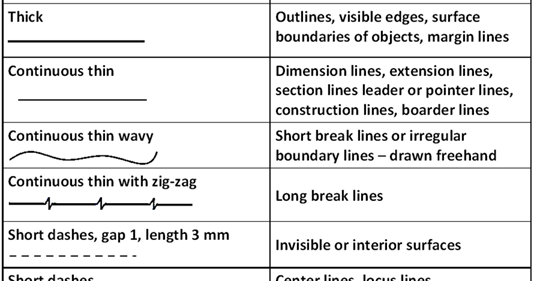
15/09/2020 LINES AND THEIR USES
- THICK CONTINOUS LINES it is used for visible outlines and edges
- THIN CONTINOUS LINES it is used for projection lines, dimension lines, hatching and construction lines
- THICK LONG CHAIN LINES it is used for cutting and viewing planes
- THIN LONG CHAIN LINES it is used for center lines
- THIN SHORT DASHES it used for hidden details
- THICK WAVY LINES it is used for short break lines and irregular boundary lines
- RULED LINE AND SHORT ZIG-ZAG it is used for long break lines
- ARROW HEAD it is used for dimensioning
ANSWER TO THE OBJECTIVES QUESTION
10/09/2020
- B
- D
- C
- B
- D
- D
- A
- B
- B
- D
DATE: 01/09/2020
TOPIC: General Review
- All the following are goals in first aid treatment EXCEPT A. Arresting bleeding and reducing pain B. Assisting the medical officer with information C. Relieving victim of pain D. Saving medical cost
- Which of the following colours usually applies to first aid box? A. Black on White B. Blue on Red C. Cream on Yellow D. Red on White
- The main cause of fainting is due to lack of ————- to the brain A. Food B. Water C. Oxygen D. Carbon dioxide
- The treatment given to a patient before the Doctor arrives is ———— A. Dialysis B. First Aid C. Scanning D. Technology
- The organization that provides first aid incase of emergency is called ————– A. NEMAN B. Fire brigade C. Police D. Red cross
- First aid box is commonly available in the following places EXCEPT —————- A. Industries B. Private houses C. Workshop D. Bus stop
- Metals can be identified through the following properties EXCEPT A. Brittleness B. Density C. Fusibility D. Conductivity
- Routine servicing of machine at regular intervals is known as ————- maintenance A.Corrective B. Preventive C. Predictive D. Mechanical
- A metal that contains iron is known as ————- metal A. Cast iron B. Ferrous C. Non- ferrous D. Wrought iron
- Which of these is a public building? A. Bungalow B. Duplex C. Flat D. Hospital
- A
- C
- C
- C
- A
- B
- A
- B
- B
- NO ANSWER every of the options are correct uses of wood
DATE: 25/08/2020
TOPIC: General
TOPIC: General View
- Which of the following metals is used for making the body of an aeroplane? ________a) Aluminium b) Copper c) Lead d) Steel
- Block engine is made from_____________a) Aluminium b) Brass c) Cast iron d) Steel
- Catapult is a weapon made from____________ material a)Metal b) Plastic c) Rubber d) Glass
- Spark plug is a product used in motor car engine, it is made from___________a) Glass b) Wood c) Ceramic d) Plastic
- Rain coat is a _____________ product a) Rubber b) Fibre c) Wool d) Fabric
- The medal given to third position in sport is a ____________ product a) Aluminium b) Bronze c) Cast iron d) Lead
- Orthopaedic limbs used to replace broken limbs is mostly made of ___________ material a) Plastic b) Metal c) Metal d) Wood
- Tyres and tubes have __________ property a) Plasticity b) Elasticity c) Ductility d) Malleability
- Wood is used for the following in building construction EXCEPT ____________a) Foundation b) Roof c) Window d) wall
- The following are uses of wood EXCEPT____________a) Pulps b) Tool handles c) Transportation d) Medicine
- Insulator
- Packaging
- Building construction
- Auto mobile (vehicle bodies)
- Medical (orthopedic )
- Furniture
- Tools and instruments
- Clothing and wears
- Electronic and electrical devices
GEOMETRIC DRAWING
Types of Angles
- Acute angle : ( less than 900).
- Obtuse angle : more than 900
- Reflex angle : more than 1800
- Supplementary angle : two angles added together to make 1800
- Complementary angle: two angles added together to make 900
- Straight line angle : the angle is 1800
- Revolution angle: angle that makes up 3600 i.e. angle at a point.
13/8/2020 USES OF CERAMICS AND GLASS
- Building construction
- Sculpture
- Insulators
- Dinner wares
- Decoration
- Furnaces
- Automobiles engines
- Pottery
- Wind screen
USES OF RUBBER
- Insulators
- Tyres and tubes
- Mechanical products
- Waterproof
- Storage cases
- Medical purposes
- Sport wears
- Cushions
- Dampers [absorber]
- Rubber cement
- Baby products
- Elastics cloths
- Weapons
- Thread for hair
- Scientific usage
Date: 11/08/2020
Topic: Materials And Their Common Uses
Different materials commonly used as raw materials in technology are:
i. Wood
ii. Metals
iii. Ceramics and glass
iv. Rubber
v. Plastic
USES OF WOOD
1. Building construction: Houses have different parts which are made from wood. Such building parts are windows, doors, roofs, wardrobes, etc. Building construction requires the use of wood for various construction works like framework for concrete work, scaffolding.
