10TH OF AUGUST,2020.
GOOD MORNING STUDENTS,HOW WAS YOUR WEEKEND AND I BELIEVE YOU ARE PUTTING IN ALL IT TAKES FOR A GOOD SUCCESS IN YOUR FORTH COMING EXAMINATION .
CORRECTION TO LAST CLASS REVISION QUESTIONS
1.Definition of Soil pH.
Soil pH is the measure of the degree of acidity or alkalinity of soil.
2.Five causes of soil acidity.
a. Leaching
b.Presence of acid parent.
c. Nutrient uptake by Plant.
d. Use of acid fertilizer
e.Presence of Sulphur in the soil.
3.Ways of reducing soil acidity.
a.By application of liming materials likeslaked lime etc.
b.By application of organic materials.
4.Liming Materials include;
a.Quick lime
b.Slaked lime
c.Gypsum
d.Dolomite or calcite
e.Wood ash
f.Basic slag
g.Limestone etc.
5. Five components of soil;
a.Soil air
b. Soil water
c.Organic matter
d. Inorganic matter or mineral matter.
6.Importance of water to crops.
1.Water provides the medium for absorption of mineral salts.
2.It facilitates the transfer of nutrients to other parts of plants where they are used in various metabolic processes.
3.It is used for hydrolysing food substances such as starch,protein,fats and oil for easy transmission to other parts of plants.
4.It helps to maintain plant turgidity.
5.It helps in seed germination.
6.Water is an essential raw materials in the process of photosynthesis.
7.Water facilitate enzymatic activities occuring in crop plant.
T O D A Y ‘S R E V I S I O N Q U E S T I O N S
- Define Organic Manure.
- Mention three types of organic manure.
- Mention five importance of organic agriculture.
- Mention five ways by which water exist in soil.
- List five ways of conserving water in the soil.
- List five ways by which soil nitrogen is lost in the soil.
- Define nitrogen cycle.
- Mention four processes of nitrogen fixation.
3rd of August,2020
GOOD. MORNING STUDENTS.HOW WAS THE WEEKEND? GRADUALLY, WE ARE MOVING CLOSER TO THE EXAMINATION DATE.KEEP WORKING HARD.BY GOD’S GRACE YOUR LABOUR WILL NOT BE IN VAIN.
CORRECTION TO LAST CLASS WORK.
1a.DEFINITION OF SOIL TEXTURE.
Soil Texture is the degree of coarseness or fineness of soil particles
b.Methods of determining Soil Texture.
i.Moulding Method
ii.Feeling Method
iii.Mechanical Analysis
iv.Sieving Method.
2a. Definition of Soil Structure.
Soil Structure is the arrangement of soil particles into different sizes or aggregate.
2b.Types of Soil Structure.
i.Single-grained Structure
ii.Crumb Structure
iii.Plate-like structure
iv.Spheroidal Structure
v.Block-like Structure
vi.Prismatic Structure
3.Range of diameter of the following soil particles.
i.Clay Below 0.002mm
ii.Silt. 0.002mm-0.02mm
iii Fine sand 0.02-0.2mm
iv.Coarse sand 0.2mm
v.Gravel Above 2.0mm
.
TODAY’S WORK.
1.Define Soil pH
2.Mention five causes of soil acidity.
3.Mention two ways of reducing soil acidity.
5. Mention five liming materials.
6. Mention four major components of soil.
7.Mention four importance of water to crops.
27TH OF JULY 2020.
GOOD MORNING STUDENTS.CORRECTION TO LAST CLAiSS WORiK.i
1.FACTORS TO BE CONSIDERED IN GIVING FEED TO FARM ANIMALS.
a.Age of the farm animals.
b.Purpose of rearing.
c.State of health of the animal.
d.Types of the animal.
3.
2. EFFECTS OF FEED SHORTAGE IN ANIMAL PRODUCTION.
1.It causes slow growth rate of livestock.
2. It leads to increased susceptibility to diseases.
3.It leads to high death rate in farm animals.
4.It causes drastic reduction in livestock production.
5.It leads to low birth weight or causes loss of weight.
3.CLASSES OF LIVESTOCK FEED.
1.Basal/Energy Feed/Carbohydrate concentrate.
2.Protein Concentrate
3.Mineral and Vitamin concentrate.
4.Roughages
3b
i.Basal Feed – maize,cassava peelings,yam peelings,guinea corn etc
ii.Protein Concentrate-blood meal,groundnut cake,soyabean meal,fish meal etc
iii.Vitamin and mineral supplement -blood meal, fish meal,bone meal,salt lick/common salt.
