LESSON: 11
DATE DELIVERED: 31-08-2020.
TOPIC: SPORTS AND SOCIETY .
LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of the lesson, you should be able to:
- Define:
- Sport.
- Society
- Sports law
- Mention the functions of sports in the society.
- List the type of sports law.
SPORTS AND SOCIETY
SPORTS is defined as any competitive activity that has recorded history and up to date development, rules and regulations involving physical exertion and organized association.
SOCIETY: Is defined as a group of people living together in an organized community.
FUNCTIONS OF SPORTS IN THE SOCIETY:
- Sports leads to effective cooperation in the society. It equally helps the society to stay together.
- It has helped to reduced social menace.
- It is used to reduced tension
- It serves as a source of employment
- It has boosted the economy of the society
- It serves as an avenue to discover budding talent.
- It serves as an avenue to dissipate excess energy.
- Sports has been effectively deployed to curb crime rate among youth.
SPORTS LAW:
Tort : this is expressed as a legal act resulting in direct or indirect injury to another individual or property.
NEGLIGENCE: this is a legal action instituted against individual or cooperate institution as compensation for injuries inflicted (eg not giving adequate warning or not taking proper care)
LEGAL LIABILITY: this is a state of being made responsible for action taken eg club vs players.
ASSUALT IN SPORTS: this occurs when a person commits an offence against official or athletes which can consequently lead to injuries in sports.
LESSON: 10
DATE DELIVERED: 27-08-2020.
TOPIC: HUMAN TRAFFICKING.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of the lesson, you should be able to:
- Define human trafficking.
- Mention the causes of human trafficking.
- State the implications of human trafficking.
- Highlight the solution to human trafficking.
HUMAN TRAFFICKING:
HUMAN TRAFFICKING: Is the moving of men, woman or children from one place to another and placing them in condition of forced labour, prostitution, and domestic services.
CAUSES OF HUMAN TRAFFICKING:
- Lack of employment opportunities.
- Social discrimination.
- Political instability.
- Profitability.
- Corruption on the part of the government.
- Economical instability.
IMPLICATIONS OF HUMAN TRAFFICKING:
- Its lead to loss of life through infectious disease.
- It affects the working population.
- It can devastate families.
- It can lead to low self esteem.
- It can lead to physiological and psychological trauma.
SOLUTION TO HUMAN TRAFFICKING:
- Security at borders should be tightened.
- Provision of employment.
- Children of a particular age should be discourage from hawking.
- Economy stability.
- Implementation of government policies on human trafficking.
- Joint effort from the religious organizations.
LESSON: 9
DATE DELIVERED: 14-08-2020.
TOPIC: Karate.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of the lesson, you should be able to:
- Brief the history of karate.
- Mention skills in the karate game.
- State the importance of karate game.
- List the rules of karate.
- Highlight the officials and terminologies of karate.
KARATE:
Karate was developed tremendously into an offensive and defensive martial art which one can defect enemies with a single fist attack or kick without weapons. karate has developed into sports and it has spread to almost all parts of the world. World Karate Federation (WKF) became an Olympics Sports which has over 20 medals at stake. Karate Federation of Nigeria is currently affiliated to the Union of African Karate Federation.
IMPORTANCE OF KARATE:
- It helps in movement of our limb that help regular proper blood flow in muscle.
- it helps in the development of speed and free movement of the body.
- it is a sports that comprises physical exercise as well as self defense.
- physical uses karate a a form of treatment for patient.
BASIC SKILLS:
- Throwing or take down.
- stance.
- movement.
- blocking.
- kicking.
- choking.
- striking.
RULES OF KARATE:
- Abiding by the rules and ethnics in your daily life whether in public or private.
- train with both heart and soul with worrying about the theory.
- your opponent must be present in your mind.
- avoid deceit and dogmatism.
SCORING SYSTEM:
In team competitions, a team normally consists five karate plus two reserves. the following scoring system will be used;
IPPON: full point (10 points)
WAZA-ARI: half point(7 points)
OFFICIALS:
- Referee
- judge
TERMINOLOGIES:
- REI – Bow
- Yoi – Ready
- Hajime – Start
- Yame – Stop
- Hansoku – Foul
- Shobu Ippon Hajime – Start of match.