2. Furniture: Tables, chairs, cupboards, beds, and cabinets are mostly made of wood. These items are very useful in offices, schools, hospitals, etc.
3. Pulp: Paper used for making books, newspapers, toilet rolls, etc are products made from wood.
4. Tools handles: poor conductivity of dried wood makes it very useful as tool handles for hammers, planes, screwdrivers, saws, chisels, axes, etc.
5. Transportation: Truck bodies, railway sleepers, canoes, walking sticks, boat paddles, etc are built from wood and manmade boards.
6. Utensils: Wood has always been used for cutlery such as chopsticks, chop boards, toothpicks, wooden spoons, etc.
7. Musical instruments: Wood is used for different musical instruments such as drums, guitars, pianos, flutes, recorders, xylophones, etc.
8. Others: Other uses of wood are: for medicine, for sports instruments like bats, hockey sticks, as weapons such as bows and arrows, spears. Electric poles, carvings, fuel to make fire for cooking, engineering works like bridges, and construction, are also some of its uses.
USES OF METALS
- Cast iron: This is useful for producing drain pipes, machine beds, car engines, piston rings, cylinder blocks, vice bodies, etc.
- Wrought iron: It is used for shackles, chains, railings, gates, bolts and nuts, etc.
- High speed steel: It is used for cutting tools, lathe, threading dies, punches, etc.
- Stainless steel: It is used for engineering construction, hydraulic, etc.
- Aluminium: It is used for cooking utensils, food containers, aircraft production, engine piston and cylinders, electric wires, window frames, coins, etc.
- Brass: It is used for ironmongeries like locks, door handles, door hinges and keys. It is also used for decorations, ammunition, electrical fittings, musical instruments, etc.
- Bronze: It is used for sports medals in third position, carvings, ornaments, fittings, etc.
- Copper: It is used for electric cables, decorative articles, coins, pipes, taps, cooking utensils, soldering iron and alloy of other metals.
Date: 06-08-2020
Topic: Rescue Operation Continue
Rescue operation includes:
- The handling of emergency calls
- The issuing of warnings to the public on impending danger, attacks, etc.
- The combating of impending accidents.
- The protection of people, property and environment against danger.
- The extinguishing of fire and danger limitation during fire outbreak.
- Giving information and communication services to the victims.
- Provision of medical care, support, relief such as provision of food, water, clothing, housing, boots to victims.
Protective Equipment Needed For Rescue Operation
The safety or protective equipment to be worn and used by rescuers during rescue operations are:
- Helmets
- Eye goggles
- Hand gloves
- Hard boots
- Overall
- Reflective clothing
- Torch lights
- Life jackets
- Respiratory masks
- Whistles, walkies talkies
Aspects of Rescue Operation
- Technical rescue: T his aspect of rescue operation involves the use of tools and skills. This includes building collapse rescue, rope rescues, and cave rescues.
- Medical rescue: This aspect of involves the use of an ambulance to provide first aid and medical services to those with critical health problems or those with epidemics like ebola.
- Mechanical rescue: This is an aspect of rescue that involves the use of specialized mechanical equipment to save a victim life in danger. Examples of mechanical rescue are rescue from earthquakes, maritime mishaps, construction accidents and mining accidents.
- Rescue robot: This rescue requires the use of robots designed for the purpose os saving people during an emergency. Examples of emergencies where robots are used are mining accidents, urban disasters, explosions and hostage situations. The advantages of robot rescue are: reduction in fatigue, reduction in the equipment to be used and it increases access to unreachable places.
- Lifeboat rescue: Lifeboat rescue is used to rescue and save the lives of people in danger at sea. There are specialized ships, boats, sea vessels designed to rescue lives in danger as a result of ship capsize, fire, etc.
Steps Involved In Rescue Operation
- Safety of rescuers: The important step to be considered in carrying out any rescue operation is to make sure that you do not put yourself at any risk of hazard (danger).
- Assessment of disaster: This is done by in-depth discussions analysis of the incident or disasters.
- Assessing the resources: The availability of personnel, equipment and tools are very important to carry out rescue work. When resources are available, rescue is possible and success is guaranteed.
- Evacuate injured persons: Casualties must be transported out of the scene of the incident. Availability of ambulance to move victims to the hospital must be ascertained.
- Provide first aid: First aid must be provided for unconscious persons, bleeding must be stopped and others with blocked air ways must be attended to as they are being moved to the hospital for medical treatment.
