from the atmosphere are mixed in the ratio 3:1 by volume ,purified ,dried and compressed to between 200 and 500 atmospheres. The mixture is now passed over a catalyst of finely divided iron mixed with alumina at a temperature of 500 degree centigrade.Ammonia produced is then liquefied by cooling,this may be stored for furthur use.
-Four uses of ammonia .
[1]It is used for softening hard water.
[2]It is used for the production of nylon.
[3]Ammonia is used as a cleasing agent.
[4]It is also used in refrigerators as a cooling agent.
CORRECTION TO LESSON 5
1[a]3H2[g]+N 2 —->2NH3
Requires high temperature and pressure in the presence of a catalyst of iron impregnated with aluminium oxide.
[ii]N2 + O2——>2NO
[iii]3Mg +N2 —->Mg3N2
[b]Uses of Nitrogen
[i]It is used in the manufacture of ammonia.
[ii]Liquid nitrogen is used as a cooling agent.
[iii]Nitrogen is used as a preservative to prevent rancidity.
[iv]It is also used as a carrier gas in gas chromatography.
23/06/2020 lesson 6
Hello students, how was your weekend? I hope to see you in school very soon as you remain safe .
COMPOUNDS OF NITROGEN
AMMONIA
Industrial preparation of ammonia
( I ) Ammonia is manufactured from nitrogen and hydrogen by the Haber’s process.
(ii ) Since the direct combination of both elements is reversible it is then done under certain conditions to obtain ammonia.
(iii) Nitrogen and hydrogen gases are mixed in the ratio 1 : 3 . The mixture is passed over finely divided iron catalyst with a temperature of 450C and pressure of about 200 atmospheres.
N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH3(g) + heat
(I v) Ammonia is then liquefied by cooling , unused gases are recirculated over the catalyst .
Uses of ammonia
Ammonia is used
( I ) in the manufacture of nitrogenous fertilizers like (NH4)2SO4 , NH4NO3 ,NH4PO4 ,NH4CL, NaCO3 (Solvay process).
( I I ) as a refrigerant in the production of nylon.
(I I i) as a cleaning agent.
(I v) in the softening of temporary hand water.
Assignment
- Write the industrial preparation of ammonia.
List four uses of ammonia.
LESSON 5
DATE; 16/05/20
TOPIC;NITROGEN AND ITS COMPOUNDS
Good morning students hope you had a wonderful weekend and you did not neglet your studies.welcome to today’s class but before that,try to look at the corrections to the previous lessons and make sure all the areas that you missed is/are corrected.The scheme of work for 3rd term is as follows .
SS 2 3RD TERM SCHEME OF WORK
1 and 2 Nitrogen and its compounds
3 and 4 Halogens
5 and 6 Chemical equilibrium
7-Qualitative analysis
8-Hydrocarbons
9-Introduction to organic chemistry
10-Stoichiometry
Now,we will discuss the Nitrogen family.
The group 5 elements are referred to as the’The Nitrogen Family’,members are Nitrogen[N],Phosphorous[P],Arsenic[Sb] and Bismuth[Bi].They have the following electonic configurations
N 2 5
P 2 8 5
As 2 8 18 5
Sb 2 8 18 18 5
Bi 2 8 18 32 18 5
Note that the number of electrons in their outermost shells is five.
Nitrogen
It is found free in nature as a gas consisting of diatomic molecules,N2,[about 78% by volume of the atmosphere]and in combination with other elements viz;
[i]Sodium trioxonitrate[v],NaNO3;
[ii]potassium trioxonitrate[v],KNO3 and
[iii]Calcium trioxonitrate [v],Ca[NO3]2
LABORATORY PREPARATION OF NITROGEN
[a]Nitrogen can be prepared from the atmospheric air by removing other constituents of the air [mainly carbon [iv] oxide and oxygen],using solution of NaOH to remove Carbon [iv] oxide and heated copper metal to remove oxygen.
NaOH + CO2 ——–>Na2CO3 + H2O
2Cu + O2 ——>2CuO
[b] It can aiso be prepared by heating a mixture of NH4Cl and NaNO2.
NH4Cl + NaNO2 ——->NH4NO3 + NaCl
NH4Cl —–>2H2O + N2
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF NITROGEN
[a] It is a colourless ,odourless and tasteless gas.
[b]It is slightly soluble in water.
[c]It is slightiy less dense than air.
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF NITROGEN
Nitrogen does not readily take part in chemical reactions but at high temperatures and pressures, it takes part in the following reactions;
[a] It reacts with certain metals e.g Mg,Ca,Al and Fe to form Nitrides.
[b]It reacts with hydrogen at high pressure and temperature and in the presence of a suitable catalyst to give ammonia and it is a reversible reaction.
