|
Upload files
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HELLO, I HOPE YOU ARE STAYING SAFE. MAY GOD CONTINUE TO KEEP US SAFE, AMEN.
AGRICULTURE, LUMBERING AND FISHING IN NIGERIA
10/09/2020 CORRECTION TO ASSIGNMENT
5 problems of lumbering in Nigeria
- Exploitation of timber causes leaching of the soil and soil erosion
- It leads to the depletion of natural forest products
- High cost of transporting forest products to where they are needed or processed for use
- Presence of buttress roots in some trees makes felling very difficult and dangerous
- It also leads to the disappearance of wild life
Solutions to the problems
- Bush fallowing and bush burning should be discouraged
- Afforestation that is planting of two trees in areas where one tree is cut should be encouraged
- Re-afforestation: clearing the bush of bad trees and planting valuable ones to replace them
- Roads should be constructed at lumbering areas to ease transportation of logs
- Forest guards should be employed to check illegal felling and ensure planting of new trees
FISHING IN NIGERIA
Fishing involves the catching of some fishes in rivers, lakes, ponds or ocean either for local consumption, sale or foe export
Fishing is done in three major areas in Nigeria and they include;
- Inland fishing: this type of fishing is carried out in rivers, ponds and lakes within the country. River Niger, Benue, Ogun, Lake Chad and Kainji are major areas for inland fishing in Nigeria.
- Lagoon and Creek fishing: this involves the catching of fishes in Lagoons and creeks along the coasts of Nigeria.
- Deep sea (ocean) fishing: this involves the catching of fishes in the seas and oceans.
Methods of fishing
- The use of fishing nets
- The use of traps to catch fish
- The use of hook and line
- The use of trawlers which can catch large quantities of fishes
Popular fishes found in Nigeria waters includes Tilipia, Claries, Mackerel, Troat, Shark, Carps, Mud fish, Lady fish, Dog fish, Electric fish and Herrings.
03/09/2020 LUMBERING IN NIGERIA
Lumbering is defined as the felling of economic trees in the forest, which can be used for domestic, industrial or commercial purposes.
The presence of equatorial climate favours the existence of tropical rain forest where economic trees are found.
Lumbering areas in Nigeria includes Benin, Sapele, Ondo, Port-Harcourt and Calabar.
Economic trees used for lumbering include Iroko, Obeche, Opepe, Sapele wood, Mahogany and African Walnut
FACTORS FAVOURABLE FOR LUMBERING IN NIGERIA
- The presence of dense tropical rainforest provides ready sources of valuable timber
- Favourable equatorial climate
- Presence of many economic trees
- High demand for hardwood in foreign countries and timber for fuel
- Efficient sawmill industries to process the raw timber
- Efficient transport like rivers and roads to move logs to either sawmill or to port for export.
METHODS OF LUMBERING
The method of lumbering in Nigeria takes the following steps:
Step 1: the lumbermen search the forest for the particular tree wanted
Step 2: platforms of about 2-3m high is built around the trees with buttress roots
Step 3: the tree is then cut down either by axe, hand-saw or powered-saw
Step 4: the branches of the tree after felling are cut off and the whole tree is cut into logs for easy transport either through roads or rivers to the saw mills for processing to useful products e.g. plywood or into the port for export
ECONOMIC IMPORTANCE OF LUMBERING
- Timber serves as a source of income to government by way of licenses and permits given to the timber contractors
- Timber is used for the construction of Canoe and Boats
- It provides raw materials like timber for timber processing industries which provides plywood and planks
- It provides employment to people who are involved in lumbering related activities
- Lumbering provides foreign exchange through the export of timber to oversea countries.
ASSIGNMENT
- Enumerate 5 problems of lumbering in Nigeria
- Provide solutions to the problems listed above.
27/08/2020 IMPORTANCE OF AGRICULTURE
Agriculture is one of the major sectors which contributes to the economic development of Nigeria, its importance includes;
- Provision of food
- Employment
- Source of income
- Provision of clothing and shelter
- Provision of market for industrial goods
- Development of towns
- Provision of raw materials for industries
PROBLEMS OF AGRICULTURE IN NIGERIA
- Lack of finance or credit facilities
- Inadequate land due to land tenure system
- Lack of basic amenities like electricity and pipe-borne water in rural areas.