EXERCISES
- List ten organizations or paramedics that carry out rescue operations
- Explain three aspects of rescue operations
Date: 03-08-2020
Topic: Rescue Operation
Meaning of Rescue Operation
A rescue operation is an organized, or planned life-saving program or activity put in place to bring a person out of danger, harm, attack, disaster, etc. Rescue is necessary when the lives of people are under treat of death as a result of natural disasters such as floods, earthquakes, or an attack on human lifes like kidnapping, militant insurgency and other dangers such as building collapse, accidents. Rescue operations are carried out by trained personnel or volunteers in government organizations and voluntary organizations. The various organizations that carry out rescue operations are:
- Police
- Fire Brigade
- Civil Defense Corps
- Federal Road Safety Commission
- National Emergency Management Agency
- Military
- Voluntary Associations such as Red Cross, Boys Scout, Girl Guides
Components of Rescue Operation
Rescue operations require the following components:
- The rescuers: These are the trained personnel and volunteers who carry out rescue operations. Rescuers form the rescue team that makes decision and carry out operations immediately after receiving distress calls or signals.
- Tools: Availability of tools is very important in a successful rescue operation. The tools to be used depend on the type of rescue to be done.
- Time: Time is an important factor in rescue operations. The first 24 hours after a disaster is known as the Golden Day. This is the period or time during which victims have an eighty percent chance of survival if rescued.
Types of Rescue
- Combat rescue operation: These are rescue operations carried out to save people within a war zone or people attacked by insurgents.
- Ground search and rescue: This is a life saving measure for people who are either lost or in danger on land or inland waterways. It is also helpful for people kidnapped or captured for human trafficking.
- Air-sea rescue: This is the rescue done to save the survivors of air crashes and ship accidents. It involves the use of aircrafts, speed boats, helicopters, sea divers, etc to rescue survivors.
- Dog search and rescue: This involves the use of trained dogs to search for lost persons and to provide assistance in their rescue.
- Road rescue: This rescue is done on the highways or roadways in response to road accidents. Specialized equipment and tools are used to free victims from auto crashes.
30/07/2020
SAFETY RULES TO OBSERVE IN FIRST AID
When giving first aid to causality the following rules should be obey
- Ensure you are safe from hazards
- Act promptly but calmly
- Do not touch or try to clean dirty wounds, including burn
- Do not remove bandage or dressing once they have been placed on a wound
- Wear protective hand gloves.
- Call emergency services such as police, fire service, FRSC, etc .
Application of ABC of first aid to workshop accident victims.
- Move the victims to a safe and comfortable position.
- Check the victim and comfirm for breathing, if victim is not breathing, clear the airway.
- If the victim is unconscious, provide mouth to mouth resuscitation.
- If the victim is bleeding as a result of injury, follow the guidelines of bleeding written above.
- After administering first aid, take the victim to the hospital for further treatment.
Application of ABC of first aid to road accident victims.
- Clear the airway of the victim. This must be done within four minutes of the accident, and follow the procedure in workshop accident.
- If the victim is bleeding as a result of injury , the bleeding should be stopped and ensure the victim is stable and respond to questions from first aider.
GOLDEN HOUR is the FIRST HOUR after the shock from road accident.
28/07/2020
FIRST AID MEASURE FOR INFECTIOUS DISEASES
Infectious diseases are diseases that are contagious that is disease that can be transfer from one person to another. They are air or blood borne pathogens . They can be transmitted by touching , breathing, biting, etc. The following measures should be observed.
- Avoid direct contact with bodily fluid and blood
- Wear protective materials such as hand gloves aprons, etc
- Wash your hands with soap and running water immediately after giving care
- Do not touch your mouth , nose ,nor drink or eat when giving first aid
- Don’t touch objects that may have been in contact with bodily fluids
- Be prepared, by having the first aid kit stored with first aid materials that can be easily accessed
ABC OF FIRST AID
The acronyms ABC stand for
A stands for AIRWAY
B stands for BREATHING/BLEEDING
C stands for CIRCULATION
THE ACRONYMS A AIRWAYS
When an accident happens, the first thing you check is where the victims is still alive. If the victim is conscious you confirms the airways is cleared.ie the mouth , the ear, and the nose are cleared. But if the victims is UNCONSIOUS, the following steps should be followed
- Place the victims head and kneel beside his head
- Clear his airway by removing obstruction in mouth and neck
- Place one of your hands under his neck and the other on his fore head. You extend the neck by pushing the fore head down such that the tongue can be lifted up from the back of the throat
THE ACRONYMS B BREATHING/BLEEDING
BREATHING you check the victims if the victims is breathing by checking the heart beat to check the heart beat, you tilt the head up, you place your finger on the throat and slides your finger down from the Adams apple to the throat to check the pulse. in case the victims is not breathing mouth to mouth respiration will be required.
BLEEDING
If the victim is bleeding, which is the major causes of shock. The following steps should be taken
- Exposed the wound by removing any clothe away from the wound
- Place first aid dressing cotton wool on it. You bandaged the wound in case the bleeding continues
- If the bleeding persist you like to block the artery that supplies the blood to the affected parts.