NOTE: The RED tape contest area means danger, while the blue is safety area.
LESSON: 8
DATE DELIVERED: 07 -08-2020.
TOPIC: RULES AND OFFICIAL IN JUDO .
LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of the lesson, you should be able to:
- State the rules of Judo.
- Mention the officials in judo game.
- List the languages of the judo game
RULES OF JUDO GAME:
- The first judoka to score one point wins the contest.
- winning by a point is called IPPON
- Deliberately going to the floor can warrant a penalty.
- Punching or putting a hand foot, leg on an opponent face is prohibited.
OFFICIALS IN JUDO GAME:
- Referee
- Judges
- Time keeper
LANGUAGES OF THE GAME:
- Jikan- Time out
- Judoka- Judo practitioner
- Kimi- Decision
- Judo- Easy way/gentle way
- Judogi-Judo suit
- Matte- Stop
- Maitte- I surrender
- Tatami- A mat
- Waza- Techniques
- Dojo- Training hall
- Ukemi- Break falling
- Yoshi- Carry on
- Hajime- Begin
- Jime- Choke
- Soremade- Finish
LESSON: 7
DATE DELIVERED: 28-07-2020.
TOPIC: JUDO .
LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of the lesson, you should be able to:
- Brief the history of Judo.
- Mention the equipment and facility in the judo game.
- List the basic skills in the judo game
HISTORY OF JUDO
Judo is a combat game founded by the Japanese. it is highly complicated and skillful form of wrestling designed for self-defense without its name from Ju-jitain about 18th century. Professor Jigoro Kano developed the sport to an appreciating level.
He also set up the kidokan school of Judo in 1882 in Tokyo Japan. in 1964 Judo became an Olympic sport. Jigoro Kano was named the father of Judo by the International Olympic Committee. The International Judo Federation (IJF) was formed with its headquarter in Berlin Germany.
NATURE OF THE GAME
Judo is an individual game. in the game, two contestants will come to the mat and stand facing each other at a distance of 3- 5 meters. each will put on their uniform called Judogi. at the signal of the referee. The contestants will bow to each other on the mat and grab each other’s jacket and begin to fight. to signal the end of the match the timekeeper throws a red bean bag on the mat, opponent rise, and face each other across the mat. referee raises his hand in the direction of the winner. in case of a tie, the judges decides.
EQUIPMENT AND FACILITIES:
- Gymnasium hall
- Contest area or Judo mat
- Judogi
- A belt is worn which indicate the judokas stand.
BASIC SKILLS
- Stance
- Grip
- Falling
- Throws
LESSON: 6
DATE DELIVERED: 01-07-2020.
TOPIC: Consumer Health .
LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of the lesson, you should be able to:
- Define consumer health.
- Mention the important of consumer health.
- List the right of a consumer.
DEFINITION:
Consumer Health: Is the process by which a consumer becomes conscious or is educated about products and services available for consumption.
Consumer Education: Is defined as a formal educational program designed to the consumer in acquiring the relevant knowledge to protect their health.
IMPORTANCE OF CONSUMER HEALTH:
- It directs the consumer on how and where to buy goods and services of high quality needed
- It safeguards consumer from the activities of quacks
- It enables the consumer to derive maximum satisfaction of the products he/she has purchased.
CONSUMER RIGHT:
- Right to know the date of production and expiry date.
- Right to safety.
- Right to choose what one wants.
- Right to know where the product is produced.
- Right to know the ingredients and nutrition used for preparing the products.
- Right to know the name and address of thee manufacturer.
- Right to be inform about the goods and services.
GOVERNMENT AGENCIES RESPONSIBLE FOR CONSUMER PROTECTION IN NIGERIA:
- WHO
- SON
- NAFDAC
- PCB
- CPC
- NHA
- PAN
- UNICEF
ASSIGNMENT:
Write the full meaning of the acronyms of the agencies responsible for consumer protection in Nigeria.
LESSON: 5
DATE DELIVERED: 25-06-2020.
TOPIC: Gymnastics.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of the lesson, you should be able to:
- Define gymnastics.