- Inadequate agricultural education and extension services
- Negative attitude of the people towards farming
- Lack of storage and processing facilities
- Problem of pests and diseases
SOLUTIONS TO THE PROBLEM
- Loans should be given to Farmers
- Basic amenities should be provided to discourage rural-urban migration
- Farmers should be trained to accept modern systems of farming
- Storage and processing facilities should be provided at reduced rates
- Farmers should use fertilizers to improve the fertility of the soil and productivity of their crops
- Modern farm implements like tractors, ploughs, ridgers and harvesters should be used
- Farmers should use irrigation system in periods of drought.
ASSIGNMENT
Write short notes on the importance of Agriculture given above
20/08/2020 CORRECTION TO THE ASSIGNMENT
Reasons for growing Rice in the middle belt
- Presence of drainage in the area
- Favourable climate of the area
- Presence of marshy areas which supports the cultivation of Rice
- Rice is one of the major cash crops being produced in the area
FACTORS THAT FAVOURS THE PRODUCTION OF SOME CASH CROPS IN NIGERIA
COCOA
Physical Factor
- It requires a well drained loamy soil
- Heavy rainfall of between 1125mm to 1500mm
- Temperature of 26 0 C
- It requires shelter from direct rays of the sun at the nursery stage
Human factor
- Availability of labour
- Availability of favourable market
- Availability of good transport network from area of production to market
OIL PALM
Physical factor
- It needs an annual rainfall not less than 1500mm
- It needs eight months of rain and sufficient sunlight
- It does not thrive well in areas with prolonged dry season
- It does well in acidic and sandy soil
Human factor
- Availability of labour
- Availability of favourable market
- Availability of good transport network from area of production to market
GROUNDNUT
Physical factor
- It requires light and sandy soil
- It requires rainfall of 625mm to 1000mm
- It requires a long dry season to mature
- It does not required prolonged rainfall
Human factor
- Availability of labour
- Availability of favourable market
- Availability of good transport network from area of production to market
6/08/2020 CORRECTION TO ASSIGNMENT
Important crops produced in Nigeria
Crops produced in Nigeria can be grouped into two which are food crops and cash crops.
- Food crops: they are grown to provide food and they grow and mature within one or two years. It can be divided into grains crops like millet, rice, guinea corn, maize which are mainly cultivated in the north due to light rainfall. AND root and tuber crops like yam, cocoyam, cassava in the south because of favourable rainfall and fertility of the soil.
- Cash crops: these are crops grown for sale to provide income for individuals or for nation if exported.
Important cash crops in Nigeria
| Crops | Areas where they are produced |
| Cocoa | Akure, Ibadan, Abeokuta |
| Kola | Akure, Ibadan, Abeokuta |
| Rubber | Sapele, Benin city, Akure, Calabar |
| Oil palm | Aba, Owerri, Port-Harcourt, Benin, Okitipupa |
| Groundnut | Kano, Kaduna, Bauchi, Katsina |
| Cotton | Zaria, Kaduna, Kano, Bauchi |
| Beniseed | Markurdi |
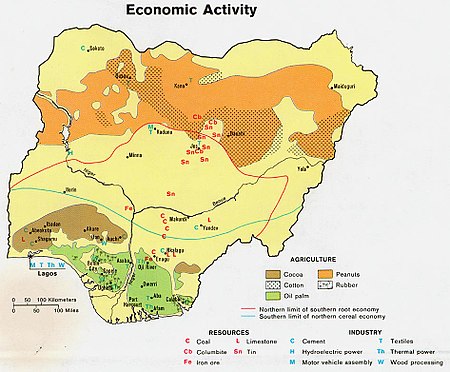
Map of Nigeria showing the distribution of some cash crops produced in Nigeria.
ASSIGNMENT
Enumerate reasons for growing rice in the middle belt
29/07/2020 AGRICULTURE, LUMBERING AND FISHING IN NIGERIA
AGRICULTURE IN NIGERIA
Agriculture is defined as the art or management of cultivation of crops and rearing of animals for man’s use.
Types of Agriculture in Nigeria
- Plantation or mechanized agriculture: its a commercial cultivation in which products are mainly for sale. It requires a large area of land, large capital investment, large or intensive labour and it usually involves the cultivation of one crop i.e. monocropping
- Subsistence agriculture: produce is mainly for family consumption. It requires small area of land, small capital family labour and it involves the cultivation of many crops at the same time i.e. mixed cropping
- Mixed farming: this is the cultivation of crops as well as rearing of animals on the same piece of land. It usually requires a small area of land which is intensively cultivated. Pasture is grown to provide grasses and legumes for the animals and the droppings of the animals are used as manure. It is mainly practised in the north especially in the Guinea and Sudan savannas.