THE ACRONYMS C CIRCULATION
CIRCULATION in case the victim is unconscious the following steps should be taken
- Position the victim flats on his back
- Place the heel of one hand in the centre of their chest the other on the fore head
- You press down firmly and smoothly for sometime
- Gives two breath using mouth to mouth respiration at interval before the arrival of the ambulance
APPLICATION OF FIRST AID MEASURES
The best first aid takes place before emergency happens. First aid application requires knowledge and availability of first aid materials. This is the main reason first aid box must be equipped with first aid materials.
First aid for different emergencies are discussed below:
1. First Measures For Bleeding
Bleeding simply means free flow of blood that result from cuts, wounds or injuries. Bleeding from small wound stop by itself in a short time, such bleeding can be treated by cleaning the wound with cotton wool and application of of iodine or menthylated spirit. The wound is bound with bandages to prevent further bleeding and exposure to other infections like tetanus etc When the wound is severe, the following are first aid measures to be observed: i. Direct pressure must be applied on the wound with dressing pad. ii. The part of the body should be raised above the rest of the body. iii. The victim should be made to sit down or lie down. iv. Secure the dressing pad with a bandage and rush the victim to the hospital or clinic.
2. First Aid Measures For Fainting
Fainting is a state, where someone standing falls to the ground while losing consciousness. It is caused by failure of oxygen supply to the brain. When a victim faints observe the following first aid measures: i. Position the victim with his back lying down. ii. There should not be crowd of sympathizers around him to allow free air around him. iii. Loosen the clothing and other tight materials like belt, necktie, wristwatch, etc on the victim. Open the air ways ( mouth and nose) and raise up the feet slightly. Blood will flow back into the head. The victim should regain consciousness gradually or promptly.
3. First Aid Measures Burn
Burns occur when the body has contact with fire, hot water, and dangerous chemicals. This results to damage of the body skin and cells. There are three categories of burns namely: First, Second and Third Degree. To apply first aid measures on burns, the following should be observed: i. First remove the clothing of the victim. II. Then apply sterile solution to the burn. iii. Dress with sterile bandage. v. Victim with severe burn should be rushed to the hospital for medical treatment.
4. First Aid Measures For Insects and Snake Bites or Stings
When insects or snake bites someone, the venom from the insect or snake is transmitted into the victim s blood stream and it can cause severe health problem or death. The measures to be taken are: i. If it is insect bites or stings, open the wound, press the blood out and apply anticeptic or iodine. II. Give pain relief in case of any pain. iii. Take victim to hospital for further treatment if necessary
In case of snake bite
i. Have the person lie down with wound below the heart. ii. Tie the part bitten with cloth to prevent spread of venom. iii. Take victim to the hospital for treatment.
21/07/2020 FIRST AID BOX AND THE CONTENTS
First Aid box is a solid structure made from either wood or metal used to store first aid materials. The box is rectangular in shape, painted white with a RED CROSS symbol on it. It must be accessible byt kept out of reach of children.
THE CONTENTS
The materials stored inside the first aid box are
- HAND GLOVES
- ANALGESTIC [pain relieving drugs]
- A PAIR OF SCISSORS
- IODINE
- BANDAGES
- METHYLATED SPIRIT
- BALMS [menthol for pain relief]
- SAFETY PIN
- COTTON WOOL
- PLASTERS
- ANTISEPTICS [anti germs solution for cleaning and washing]
- NOSE MASK
NOTE ANY OTHER MATERIALS APART FROM THE ABOVE LISTED MATERIALS SHOULD NOT BE FOUND IN THE BOX
16/07/2020 FIRST AID
FIRST AID is the initial treatment or care given to victims of an accident or health issues before the arrival of medical personnel or before taken him /her to hospital OR The emergency treatment given to accident victims or other medical or health problem.
FIRST AIDER is the person that administer first aid. It must be a trained personnel
TYPES OF FIRST AID
Emergency first aid This is the first aid treatment given to major health problem before he/she get to hospital example are snake bites, head injuries, electric shock, etc
Non – emergency This is the treatment given to minor health problem either in home, office, or workshop. Example are, falls, bruises, minor injuries, etc.
IMPORTANCES OF FIRST AID
- 1t prevents sudden death of victims
- It prevents excess loss of blood during bleeding
- It prevent medical complication to the victims
- It relieves pains in case of injuries
- It saves medical bills in case of minor injuries
14/02/2020
PREDICTIVE MAINTENANCE ;This is futuristic type of maintenance that involed the fixing of defective devices in the machine to prevent foreseen and forestall impending faults.
ADVANTAGES OF PREDICTIVE MAINTENANCE
- It increase the life span of the machine
- It allows foresight repair work
- It saves cost of labour and spare parts
- It saves time and energy
- It increase machine efficiency
DISADVANTAGES OF PREDICTIVES MAINTENANCE
- It is tedious sometime in detecting faults
- It require specialist to handle the faults
- It is more expensive
IMPORTANCE OF MAINTENANCE TO TOOLS AND MACHINES
- It prevents unnecessary breakdown of machine
- It prolong life-span of machine
- It increase the efficiency of machine
- It saves time used in repairs
- It saves cost and unnecessary expenses
- It increase productivity
- It prevents accidents
09/07/2020
MAINTENANCE OF TOOLS AND MACHINES
MEANING OF MAINTENANCE :Is the process of keeping machine in good working condition to prevent unnecessary breakdown.