- Mention the division of gymnastics.
- List the equipment used in gymnastics.
DEFINITION:
Gymnastics is a sport that includes physical exercises requiring balance, strength, flexibility, agility, coordination, and endurance. The movements involved in gymnastics contribute to the development of the arms, legs, shoulders, back, chest, and abdominal muscle groups.
DIVISION OF GYMNASTICS:
- Artistic Gymnastics.
- Rhythmic gymnastics.
- trampoline gymnastics.
- power tumbling.
- Acrobatic Gymnastics.
EQUIPMENT.
Gymnastics equipment is usually divided into Men’s and Women’s Gymnastics. Floor Exercise, Pommel Horse, Still Rings, Vault, Parallel Bars, and Horizontal Bar, Uneven Bars, Balance Beam, and Floor Exercise, rings, parallel bars, high bars, trampoline, and maximizer. vaulting board, vault runway, and vault horses foam.

IMPORTANCE OF GYMNASTICS:
- Gain strength and power.
- Good Flexibility.
- Improve your coordination.
- Learn a range of movements.
- Learn to Listen.
- Learn to set goals.
- Gain Self Esteem.
- Skills which will benefit other sports.
- Social Interaction.
- Having Fun.
ASSIGNMENT:
What is gymnastics equipment called.
LESSON: 4
DATE DELIVERED: 18-06-2020.
TOPIC: Environmental Pollution.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of the lesson, you should be able to:
- Define environmental pollution, pollution, and pollutant.
- Mention the types of pollution.
Environmental Pollution:
Environmental Pollution can be defined as any undesirable change in physical, chemical, or biological characteristics of any component of the environment i.e. air, water, soil which can cause harmful effects on various forms of life or property.
Pollution: The term pollution can be defined as influence of any substance causing nuisance, harmful effects, and uneasiness to the organisms.
Pollutant: Any substance causing Nuisance or harmful effects or uneasiness to the organisms, then that particular substance may be called as the pollutant.
Types of Pollution:
- WATER POLLUTION
- AIR POLLUTION
- LAND POLLUTION
- NOISE POLLUTION
WATER POLLUTION:
Water Pollution can be defined as alteration in physical, chemical, or biological characteristics of water through natural or human activities and making it unsuitable for its designated use. Fresh Water present on the earth surface is put to many uses. It is used for drinking, domestic and municipal uses, agricultural, irrigation, industries, navigation, recreation. The used water becomes contaminated and is called waste water.
Sources of Water Pollution
Most of Water Pollution is man made It may also occur naturally by addition of soil particles through erosion animal wastes and leaching of minerals from rocks
The sources of water pollution can be classified as
- Municipal Waste
- Water Industrial Waste
- Inorganic Pollutants
- Organic Pollutants
- Agricultural Wastes
- Marine Pollution
- Thermal pollution.
Air Pollution:
Air pollution is the introduction of chemicals, particulate matter, or biological materials that cause harm or discomfort to humans or other living organisms, or cause damage to the natural environment or built environment, into the atmosphere.
A substance in the air that can cause harm to humans and the environment is known as an air pollutant.
Causes of Air Pollution:
1. Carbon dioxide-this This happens because of Deforestation and fossil fuel burning.
2. Sulfur dioxide –Due to the burning of sulfur-containing compounds of fossil fuels.
3. Sulfur oxides- very dangerous to humans at a high concentration.
4. Sulfur in the atmosphere is responsible for acid rain.
Consequences of Air Pollution:
CO2 is a good transmitter of sunlight, but it also partially restricts infrared radiation going back from the earth into space, which produces the so-called greenhouse effect that prevents a drastic cooling of the Earth during the night. CO2 in atmosphere –> GLOBAL WARMING
Land Pollution:
Land pollution: is the demolition of Earth’s land surfaces often caused by human activities and their misuse of land resources. It occurs when waste is not disposed of properly. Urbanization and industrialization are major causes of land pollution.
Causes of Land Pollution:
Four main causes of land pollution:
- Construction.
- Agriculture.
- Domestic waste.
- Industrial Waste.