- Intensive agriculture/ Market gardening/ Truck farming: it is practised in thickly populated urban areas e.g. Kano, Ibadan etc. it requires small area of land which is intensively cultivated throughout the year, it involves the cultivation of vegetables, fruits and flowers and the use of fertilizers to improve the fertility of the soil
- Crop rotation: crops are rotated in sequence year after year to maintain the fertility of the soil. Deep-rooted crops like yam is followed by shallow rooted crops like maize during rotation.Three to five different crops can be grown on the same piece of land but on different plot and a legume is always incorporated to add nutrients to the soil
- Shifting cultivation: this involves the movement of farmer and his family from one piece of land to another when the land is no more fertile. Production is mainly for family consumption so simple farm tools and family labour are employed
- Pastoral farming/Nomadic herding: it is practised in the savannah belt of the north especially in the Sudan savannah. It involves the constant movement of cattle and herdsmen from one place to another in search of pasture and water. Production is favoured by the presence of plenty grasses and the absence of tsetse flies
- Transhumance: this involves the seasonal movement of animals up and down hill slopes in search of pasture. When lowland grassland withers during the dry season, the animals move up a hill or plateau where there is still grass because of the cooler climate
- Terrace farming: it is practised on slopes in upland areas, e.g. Jos Plateau and Udi hills. Ridges are made to cut across the slope thereby forming steps to check erosion
- Irrigation farming: it is practised mainly in the northern parts where there is little or no rainfall. Dams are constructed to store water, canals and pipes are used to channel the water to farms
- Ranching: it is a scientific and modern method of animal rearing. Effort is made to grow pasture for the animals which remains on the farm.
ASSIGNMENT
Read and write a short note on important crops produced in Nigeria
22/07/20
REVISION QUESTIONS ON ENVIRNMENTAL CONSERVATION
- Define environmental conservation
- List 4 natural resources that may be conserved
- List 4 methods of conserving each of the following: water, wildlife, forest and soil
- state 5 reasons for environmental conservation
16/7/20
NOTE: please write out all these notes in your school notebook.
ENVIRONMENTAL CONSERVATION
CORRECTION TO ASSIGNMENT
CONSERVATION OF MINERAL RESOURCES
- There should be legislation against indiscriminate mining of mineral resources
- Effective and efficient extraction methods of mining should be adopted to prevent wastages
- There should be effective and efficient utilization of available mineral resources for man’s use
- Over-dependence on a particular mineral resource should be discouraged as this can lead to the depletion of such mineral resources
- There should be proper pricing of mineral resources and their by-products to ensure maximum value for the mineral products.
IMPORTANCE OF CONSERVING THE ENVIRONMENT
- Environmental conservation helps to keep the environment safe and healthy
- It helps to control erosion, both sheet and gully erosion
- It prevents some plants and animals species from going into extinction
- Environmental conservation also enables man to have the full enjoyment of the environment as nature has provided
- It also helps to maintain the natural beauty of the environment
- It helps to control global warming and climate change.
Ways/methods of conserving soil
- Improved farming methods : the practice of mixed farming, strip Cropping and crop rotation helps to control soil erosion
- Afforestation and reforestation should be practised in order to reduce exposure of the soil to erosion
- Enlightenment programmes : people should be educated on the effects of soil erosion and on soil conservation measures
- Legislation : these are laws made to combat erosion through soil conservation bard
- Shelter belts: this is the planting of trees in form of belts where wind erosion is dominant so as to serve as wind break and reduce wind erosion.
METHODS OF CONSERVING AIR
- Chemical wastes should be discharged high into the air through fume chambers
- Industries should be sited away from residential houses
- There should be proper monitoring of air pollution
- There should be government legislation on air pollution
- Provision of filters or absorbers to reduce pollutants from waste gases.
ASSIGNMENT
Enumerate 5 ways of conserving mineral resources.
Conservation is defined as the planned, control exploitation or judicious use of natural resources to ensure their continuous availability and to preserve the quality or original nature of the environment.
REASONS FOR CONSERVATION: To prevent destruction of natural environment or to allow for continued use of natural resources for man’s benefit.
Natural resources that need to be conserved include: wildlife, water, forest, soil, air and mineral resources.
METHODS OF CONSERVING WILDLIFE
- Establishment of game or forest reserves
- Establishment of zoological gardens
- Control of hunting to prevent extinction of some animal species
- Prohibition of deforestation and encouragement of afforestation or reafforestation
- Prevention of pollution to prevent the destruction of aquatic life.