DIFFERENT TYPES OF MAINTENANCE
There three type [3] types of maintenance
a preventive maintenance
b corrective maintenance
c predictive maintenance
PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE [Routing maintenance] : this type of maintenance is done while the equipment is still working to prevent sudden breakdown. This includes dusting, greasing, regular checking of oil etc .
ADVANTAGES OF PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE
- It save cost of buying new machine
- It prolong the life span of the machine
- It saves time and energy
- It reduces the unnecessary breakdown of machine
DISADVANTAGE OF PREVENTIVE MAITENANCE
- It is monotonous [it cause tiredness since it is done regularly]
- It is a planned maintenance
- It is more difficult to operate compare with other types of maintenance
CORRECTIVE MAINTENANCE :This type of maintenance is carried out when the machine developed fault. In this type of maintenance repair are been done to replace the damaged parts
ADVANTAGES OF CORRECTIVE MAINTENANCE
- It help to restore machine to full working capacity
- It help to detect other unknown fault
- It help to plan ahead
DISADVATAGES OF CORRECTIVE MAINTENANCE
- it is costly
- it waste time[time of repairs]
- it reduces the life span of the machine
- it affects productivity and efficiency
CUTTING TOOLS CONTD
3 SCRAPERS : They are used to remove small metal for finishing outlook
Types of scrapers
a Flat Scraper
b Half-round scrapers
c Triangular scrapers
4 HACK SAW : It consist of metal frame, swingnut and blade made of high carbon steel
5 SNIPS :It is used to shear {cut} metal plates into smaller sizes
Types of snips
a straight snip
b bent snip
c universal snip
DRILLING TOOLS They are used for making round holes in metals. The drills are made of high carbon steel fitted into the jaws of braces
Types of Drills
a Twist drill
b Flat drill
c Straight-fluted drill
d Counter-sink drill
e Center drill
HOLDING AND FORMING TOOL They are used for holding metal for various operations like forming, cutting ,bending ,etc.
a PLIERS It is used for cutting , holding and bending operation.
Types of pliers
a flat nose pliers
b round nose pliers
c combination pliers
b BENCH VICE It is used to secure metal firmly in position for easy operation like cutting, bending, drilling, etc
C STAKES It consist of three [3] parts the shanks, head and horn. It is used to perform bending , forming, and seaming operation in metal works.
Types of stakes
1 Bench horn stake
2 Blow horn stake
3 Hollow and soft mandrel stake
4 Creasing stake
5 Mandrel stake
6 Funnel stake
7 Extinguisher stake
8 Canister stake
9 Bottom stake
10 Tin men’s anvil
11 Half moon stake
D FOLDING BAR They are used for bending and folding of metals into shapes.
DATE: 7/7/2020
TOPIC: METALWORK HAND TOOLS
DRIVING TOOLS



DATE: 30/06/2020
TOPIC: METALWORK HAND TOOLS
INTRODUCTION
Metalwork is the craft of working and producing articles from metal. It involves the forming, cutting or joining processes of metals.
Metalwork involves the use of various metals in producing or forming workpiece(items) useful for man. Examples of items made from metals are: furniture, jewellery,etc. There are different operations involved and each operation requires specific tools designed for it.
MARKING OUT TOOLS
Marking out tools used in metalwork are hand tools made of hardened metals. They are used for marking guide lines and drawing patterns on metal surfaces for designing and cutting processes.
The following are types of marking out tools used in metalwork.
- Surface plates: Surface plates are made of cast iron, having rectangular or square surfaces with small stands. They are used as a reference base and support for other hand tools for marking out process.
- Scribers: Scribers are made of high carbon steel having one conical sharp point of angle 30. They are used for marking straight lines on metal surfaces.
- Odd-leg calipers: The calipers are made of stainless steel having two legs which are unequal. They are used for marking parallel lines to the straight edges of metals.
- Scribing blocks: Scribing block is made of cast iron. It has a rectangular base and a steel rod holding a scriber. It is used for marking lines on metal surfaces.
- Try-squares: A try-square is made of up of a steel blade and a stock. Try-squares are used for testing the squareness of surfaces and marking lines on metal surfaces at right angle to the edges.
- Dividers: They are used to draw curves and circles on metal surfaces, especially on metals with glossy surface to make the marks and lines more visible. It is also used to transfer measurement from rules to the places of use.
MEASURING TOOLS
Measuring tools are hand tools which are calibrated for the purpose of taking readings or measurement of metals to be worked upon. Different measuring tools used in metalwork are discussed below
- Tape rules: They are used for taking long linear measurements on wider sheet metal and longer metal pipes, plates, tubes, etc.