NOISE POLLUTION:
Noise pollution is excessive, displeasing human, animal, or machine-created environmental noise that disrupts the activity or balance of human or animal life. Sound becomes undesirable when it disturbs the normal activities such as working, sleeping, and during conversations. World Health Organization stated that “Noise must be recognized as a major threat to human well-being.
Sources of Noise Pollution:
Transportation systems are the main source of noise pollution in urban areas. Construction of buildings, highways, and streets cause a lot of noise, due to the usage of air compressors, bulldozers, loaders, dump trucks, and pavement breakers. Industrial noise also adds to the already unfavorable state of noise pollution. Loudspeakers, plumbing, boilers, generators, air conditioners, fans, and vacuum cleaners add to the existing noise pollution.
Effects Of Noise Pollution:
According to the USEPA, there are direct links between noise and health. Also, noise pollution adversely affects the lives of millions of people. Noise pollution can damage physiological and psychological health. High blood pressure, stress-related illness, sleep disruption, hearing loss, and productivity loss are the problems related to noise pollution. It can also cause memory loss, severe depression, and panic attacks.
Solutions for Noise Pollution:
1. Planting bushes and trees in and around sound generating sources is an effective solution for noise pollution.
2. Regular servicing and tuning of automobiles can effectively reduce noise pollution.
3. Social awareness programs should be taken up to educate the public about the causes and effects of noise pollution.
4. Workers should be provided with equipment such as earplugs and earmuffs for hearing protection.
ASSIGNMENT:
What is the full meaning of USEPA.
LESSON: 3
DATED: 10-6-2020.
TOPIC: Safety Education.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of the lesson, you should be able to:
- Define accident, safety education, and First Aid
- State safety measures to be taken at home, school, sporting events, and on the road.
Safety education: This is the process of learning activities that help to acquire knowledge and skills, to cultivate a good attitude as well as practical measures that will enable an individual to avoid an accident and live safely anywhere they find themselves.
First aid: is the immediate and temporary assistance or care given to an injured or sick person before being taken to the hospital or before the arrival of medical personnel.
Safety measures: are methods or steps taken to prevent accidents from happening.
Objectives of first aid:
- Prevent a condition from becoming worse
- sustain life
- aid or promote recovery
- Assist victims to obtain or get medical attention.
Accident: Accident can be defined as an unplanned unforeseen and unexpected occurrence or event which can lead to damage, loss of body parts, injury or death.
Types of Accident:
1. Home accidents.
2. Sports ground or playground accident.
3. School accident.
4. Road accidents.
Safety Measures to be taken is as follows:
- Home Accidents:
a. Wet floors should be properly mopped and dried.
b. Fruit peels like banana, orange, mango etc should not be left on the floor.
c. Electrical gadgets at home should be taken to professionals for repair.
d. Electrical sockets should be switched off when not in use.
e. Good safety habits should be adapted in all homes.
2. Sports ground/play ground accidents
a. Play area must be free from dangerous people, objects etc.
b. Participants in any sporting activity must be medically fit for the activity they intend to perform or engage in.
c. Warm-up activities must precede any sports or games.
d. Equipment to be used for sporting activities should be inspected and ascertained to be safe for use.
e. Teaching instruction must be in simple and clear language.
3. School accidents:
a. Accident and safety education should be included in the school curriculum.
b. Rules and regulations governing the “dos” and “don’ts” in the Laboratory should be visibly spelled out for everyone to see.
c. Chemicals and laboratory equipment should be handled with care.
d. Time should be effectively managed. Rushing should never be allowed on the sports field.
4. Road accident:
a. Road users should possess adequate driving skills before they are given driving licenses.
b. Drive only when you are calm and fully alert.
c. Obey traffic lights where available.
d. Also avoid speeding
e. Doubled check before crossing roads, do not be in a hurry.
ASSIGNMENT:
Mention 10 duties of a first aider.
LESSON 2.
DATED:-4-06-2020
TOPIC: Human Trafficking
LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of the lesson, you should be able to:
- Define human trafficking.
- mention the 3types of human trafficking.
- state the causes of human trafficking.
- List the health implications of human trafficking.