METHODS OF CONSERVING WATER
- Trapping or storing of water in tanks or wells
- Treatment and recycling of used water
- Tree planting which provides vegetation cover and reduces evaporation and promotes water retention
- Damming of rivers to allow for more effective management of water
- The existence of vegetation also brings about the formation of rainfall
METHODS OF CONSERVATION OF FOREST
- Cutting of trees without destroying the undergrowth
- Educating the public on the value of forests and the importance of conservation
- Establishment of forest reserves
- Prevention of plant pests and diseases
- Prevention of bush burning or careless forest fires.
ASSIGNMENT
Enumerate 5 ways of conserving soil.
NVIRONMENTAL PROBLEMS
Revision Questions on Environmental Problems
- what is environmental problem or hazard
- discuss desert encroachment, flooding, drought, deforestation, land, air and water pollution on the following topic ; causes, effects and control.
ND POLLUTION
This is defined as the release or injection of substances into the land in quantities that are harmful to man, animals and plants
CAUSES
- Dumping of refuse, sewage, metal scraps, plastic wastes, chemicals, toxic wastes
- Oil spillage
- The use of pesticides and fertilizers in an area
EFFECTS
- It causes offensive odour
- It could be poisonous to man and animals
- Some renders soil infertile
- Some can kill useful soil organisms
CONTROL
- Urban wastes should be buried
- There should be proper disposal of sewage
- Refuse should be burnt in an incinerator
- Pesticides and fertilizers etc. should be applied as instructed
- Oil pipelines should be maintained and checked regularly to prevent oil spillage
- There should be legislation by government against dumping of refuse or toxic wastes at any place
WATER POLLUTION
This is the release or discharge of toxic substances into water bodies in quantities that are harmful to man, animals and plants
CAUSES
- Discharge of domestic wastes in water
- Oil spillage
- Discharging industrial wastes in water
- Fishing with chemicals such as Gamalin 20
- Acid rain
EFFECTS
- It causes the death of aquatic animals and plants
- It causes water borne diseases
- It encourages the growth of seaweed and algae which disrupt water transport
- It impairs he use of water for domestic and industrial purposes
- It can lead to unemployment among fishermen
CONTROL
- Avoid dumping of untreated wastes into the water
- There should be proper legislation on the proper use of water bodies
- There should be treatment of industrial wastes
- Good fishing practices
- Public enlightenment
ASSIGNMENT
Read environmental conservation.
11/06/2020
ENVIRONMENTAL PROBLEMS
correction to assignment
Areas affected by drought are;
1. Sahelian region, e.g, Senegambia, Mali, Burkina Faso, northern Nigeria, northern Ghana
2. Desert areas e.g, Indian desert, sahara desert, Antarctic desert, Bambi desert etc.
ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION
This is the release of harmful substances to the environment (air, land and water), in quantities that are harmful to man, animals and plants.
Types of Environmental Pollution
1. Air pollution
2. Land pollution
3. Water pollution
1. Air pollution: this is the release of harmful substances into the air in quantities that is harmful to man, animals and plants.
CAUSES
1. Fumes from industrial processes and vehicular exhausts
2. Noise from loud speakers, sirens, construction and mining sites etc
3. Poor refuse disposal
4. Spray of liquid and gaseous herbicides and pesticides
5. Harmattan
EFFECTS
1. Health; it causes irritation of eyes, lungs and skin ( skin cancer)
2. Noise pollution can cause temporary deafness
3. It causes change in the climate of an area
4. It causes the destruction of the ozone layer
5. It can cause accident due to poor visibility
CONTROL
1. Industries should be sites away from residential houses
2. The level of noise from loud speakers, sirens etc should b controlled
3. There should be proper education on refuse disposal
4. There should be proper monitoring of air pollution
5. There should be government legislation on air pollution.
EXERCISE
Read land pollution.
F
LOODING
Flooding can be defined as the accumulation of an abnormal large volume of water in an area which does not percolate or flow away.
CAUSES
- Excessive rainfall in an area which causes flooding of river channels
- Refuse dumping on drainages, block culverts or river channels
- Erection of buildings on watersheds, roads and culvert sites
- Breakdown of dam an d embankments
- Strong tidal waves can also cause flooding
EFFECTS
- It causes loss of lives and properties
- It leads to the interruption of socioeconomic activities
- It makes vehicular movements difficult
- It causes pollution of the environment due to deposition if debris
- It can spread water-borne diseases.