- Steel rules: Steel rules are made of steel materials. They are used to take short linear measurement.
- Protractors: Metal protractors are made of steel materials having stocks and blades. They are used for measuring angles.
- Veneer calipers: Veneer calipers are made from aluminum steel alloy materials. They have long calibrated blades with internal and external fixed jaws with short calibration. Veneer calipers possess higher measuring accuracy than steel rule. They are used to make measurement of round metals and internal bore of metals.
25/06/2020 JSS1
CUTTING AND PARING TOOLS
- SAWS
TYPES OF SAWS
- Rig saw
- Cross-cut saw
- Panel saw
- Tenon saw
- Dovetail saw
- Bow saw
- CHISEL
TYPES OF CHISELS
- Firmer CHISEL
- Bevelled edge chisel
- Mortise chisel
- Gouges (types insides and outsides)
- PLANES
TYPES OF PLANES
- Smoothing planes
- Jack planes
- Trying planes
- Spoke shaves(types flat faced and round faced)
- SCRAPER
- SPRIT LEVEL
- AXE
MAINTENANCE OF WOODWORK HAND TOOLS
1. Always sharpen the cutting edges of tools
2.Do not expose tools to water or chemicals to prevent rust.
3 Do not leave tools on the work bench after use
4 Always keep tools in the tools box
5 Oil the metal parts of the tools when using
23/06/2020
BORING TOOLS
1 Brace and Bits Types of brace Wood brace, Ratchet brace,
Types of Bits Centre bits, Twist bitts, Rose countersink, Snail bits, Shell bits
2 Bradawl
3 Gimlet Types of gimlets (twist and sheii gimlets)
HOLDING DEVICES
1 Work bench
2 Bench hook
3 Bench vice
4 Bench stop
5 G-Cramp
6 Sash cramp
WOODWORK HAND TOOLS
Wood work hand tool can be divided into 4
- Measuring tools
- Setting and marking out tools
- Driving tools
- Boring tools
- Holding devices
- Cutting and pairing tools
*Measuring tools
1. Metric rules they are
i. Steel tape
ii.. Steel rules
- Outside caliper, inside calipers, odd leg calipers.
- A pair of dividers
*Setting and marking out tools
1. Try square
2. Sliding bevel
3. Mitre square
4 A pair of compass
5. Trammels
6. Marking knife
7. Marking guage
8. Mortise guage
9. Plum-bob
*Driving tools
1. Hammers types include claw hammer, warrington hammer
2. Mallet
3. Screwdrivers types are flat screwdrivers, star screwdrivers, allen screwdriver
4. Spanners types are flat head spanner, ring head spanner, adjustable spanner, box head spanner
5. Nail punch
6. Pincer
* Boring tools
- Brace and bits types are wood brace, ratchet brace. bits types are center bits, twist bit, rose countersink, snail bits, shell bits.
- Bradawl
- Gimlet, there are two types of gimlet i.e twist gimlet
- Shell gimlet
* Holding devices
- Work bench
- Bench hook
- Bench vice
- Bench stop
- G-cramp
- Sash cramp
*Cutting and pairing tools
- Saws types are rip saw, cross-cut saw, panel saw, tenon saw, dovetail saw, bow saw, coping saw.
- Chisel types are firmer chisel, bevelled edge chisel, mortise chisel, gouges( types of gouges are inside ground gouges, outside ground gouges)
- Planes types are smoothing planes, jack plane, trying plane, spoke shave( types of spoke shaves are flat faced spoke shave and round shave spoke shave)
- scraper
- Spirit level
- Axe
Good morning students, hope you are keeping safe.
Date: 16/6/2020
Topic: Revision on properties of material
Alloys of metals
An alloy is a metal that is made by mixing two or more metals, or a metal and another substance to give greater strength or resistance to corrosion.
Examples are:
Bronze is the mixture of copper, tin and phosphorus;
Brass is the mixture of copper and zinc;
Stainless steel is the mixture of steel, chromium and nickel;
Duralumin is the mixture of aluminium, copper, magnesium and manganese;
Soft solder is the mixture of tin and lead.
RUBBER
Rubber is a non-metal product, it is made from raw material called latex.
There are two types of rubber namely:
Natural Rubber: This is made from milky substance called latex which is obtained from rubber trees.
Synthetic Rubber: This is made from organic materials processed from petroleum.
Properties of Rubber
Elasticity: Rubber stretches and returns to its original size and shape when released. This is the main property of rubber over other materials.
Conductivity: Rubber does not allow heat to pass through itself easily. Therefore, rubber is an insulator.
Absorbent: Rubber absorbs vibration and noise in machines.
Non-corrosive: Rubber cannot rust when exposed to weather or chemicals.
PLASTICS
Plastics are synthetic organic materials moulded into any desired shape when subjected to heat and pressure. They are made from natural or synthetic resins.
There are two types of plastics namely:
Thermoplastics: These are plastics that can be reheated and remoulded. Examples are jerry cans, buckets, cups,plates, etc
Thermosetting plastics: These are plastics that cannot be reheated and remoulded. Examples are cooking utensil`s handles, dress buttons, radio and television cabinets, electric plugs and sockets.