4a.Four forms of Rouphages.
a. Silage
b.Soilage
c.Hay
d.Straw
4b.Preserved form of Roughages-
i.Hay
ii.Silage
5.Carbohydrate- staw,maize,yam peelings,guinea corn etc
i.Protein-fish meal, groundnut cake,soyabean meal,cotton seed meal,blood meal etc
ii.Vitamins-blood meal,fish meal,bone meal,salt lick etc
iii.Minerals/Mineral salt-same as above
T O D A Y ‘ S R E V I S I O N WORK.
S O I L
D E F I N I T I O N O F S O I L
Soil is the uppermost layer of the earthcrust that provides support and nutrients for plant growth.
There are 3 main types of soil.
These are:
1.Clay soil
2.Sandy soil
3.Loamy soil
SOIL PROPERTIES
Soil properties include:
1.Soil structure
2.Soil Texture
3.Soil pH
4.Soil Temperature
R E V I S I O N Q U E S T I O N
1a.Define Soil Texture
b.Mention four methods of determining soil texture.
2a.Define soil structure
b.Mention four types of soil structure.
3. Mention the range of diameters of the following particles:
1.Clay
ii.Silt
iii.Fine sand
iv.Coarse sand
v.Gravel
20TH OF JULY, 2020
GOOD MORNING STUDENTS .BELIEVE YOU ARE KEEPING SAFE . GOD IN HIS INFINITE MERCY WILL CONTINUE TO INTERVENE TO ENSURE YOUR EXAMINATION IS CONDUCTED THIS YEAR IN JESUS NAME.
CORRECTION TO LAST WEEK WORK.
1.TYPES OF INCUBATOR
i.Cabinet Type or Forced Draught type.
ii.Natural Draught or Table Type.
2.Components of an incubator and their functions
i.Insulator : To prevent heat loss.
ii.Vent or fan:For ventilation
iii.Thermometer:To detect the degree of hotness or coldness of the machine.
iv.Felt Tray/Egg Tray/Egg Rack:To hold eggs and to prevent cracking.
v.Thermostat:To regulate the temperature of the incubator.
vi.Egg Turning Device::For regular turning of eggs.
vii.Heat Distribution Unit:Helps in the distribution of heat within the incubator.
viii.Heat Source [e.g electric heater,lantern etc]helps in provision of heat.
3.Five operations to be carried out after hatching of eggs in the hatchery:
i.Drying of chicks
ii.Sexing of chicks
iii.Intra- ocular [1] NDV vaccination.
iv.Sorting out abnormal eggs’
v.Packing normal eggs
T O D A Y’S R E V I S I O N Q U E S T I O N S
REVISION QUESTIONS ON ANIMAL FEED
Animal feed are food/feed given to farm animals for growth,energy,repair of worn out tissues and general well being of the animals.
1.Mention four factors to be considered in giving feed to farm animals.
2.Mention five effects of feed shortage in farm animals.
3a.Mention four classes of animal feed.
b.Mention three examples each of feedstuff that can be classified under the classes of feed mentioned above.
4a.mention four forms of roughages.
b.Mention two preserved form of roughages.
5.Mention three examples each of feedstuff that can supply the following food nutrients.
a.Carbohydrates
b.Protein
c.Vitamins
d.Minerals.
13TH OF JULY 2020
GOOD MORNING STUDENTS.
TRUST YOU ARE FINE.
DO NOT BE DISCOURAGED AT THIS TIME , NOTHING WILL STOP OR SLOW DOWN YOUR PROGRESS IN LIFE IN JESUS NAME.
PLEASE, BELIEVE WITH ME THAT GOD WILL TAKE ABSOLUTE CONTROL AND YOU WILL WRITE YOUR WAEC [EXAMINATION] THIS YEAR IN JESUS NAME. DO NOT ALLOW YOUR PREPARATION LOSE STEAM.IT IS WELL WITH YOU.
BELOW IS THE CORRECTION TO LAST WEEK WORK AND TODAY’S REVISION WORK.
CORRECTION TO LAST WEEK CLASS WORK
LIVESTOCK MANAGEMENT
A. Examples of Poultry Birds
Domestic fowl,Duck,Pigeon,Guinea fowl,Turkey,Geese.
B.Definition of the following terminologies
1.Pullet:Female fowl below one year of age.
2.Hen:Female fowl above one year of age.