CONTROL
- Construction if wider culverts or gutters
- Avoid refuse dumping in water channels
- Legislation against indiscriminate dumping of waste and erection of buildings in swampy areas
- Construction of dams to act as flood reservoirs
- Proper urban planning to avoid urban flooding
DROUGHT
This is another environmental problem which is defined as the state of prolonged dryness or absence of rainfall long enough to cause total dryness in an area.
CAUSES
- Absence of rainfall
- High rate of evapo-transpiration
- Changes in weather and climate
- Low humidity
- High daily temperature without a corresponding rainfall
EFFECTS
- It leads to high loss of crops and livestock
- It may lead to migration of man and animals
- It makes land lose its biological and economic values
- It causes reduction in agricultural productivity
- It leads to famine
CONTROL
- There should be legislation against cutting of trees and bush burning
- Afforestation: the planting of trees to encourage rain formation
- Irrigation: artificial application of water to soil aids the growth of plants
- Planting of cover crops: it helps to reduce the rate of evaporation and helps to retain water in the soil
- There should be cloud seedling or artificial rainfall
EXERCISE
- Mention some areas affected by drought
- Briefly explain cloud seedling
TOPIC : ENVIRONMENTAL PROBLEMS
Another environmental problem is DESERT ENCROAHMENT
This is the extension or spread of deserts to areas which were originally not deserts before. It is common in areas closer to deserts e.g, Sahel regions in northern Nigeria like Maiduguri, Damaturu etc
CAUSES
- Overgrazing: this is the excessive removal of grasses by animals, thereby leaving the soil bare to desert encroachment
- Changes in climate: sudden change in the climate of a place from wet or partially wet climate to dry one can cause desert encroachment
- High speed of winds: high speed of winds across the desert carries sand and deposits them on the land
- Prolonged drought: when there is a long period of time without rainfall (drought) or prolonged drought, it leads to desert encroachment in an area
- Deforestation: the cutting down of trees can also encourage desert encroachment
EFFECTS
- It can lead to displacements of people and settlements
- It can lower the water table of an area
- It can result in hot and dusty environment
- It leads to climatic changes
- It can cause the loss of pastures and livestock.
CONTROL
- Afforestation: the planting of tress can control desert encroachment, by controlling the speed of winds. (wind breaker).
- Irrigation: artificial application of water to land encourages the growth of vegetation
- Creation of shelter belts: the setting up of shelter belts can reduce the wind speed, thereby discouraging desert encroachment
- Controlled use of wood as fuels: the use of wood as fuels should be discouraged ass this encourages desert encroachment
- Environmental education: people in the affected areas should be educated on the danger of desert encroachment and how it can be prevented.
ASSIGNMNENT
Read on flooding.
TOPIC : ENVIRONMENTAL PROBLEMS
Environmental problems are any natural or human-induced event which poses a serious danger or risk to the lives and properties of people in the environment.
Some environmental problems include: volcanic eruptions, soil erosion, desert encroachment, flooding, drought, deforestation, coastal erosion, environmental pollution, earthquakes, oil spillage etc.
1.) soil erosion: this is the process whereby the top soil is gradually removed or transported away by water, wind etc.
CAUSES
- Deforestation: this the removal of vegetation, thereby exposing the land to erosion
- Overgrazing : this is the excessive removal of grasses by animals that feed on them, also exposing soil to erosion
- Population pressure on land : continuous cultivation of the land due to high population eventually exposes the soil to erosion.
- Mining and construction: this is the digging of soil for building construction or for mining which can later cause soil erosion
- Nature and composition of the soil : can determine the level of soil erosion e.g clay soil easily causes soil erosion while sandy does not.
EFFECTS
- Soil erosion causes the removal of fertile top soil needed for cultivation
- It causes the loss of farmlands
- It causes the loss of lives and properties
- It leads to the damage of roads and railway lines
- It pollutes rivers and lakes due to deposition of debris
CONTROL
- Afforestation: this is planting of trees to control erosion
- Controlled grazing: few animals should be allowed to graze at a time in a particular area
- Improved farming methods: the practice of mixed farming, strip cropping and crop rotation helps to control erosion
- Legislation: there should be laws made to control erosion through soil erosion conservation boards.
- Shelter belts: this is the planting of trees in form of belts where wind erosion is dominant to serve wind breakers and reduce erosion.
ASSIGNMENT
Discuss earthquake under the following topic:
- Definition
- Causes
- Effects
- Control