Properties of Plastics
Weight: Plastics are lighter in weight compared wood and metals.
Colours: Plastics are available in various colours like green, red, white, blues, etc
Conductivity: Plastics are poor conductors of heat and electricity. They are insulators.
Easy Workability:Plastics are easy to be moulded, machined, casted and drilled.
CLASS ACTIVITY
Select different metals, test for magnetism, sound, and conductivity.
Take a rubber band or catapult, test for elasticity.
DATE:11|6|2020
To Revisions on properties of materials
WOOD
Wood is a material obtained from trees. wood is commonly called “timber”, it is used for building, carpentry and joinery work.
Classification of Wood
wood is broadly classified into two:
- Softwood
- Hardwood
Softwood: Softwood is called “conifers”. They are wood obtained from trees having needle-like, thin and evergreen leaves. That is, they do not shed their leaves during the dry season. They are grown in the temperate region, they are fund in countries like Europe, New Zealand, Japan, Canada, etc Examples of softwood are spruce, cedar, fir yew, etc
Hardwood: Hardwood is obtained from “deciduous trees”. They have broad leaves and shed their leaves during dry season. They are grown in both temperate and tropical climates like Africa, India, Europe, etc. Examples of hardwood are Oak (Iroko), Teak, Masonia, Mahogany etc.
Metals
Metals are solid materials at room temperature and liquid or gaseous at higher temperature.
Classification of Metals
There are two classes of metals namely:
- Ferrous Metals
- Non-Ferrous Metal
Ferrous Metals: The ferrous metals contain some Percentage of iron and can be magnetized. Examples are cast iron, wrought iron, steel,pig iron, etc
Non-Ferrous Metals: The non-ferrous metals contain no iron at all and cannot be magnetized. Examples are aluminium, copper, brass, etc.
Identification of metals by Physical Properties
The following are properties of metals:
- Density: This property of metal reveals the heaviness or lightness of different metals.
- Luster: This is the colour in form of appearance when a metal is polished. it can be glossy, luminous and shiny.
- Magnetic Effect: This is the property of metals which enable them to be attracted by magnet. All ferrous metals are attracted by magnet because they contain iron. But non- ferrous metals cannot be attracted by magnet because they do not contain iron.
- Conductivity: This is the ability of metals to transfer it from one end to another. Also, metals are good conductor of electricity. This is the reason why metals are used to produce electrical cables and electronic devices.
- Malleability: This property makes it possible for metals to be easily changed into other shapes by machines and tools without breaking
- Fusibility: Metals can be melted from solid state into liquid state when heated to its melting point an oven .
Class Activities
- List two examples metals that can not be magnetized
- Write two alloys of non-ferrous metals
- List two forms /shapes of metals
- Explain any four properties of metals.
Good morning students, hope you are fine.
Date: 9|6|2020
Topic: Revision on board practice
Setting Drawing Paper on the Board
Setting drawing paper on the board is the first step to carry out in preparation for good draughtmanship. The following steps should be taken to set drawing paper on the board.
STEP 1: Place the drawing board on the table with the square edge to the left hand side.
STEP 2: Place the drawing paper on the drawing board, leaving equal space round the drawing board.
STEP 3: Use the tee-square from the left hand side to adjust the drawing paper to a parallel line to achieve a square edge.
STEP 4: Slide the tee-square gently down on the paper without shaking or moving the drawing paper to lose its squareness.
STEP 5: Cut four pieces of adhesive papers to hold the drawing papers on the four corners on the drawing board.
Drawing Border Lines using Tee square and Set square
Border lines are vertical and horizontal outlines drawn at right angle to form margin around the edges of the drawing paper. The border lines are usually between 10 – 15 millimetres from the edges of the drawing paper to provide layout for drawing.
Title Block
The title block is an essential part of the drawing. It is an information corner placed at the bottom right hand corner of the drawing paper. It consists of useful information about the drawing like: Name of student, School, Class, Title of drawing, Date and Scale.
Drawing Horizontal and Vertical Lines Using Tee square and Set square
Technical drawing involves the use of different lines. Horizontal lines are drawn with tee-square and vertical lines are drawn using set-square with the support of tee-square.
Lines and their uses
CLASS ACTIVITY:
- List four(4) professionals that use technical drawing
- Write two(2) major drawing materials useful in setting board.
- List two types of pencil used in technical drawing and state their uses.
|
Upload files
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DATE: 4/6/2020
TYPES OF LETTERING
There are two basic styles of lettering :
- The VERTICAL Style;
- The SLANT Style.
| A B C D E F G H I J K L M |
| N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
| a b c d e f g h i j k l m |
| n o p q r s t u v w x y z |
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 |
The vertical style.
| A B C D E F G H I J K L M |
| N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
| a b c d e f g h i j k l m |
| n o p q r s t u v w x y z |
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 |
The slant style.