Human trafficking:
Human trafficking is the trade of humans for the purpose of forced labour, sexual slavery, or commercial sexual exploitation for the trafficker or others. This may encompass providing a spouse in the context of forced marriage, or the extraction of organs or tissues, including for surrogacy and ova removal.
Human trafficking is the process of trapping people through the use of violence, deception or coercion and exploiting them for financial or personal gain.
Trafficking: Really means girls groomed and forced into sexual exploitation; men tricked into accepting risky job offers and trapped in forced labour in building sites, farms or factories; and women recruited to work in private homes only to be trapped, exploited and abused behind closed doors with no way out.
People don’t have to be transported across borders for trafficking to take place. In fact, transporting or moving the victim doesn’t define trafficking, it can take place within a single country, or even within a single community.
Types of Human Trafficking:
The 3 most common types of human trafficking are:
1. Sex trafficking.
2.Forced labor.
3.Debt bondage.
Causes of Human Trafficking:
Human trafficking happens in every country in the world, in many different forms; however, the causes behind human trafficking are essentially the same for labor trafficking, sex trafficking, child trafficking, and all other types of modern day slavery. Although different countries face different causes, the root causes remain similar throughout the world. What are the causes of human trafficking? When we know where the root of the issue is, we can start to address trafficking at a deeper level and promote sustainable change. Here are the 10 causes of human trafficking around the world.
- Poverty:
Poverty is one of the largest contributors to human trafficking. It can drive people to become traffickers; it can drive parents to sell children or other family members into slavery. People in poverty are targeted by traffickers, who offer them a way to earn money when, in fact, they will actually earn nothing and be treated as a slave. Poverty also plays a large piece in many of the other root causes of trafficking, driving people to migrate, making education and legitimate work difficult to obtain, making recovery and safety from war and disaster impossible, and more.
2. Lack of education:
A lack of education can lead to decreased opportunities for work at a living wage, and it can also lead to a decreased knowledge in rights. Both outcomes can cause people to be at a greater vulnerability for human trafficking. In prevention of trafficking, education can also empower children to make changes in their community as they grow older that will prevent situations and vulnerabilities of which traffickers take advantage.
3. Demand for cheap labor/demand for sex:
Basic economics tell us that for a market to form, supply and demand need to exist. The demands for cheap labor and for commercialized sex lead to opportunities for traffickers to exploit people. Traffickers can make a large profit by producing goods and services through cheap or free labor and selling the products or services at a higher price. Commercialized sex is a lucrative market that allows traffickers and pimps to become the only profiter from their victims through an endless cycle of buyers and high prices.
4. Lack of human rights for vulnerable groups:
In many countries, groups that are marginalized in society lack institutionalized human rights, which can lead to them be potential victims of trafficking. Traffickers can prey on these marginalized groups because they lack protection of the law enforcement, their families, and even the society they live in. Also, when countries lack fundamental laws regarding human rights, traffickers feel as though they can get away with what they are doing more easily. A lack of human rights laws can also end in punishment for victims, if the laws and government don’t recognize that human trafficking is exploitation of other people.
5. Lack of legitimate economic opportunities:
When people lack legitimate economic opportunities, that can also lead to increased vulnerability to human trafficking. Groups that are especially vulnerable in this area are migrants without work permits, those who lack education, those who live in rural areas where there are less jobs available, as well as women and certain ethnic groups who may not be able to get jobs due to discrimination. Traffickers offer seemingly legitimate jobs to people who cannot get them otherwise, only to lure them into forced labor, sex trafficking, bonded labor, and more.
6. Social factors and cultural practices:
In many countries, cultural practices and social factors are a major cause of human trafficking. In some places, bonded labor is seen as an acceptable way to pay off debt. In other places, selling children to traffickers is the norm, especially for poorer families in rural areas. Some countries, such as Mauritania, still practice antiquated slavery, where families are held for generations by slave-masters. There are also instances, like in Uzbekistan, where forced labor is institutionalized. During the cotton harvest, all adults and children are expected to work in the cotton fields until the crops are harvested. Cultural and social factors can also lead victims not to speak up about being trafficked or who their traffickers are, especially if they come from groups who lack human rights protections.