[c] It reacts with oxygen at a very high temperature to form Nitrogen [ii] oxide.
USES OF NITROGEN
[a]It is used in the manufacture of ammonia.
[b]Liquid Nitrogen is used as a cooling agent.
[c]Nitrogen is used as a preservative to prevent rancidity.
[d]It is also used as a carrier gas in gas chromatography.
We will stop here today,make sure you copy this note into your chemistry notebook.
ASSIGNMENT/CLASSWORK
1.[a]With the aid of balanced chemical equations describe the reaction of Nitogen with
[i]hydrogen;
[ii]Oxygen;and
[iii]Magnesium.
[b]List four uses of Nitrogen.
CORRECTION TO LESSON 4
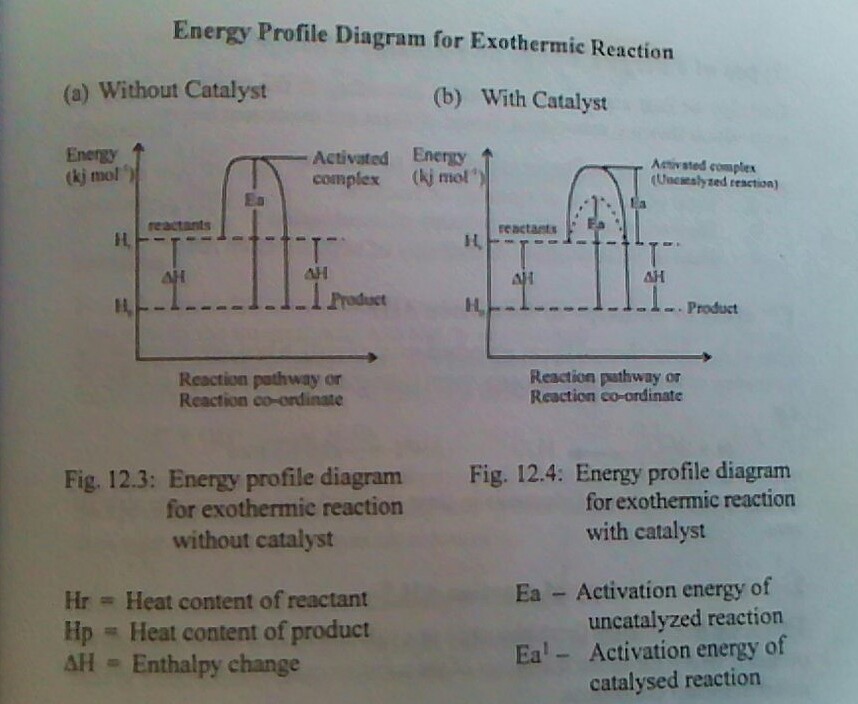
[1ai]ACTIVATION ENERGY is the energy required for a chemical reaction to occur
[ii]ACTIVATED COMPLEX is a complex of high energy content than the reactant or product in the graphical representation of energy changes during a chemical reaction.
[iii]ENERGY PROFILE DIAGRAM this is a graphical representation of the energy change that occurs during a chemical reaction.
[c]Collision between reactants may not produce new species because the reactants may not have enough kinetic energy to penetrate each other so as to lead to a rearrangement of electrons.OR because molecules may not gain enough energy to overcome the energy of activation..
LESSON 4
DATE: 09-06-20
TOPIC: CONTINUATION OF RATE OF REACTION
Good morning my students and how are you today? Hope you are doing great. The corrections for lesson 1&2 should be checked properly, ensure that you check those areas that you missed and always show your workings in calculation. For lesson 2 correction (Hydrogen) the number 2 question, some of you did not indicate how the series increases or decreases. So please take note of that. In the next lesson I shall give you the scheme of work for third term.
TAKE NOTE: ENSURE THAT ALL NOTES GIVEN MUST BE COPIED INTO YOUR CHEMISTRY NOTEBOOK AND NOTES WILL BE CHECKED WHEN WE FINALLY RESUME.
Today we will discus other terms in reaction rate.
Listen to the voice note below
Activation energy
This is minimum energy that is required for a chemical reaction to occur. It is equivalent to the energy barrier that must be overcome before a chemical reaction can take place. The activation energy is reduced or lowered by the use of positive catalyst. Once the activation energy is achieved, a complex of high energy content than the reactant or product called the activation content is formed.
Activated complex
This is a complex of high energy content than the reactant or products in the graphical representation of energy changes during a chemical reaction. It is unstable intermediate particle that is formed when a reactant gradually proceeds to the products during a chemical reaction.