3.Cockerel.:Male fowl below one year of age.
4.Cock:Male fowl above one year of age.
5.Act of mating in fowl.
6.A castrated male fowl.
7.Flock:A group of fowl.
8.Clutch:A group of young chick.
C.Three systems of Poultry Management.
1.Extensive System
2.Intensive System
3.Semi-Intensive System
Extensive System
Advantages
1.It is cheap.
2.Labour involved is small.
3.Poultry birds get vitamins and minerals from grasses and other plants they pick from the ground.#
Disadvantages
1.There is economic losses through predators,thieves and laying of eggs in the bush.
2.It exposes the birds to extremeor adverse weather conditions.
3.The birds are exposed to pests and disease attack.
Intensive System
Advantages
1.It increases efficiency in poultry management.
2.It maximises the use of land.
3.Poultry birds are protected against adverse weather conditions.
4. It reduces loss of eggs to thieves etc.
Disadvantages
1.It is capital intensive.
2.There are occurrences of cannibalism,feather picking and egg pecking.
3.Unproductive birds are difficult to detect especilly in deep litter system.
4.Thin shelled eggs crack easily.
Semi -Intensive System
Advantages
1.There is protection against pests and diseases.
2.The birds are protected against adverse weather conditions.
3.The system is suitable for poultry birds of all ages and kinds.
4.The birds have access to natural vegetation which provides vitamins and minerals to poultry birds.
Disadvantages
1.Cost of feeding is high.
2.There is occurrence of cannibalism,feather picking,egg pecking etc among poultry birds.
3.It leads to low egg production.
T O D A Y ‘ S W O R K
INCUBATORS
DEFINITION
Incubators are machines used tohatch fertilised eggs of poultry birds artificially.
Questions
1.Mention two types of incubators.
2.Mention eight components of an incubators and their functions.
3.Mention five operations to be carried out after hatching of eggs.
6TH OF JULY, 2020
GOOD MORNING STUDENTS.BELIEVE YOU ENJOYED THE WEEKEND.
THE ON-LINE LEARNING CONTINUES DESPITE THE NORMAL SCHOOL REGULAR TEACHING THAT COMMENCES TODAY.THIS WILL AVAIL YOU THE OPPORTUNITY FOR THOROUGH REVISION BEFORE YOUR EXTERNAL EXAMINATION.
Below,is the correction to the previous revision questions before today’s work.
CORRECTION TO PREVIOUS LESSON
CORRECTION OF REPRODUCTIVE HORMONES.
A
Female Reproductive Hormone
I.Testosterone or Androgen
Functions
I .It initiates spermatogenesis.
II.It promotes the growth of accessory sex organs.
III.It sustains the life of sperm in the epididymis.
IV.It maintains sex drive
V.It is responsible for the initiation of the male secondary sex characteristics.
B.
Female Reproductive Hormones.
Female Reproductive Hormones include:
1.Progesteron.
Functions
i.It ensures continuance of pregnancy.
ii.It inhibits oestrus.
iii.lt causes the development of alveoli in mammary glands.
2.Relaxin
Function
It causes the relaxation of pelvic ligament during parturition for easy passage of the young ones.
3.Follicle Stimulating Hormone
Function
It stimulates the growth of ovarian follicle.
4.Lutenizing Hormone
Function
i.It stimulates the secretion of ovarian hormones i.e oestrogen and progesterone.
ii.It causes the rupture of the follicle and subsequent release of the ova.
5.Oxytocin
Functions
1.It promotes the transport of spermatozoa in the female genital tracts.
2. It helps in the let down of milk from the mammary gland after parturition.
3. It aids the contraction of the uterine muscles during pregnancy.
6.Oestrogen
Functions
It helps in the preparation of the uterus lining for the reception of the fertilised ovum.
2.It increases the blood supply and the water content of the uterus.
3.It stimulates the development of the female secondary sexcharacteristics.
4.It stimulates the growth of the duct system in the mammary gland.
5.It helps to increase cilliary activities and mucous secretion in the oviduct.
CORRECTION TO REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS
A. Functions of the following organs of male RUMINANT reproductive system:
1.Testes:
Testes produce spermatozoa and sex hormones called testosterone.
2.Scrotal sac
It suspends and protect the Testes.
3.Epididymis
It ensures the maturation and storage of sperm cells in the testes.
3.Vas Deferens
It transports sperms from the testes to the uterus masculinus.
5.Spermatic cord
it supplies nutrients and oxygen to the testes.