7. Conflict and natural disaster:
Conflict and natural disaster can lead to economic instability and lack of human rights, giving traffickers an advantage and making people more vulnerable to human trafficking situations. In conflict zones and wars, some rebel or military groups will use child soldiers and keep sex slaves. Additionally, both conflict and natural disaster can lead people to migrate out of their hometowns and home countries, making them more vulnerable to traffickers, especially if they are looking for work or paying smugglers to get where they want to go. And with increased economic instability, traffickers have opportunities to offer false job offers to people, leading them into trafficking situations.
8. Trafficking generates a large profit:
One major cause of human trafficking is the large profit that traffickers gain. This is an incentive for them to continue trafficking people in both forced labor and sex trafficking. For traffickers using forced laborers and bonded laborers, they get cheap labor and can sell their product or service at a much higher cost. For those using sex trafficking, they can easily take all of the profit, forcing women to make a certain amount each night, and keeping them in the situation through drugs, violent force, threats, and more.
9. Lack of safe migration options:
For those looking to migrate out of their home countries due to safety concerns or economic opportunities, they are especially vulnerable to traffickers. Traffickers can use illegal smuggling as a way to trick people into forced labor or sex trafficking. And for migrants looking for jobs in other countries, traffickers typically offer them job opportunities that seem legitimate, only to force them into a trafficking situation.
10. Traffickers:
Above many other factors that cause human trafficking are the traffickers themselves. Beyond cultural practices, the profit, vulnerabilities of certain people groups, lack of human rights, economic instability, and more, traffickers are the ones who choose to exploit people for their own gain. While many of these factors may play into the reasons why traffickers get into the business, they still make a willful decision to enslave people against their will—either because of the profit or because of a belief that certain people are worth less or because of a system of abuse and crime that they were raised in. Trafficking ultimately exists because people are willing to exploit others into trafficking situations.
Health Implications Of Human Trafficking:
As noted, many health issues are associated with trafficking:
* Disease.
*Substance Abuse
*Complications from abortion
*Maternal Morbidity and Mortality
*Depression
*Anxiety
*Sexual disorders
*Reactions to trauma
ASSIGNMENT:
Which country has the most human trafficking?
LESSON 1:
DATE DELIVERED: 27 /5/2020
TOPIC: HANDBALL.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of the lesson, you should be able to:
- Brief explain the history of handball.
- State the basic skills in the game of handball.
- Explain the nature of handball game.
- List some of the officials in the game of handball.
- Mention the facilities and equipment in handball game.
BRIEF HISTORY OF HANDBALL:
The game of handball originated in Germany and was introduced by Konrad Kock. In 1919 Mr Karl Schelenz known as the father of modern handball because he was the first to give the name HANDBALL and developed the rules.
THE NATURE OF HANDBALL:
T he game is started with a throw off at the center by any of the team that wins the toss. After the pass, the players can use the various skills to dislodged their opponents. The game is played by two teams of 7 players each. Five substitutes or reserve players are allowed. The duration of the game is 60 minutes i.e. 30 minutes per halve and 10 minutes for rest at half time.
BASIC SKILLS IN THE GAME OF HANDBALL:
The fundamental skills in the game handball are:
1. Passing
2. Dribbling
3. Shooting
4. Pivoting
5. Faking and feinting
6. Guarding
7. Goal keeping
FACILITIES AND EQUIPMENT:
Facility: i. Handball court
Equipment:
1. Net
2. Ball
3. Costume (jersey, tennis shoe)
4. Whistle
5. Stop watch
6. Score sheet
THE OFFICIALS IN THE GAME OF HANDBALL:
1.Two Referee: i. Court referee
ii. Line referee
2. Scorer
3. Time keeper
HANDBALL COURT:
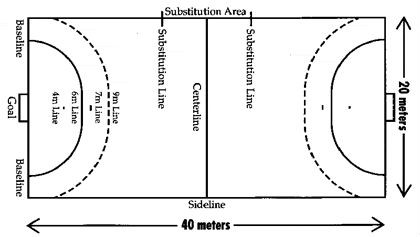
ASSIGNMENT:
States five rules and regulations of the game Handball.