CLASS ACTIVITY:
Student should practice these two styles of lettering using A3 or A4 paper.
LESSON FOUR
Date: 2/6/2020
Topic: Types of Building and Materials
INTRODUCTION
Building is a very important structure which provides basically shelter for man and his properties. The early man`s first shelter was a cave. As technology advanced, man started to use different materials available to build his house.
Types of Building
The types of building to be constructed depend of the following factors:
1. The purposes and functions of the building.
2. The types of materials used for the building construction.
1. Types of building based on the purposes or functions of the building are:
Bungalow for family residential purpose
Duplex for family residential purpose
Storey building for estate and commercial purposes
Detached and semi-detached houses for residential and commercial purposes.
Hall of residence for students` hostels.
Sky scrapers for offices, hotels and business accommodation.
Warehouses and factories for industries and storage facilities.
Educational building for academic purpose.
Types of building based on the materials used are:
Wood building
Mud building
Glass building
Marble buildig
Stone building
Hut
COMMON BUILDING MATERIALS
The following are the common materials used for building construction:
Cement: The raw materials used to produce cement are: chalk or limestone and clay. It is used as binding material for concrete, mortar, block moulding, etc.
Sand: Sand is dug from the ground. It has fine texture and are used for making blocks, concrete, mortar, etc
Granite/Hard Cores: They are crushed stones used to prepare concrete. The hard cores are bigger than granite in size. They are used for foundation of buildings and construction of walls
Mortar: Mortar is the mixture of sand, cement and water. Sand in mortar reduces cracking and reduces cost. Cement is the binding material and the water allows easy mix softness of the mortar.
Cement Blocks: Cement blocks are made from mixture of sand, cement and water in proportional ratio. The standard sizes are 225x225x675mm and 150x225x675mm.
Wood: Wood is obtained from trees and they are used flooring, walling, roofing, doors, windows, etc.
Metal: They are available in different forms. They are used to reinforce concrete, roofing, door, window, etc.
Ceramics: Water closet, bath, tiles, and other toilet wares are ceramic products.
Functions of Building
The functions of building are for:
1. Shelter
2. Protection against rain, sun, cold, snow etc
3. Business purposes like office complex, shopping complex, supermarket, hotels, airport, etc.
4. Storage facilities like warehouses
5. Educational facilities like classrooms, laboratories, hostels, etc.
EXERCISES
1. what is building?
2. List twelve materials commonly used for building construction.
3. State four functions of buildings
No Fields Found.LESSON THREE
Date: 25/5/2020
Topic: Freehand Sketching
Introduction
Freehand sketching is the act of making drawing with the aid of hand using pencil and paper only without using drawing instruments. Freehand sketching enables students to draw any idea or picture of picture of objects in their minds quickly and conveniently. It enables easy communication of imaginary ideas objects to others. The pencil used for freehand sketching is HB. Objects sketched must be proportional and should not be drawn to scale.
Sketching A Straight Line
To sketch a straight line, the following procedures should be followed:
1.Make points or dots along a straight path on the paper.
2.Beginning to draw a line along the straight points to join them together.
3.Fix your eyes on the points when joining and not the line.
Since the topic has been taught in class before, the students are to answer the questions below
Sketch the following items.
1.Tee square 2.French curve 3.Set square 4.A pencil
No Fields Found.Date: 20/5/2020
LESSON TWO
Topic: Drawing Instruments And Materials
The following are drawing instruments in Technical Drawing:
1 Drawing board
2 Tee square
3 Set square
4 Protractor
5 French curve
6 Metric rules
7 Sharpener
8 Metric rules
DRAWING MATERIALS:These are consumables items used for technical drawing. The following are the necessary drawing materials: 1. drawing paper 2. drawing pencil 3. erasers 4. handkerchief 5. emery clothes/glass paper 6. adhesive paper
LESSON ONE
Date:18/05/2020
Subject: Basic Technology
Class:Jss1
Revision of previous terms work
Topic: Workshop Safety Rules and Regulations
Introduction: In technology, practical work is very important just as experiment is very necessary in science
Practical work is the means through which engineers, technologists and technicians produce things by using tools and machines with the available materials in the workshop. The use of tools and machines during practical work has caused harm and injuries to workers in the workshop. Therefore, the need to be Safety conscious and carry out work in the workshop with carefulness are vital to create an accidental free environment for workers and students of technology.
Meaning and Causes of Workshop Accidents Workshop Accidents are unexpected happenings that cause injuries or pain to workers or students, and damage to machines or tools
Many accidents have resulted in the loss of different body parts of workmen and caused loss of lives and properties.
The causes of workshop accidents include the following ignorance, carelessness, fatigue, horse play, slippery floor, lack of safety devices, lack of maintenance and poor storage
Since the students have been taught the topic and note given, they are to answer the following questions on the topic
1 What is workshop accidents? 2 List four causes of accidents in the workshop 3 List four methods of preventing accidents in the workshop 4 List four types of workshop accidents 5 Define safety devices and list six of them
No Fields Found.