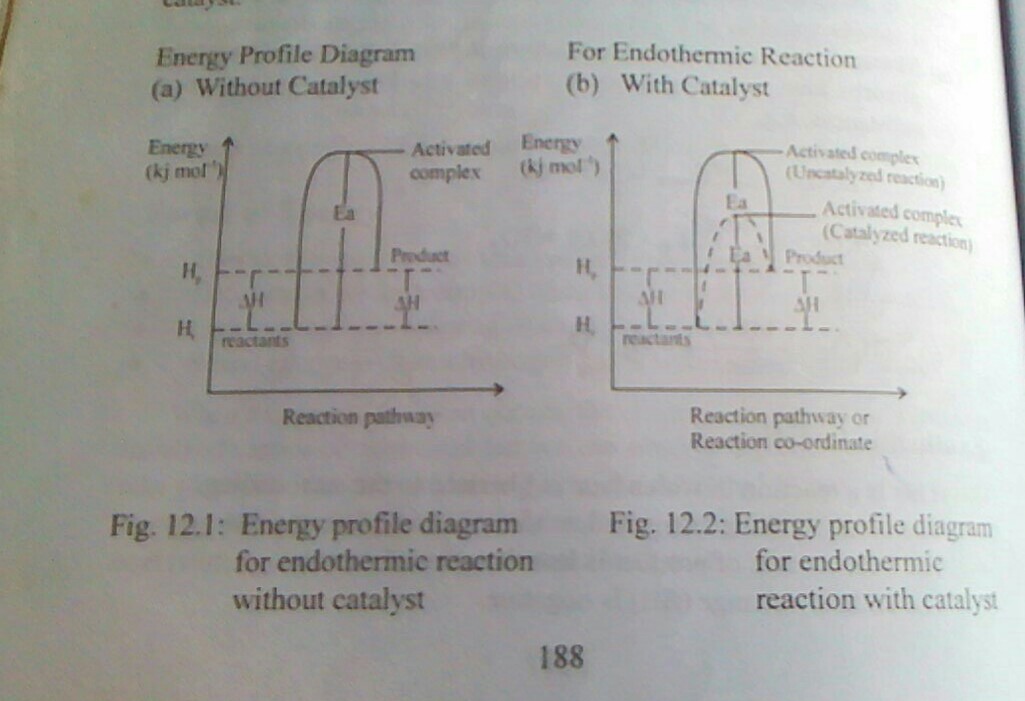
ENERGY PROFILE DIAGRAM OR REACTION PROFILE DIAGRAM
An energy profile diagram or a reaction profile is a graphical representation of the energy changed that occurs during a chemical reaction. It shows the gradual steps in which the reactant proceeds to form an intermediate particle called activated complex and the the product. An energy profile diagram can be drawn for endothermic and exothermic reactions with or without catalyst.
ASSIGNMENT
1a. Explain each of the following terms
i. Activation energy
ii. Activated complex
iii. Energy profile diagram
b. Using energy diagram only,show the difference between endothermic and exothermic reactions.
c. Give one reason why a coalition between reactants may not produce new species.
CORRECTION TO LESSON ONE SS2 CHEMISTRY
SOLUTION
(1) Ca. C O
40/40 12/12 48/16
1 1. 3.
1/1. 1/1. 3/1
1 1. 3
Empirical formula = CaCO3
2.(I). C. H. Cl
24.8/12. 3.9/1. 71.3/35.5
2.06. 3.9. 1.95
2.06/1.95. 3.9/1.95. 1.95/1.95.
1 2 1
E.F= CH2Cl.
(ii). (CH2Cl)n = 99
(12+2*1+35.5)n. = 99
(49.5)n = 99
n=2
Molecular formula
C2H4Cl2
(3) Zn. S. O. H2O
22.7/65. 11.1/32. 22.3/16. 43.9/18
0.349. 0.347. 1.394. 2.439.
0.349/0.347. 0.347/0.347. 1.394/0.347. 2.439/0.347
1 1. 4. 7.0
ZnSO4.7H2O
CORRECTION TO LESSON TWO
Na. & Ca attack cold water to form alkalis and hydrogen gas.
Mg&Fe attack steam to form oxides and hydrogen gas.
Cu has no reaction with either cold water or steam
Arrangement of metals in order of their relative reactivities.
From Na, Ca, Mg, Fe, C
Electro positivity increases from Cu to Na while chemical activities decreases from Na tchange that occurs during a chemical reac reactants may not have enough kinetic energy to penetrate each other so as to lead to a rearrangement of electrons.OR because molecules may not gain enough energy to overcome the energy of activation..
CORRECTION TO LESSON 3
[6] Light
1a The rate of a chemical reaction is the amount [in grams or moles] of the reactants converted to product or the amount [in grams or moles] of the product formed per unit time.
B Factors are ;
[1]Nature of the reactants [physical state]
[2]Concentration of the reactants[pressure for gases]
[3]Temperature
[4]Surface area
[5]Catalyst
[c]Surface
area—–The higher the surface area,the higher the rate of reaction.The surface area of a solid substance is increased by grinding it into a powdery form.For example ,powdered form of marble[CaCO3] react faster with dilute HCl to give effervescence than when it is chips or lump form.
Catalyst—–Positive catalyst increase the rate of chemical reaction by lowering the activation energy while negative catalyst decreases the rate of chemical reaction by raising the activation energy.
[d]Two ways are …..increase in surface area by grinding and increase in the concentration of the reactants.
SS 2 CHEMISTRY REVISION
DATE;02/06/2020
LESSON 3
H ello students,warm regards to you all and hope you are doing great.In the last class we discussed
hydrogen
TOPIC; RATE OF CHEMICAL REACTION
The rate of a chemical reaction is the amount[in grams or moles] of the reactants converted to products or the amount [in grams or moles] of the product formed per unit time.It can also be defined as the change in the concentration of reactants used or product formed per unit time.
Mathematically,
Rate of reaction =amount or quantity of reactant used/time
ORr amount or quantity of product used/time
OR Change in concentration of reactants or products/time
Factors Affecting the Rate of Chemical Reaction.
1.Nature of the reactants.
2.concentration of the reactants.
3.Temperature.
4.Surface area.
5.Catalyst
6.Light
ASSIGNMENT
1[a]what is meant by rate of a chemical reaction?
[b]list the factors that can affect the rate of a chemical reaction and
[c]state how each of the following will affect rate of reaction.
-surface area of solid reactants
-catalyst
[d]Consider the reaction ;2HCl[aq] +CaCO3[g] CaCl2[aq] +CO2+H2O[l]
List out two ways by which the rate of the reaction can be increased.
LESSON TWO
DATE:20/05/20
Hello students, hope you are fine and keeping safe as well.
TOPIC:HYDROGEN
Hydrogen is the lightest gas ,it is prepared in the laboratory by the action of water,steam or dilute mineral acids on metals above copper in the activity series.
Industrally ,hydrogen can be produced from water gas, methane or by eletrolytic methods.
The activity series of metals gives the order of reactivity of metals,with the most reactive metal at the top and the least reactive at the bottom.Metals above Hydrogen in the series displace it from dilute acids ,while metals below hydrogen cannot do so .
Hydrogen is neutral to litmus,burns air in but does not support combustion,is a strong reducing agent,undergoes direct combination with active metals to form ionic hydrides ,reacts with oxygen to form oxides ,reacts with halogens to form halides ,and reduces the metallic oxides to their metals .
With a lighted wooden splinter,gives a pop sound and burns with a pale blue flame.This is a test for hydrogen .
Hydrogen has three isotopes- protium,deuterium,and tritium.
Hydrides of alkali and alkali -earth metals are ionic and reac with water to form hydroxides and liberate hydrogen .Hydrides of non-metals are mainly covalent.
ASSIGNMENT
[1]Under what conditions do the following metals react with water? Na,Ca,Mg,Fe,Cu.
How would you arrange the metals listed in order of their relative reactivities?.
No Fields Found.LESSON ONE
Good day students,hope you have been coping with the present situation? Keep staying safe.
On this platform, we shall have revision and questions on previous term’s work.
Topic: Calculations based on empirical, molecular and structural formulae.
- Empirical formular: this is the simplest formular of a compound that tells us the component elements in a molecule of a compound and also, the mole ratio of the elements e.g CH2 .
- Molecular formular: This gives us all the information obtainable from empirical formular and also gives us the exact number of mole of each of the elements present in the compound . e.g ethyne, molecular formular is C2H2 while for benzene, it is C6H6.
- Structural formular: This formular gives us all the information that can be obtained from both empirical and molecular formular and further tells us how the atoms in the molecule of the compound are linked together i.e arranged. For example the empirical formular of ethane is CH3 molecular formular is C2H6.
Class work
- A compound contains the following 40% Ca, 12%C and 48% O. Find its empirical formular ( Ca = 40%, C = 12, O = 16.
- A compound has a molar mass of 99 and contains 24.8% carbon, 3.9% hydrogen and 71.3% chlorine. Determine the: i empirical formular ii molecular formular ( H= 1,C=12, CL = 35.5 )
- The composition by mass of a hydrated compound was found to be zinc 22.7%, sulphur 11.1%, oxygen 22.3%, water of crystallization 43.9%. calculate the formular of the compound. (Zn=65,S=32,O= 16, H=1).
Fill the following below; your name in the box,Email address and [subject and answers ]in the message box.
No Fields Found.