6.Urethra
It is a uro-genital organ which helps to inject sperms into the vagina of a female reproductive tract.It also help to remove urine.
B.Functions of the following female reproductive system.
1.Ovary
It produces the ovum or ova.
2.Fallopian tube
Fertilisation of egg by spermatozoa takes place in the fallopian tube.
3.Uterus
It is the organ where fertilised egg is implanted for further development.
4.Vagina
It receives the spermatozoa during corpulation.
5.Cervix
It allows passage way for sperm at mating and expulsion of the fetus at the time of birth.
6.Cowper’s gland
It forms a gelatinous plug that traps the semen after corpulation.
T O D A Y’S W O R K
LIVESTOCK MANAGEMENT
Definition
Livestock Management is the rearing of domestic animals which include poultry birds etc on the farm.
POULTRY MANAGEMENT.
Poultry refers to group of birds raised for food and other purposes.
REVISION QUESTIONS
A.Mention five examples of poultry birds.
B.Define the following terminologies in poultry management.
a.Pullet
b.Hen
c.Cockerel
d.Cock
e.Treading
f.Capon
g.Flock
h.Clutch
C.Mention 3 systems of poultry management .
i.Mention 3 advantages and 3 disadvantages each of the three systems mentioned above.
29TH OF JUNE 2020
GOOD MORNING STUDENTS.HOPE YOU ARE GRADUALLY ADJUSTING TO RESUME THE NORMAL CLASSROOM INTERACTIVE TEACHINGS.IT IS WELL WITH YOU IN JESUS NAME.
TODAY’S TOPIC:
REPRODUCTIVE HORMONES
Definition of Hormones.
Hormones are chemical substances secreted by ductless glands and transferred to targeted organs through the blood stream for the coordination of the body activities.
Reproductive hormones in animal production is classified into two namely:
1.Female Reproductive Hormones.
2.Male Reproductive Hormones.
Answer the following questions.
1a..Mention one male reproductive hormone .
b.Mention three functions of the male reproductive hormones mentioned I la above .
2.Mention four female reproductive hormones.
b.Mention two functions each of the female reproductive hormones mentioned above.
22ND OF JUNE,2020
GOOD MORNING STUDENTS.HOW DO YOU DO?
I DO APPRECIATE MOSADOLUWA OLADIRAN FOR MAKING GOOD EFFORT TO ANSWER LAST WEEK QUESTIONS.DON’T RELENT. KEEP IT UP.
BELOW IS THE CORRECTION TO LAST WEEK QUESTIONS BEFORE GOING TO TODAY’S WORK.
A. Define the following Terminologies:
I.Oestrus Cycle
This is the interval from the end of one heat period and the beginning of another.
ii.Heat Period
It is the time a female farm ani m al shows signs t o be mated .
iii. Mating
This is the act in which the penis of the male is inserted to the vagina of the female, leading to ejaculation of spermatozoa.
iv.Gestation Period
This is the perid between the fertilization of an ovum to the birth of the young ones,[i.e the period between conception and birth or period of pregnancy].
v.Ovulation
It is the rupturing of the ovary wall to release matured eggs into the fallopian tube in animals.
vi.Parturition
Parturition is the act of giving birth in farm animal.
vii.Fertilisation
It is the fusion of the male sex cell or gamete[sperm] and female sex cell in the oviduct or fallopian tube leading to for5mation of zygote.
viii.Colostrum
Colostrum is the first milk produced immediately after parturitrion.
B. Definition of Artificial Insemination.
Artificial Insemination is the act of injecting spermatozoa artificially into the vagina of female animal on heat period.
C. Advantages of Artificial Insemination
i.Sperms can be used for a long time even after the death of the male animal.
ii.Sperms collected can be used to fertilise many female animals of various sizes.
iii.It is cheaper to import sperms than to import the male animal.
iv.It is more economical as it reduces the cost of feeding and managing male animal.
D.TYPES OF MATING
i.Natural Mating
ii.Artificial Mating
TYPES OF ARTIFICIAL MATING
i.Flock Mating
ii.Pen Mating
iii.Stud or Hand Mating
i.Flock Mating
Male and Female animals are allowed to move together and mate freely.
ii.Pen Mating
This is a type of mating in which very few number of males are kept with limited number of female that are on heat, so that they can mate at anytime.
iii.Hand Mating or Stud Mating
It is a type of natural mating in which males are kept separately to be mated with individual females when on heat period.
T O D A Y’ S W O R K
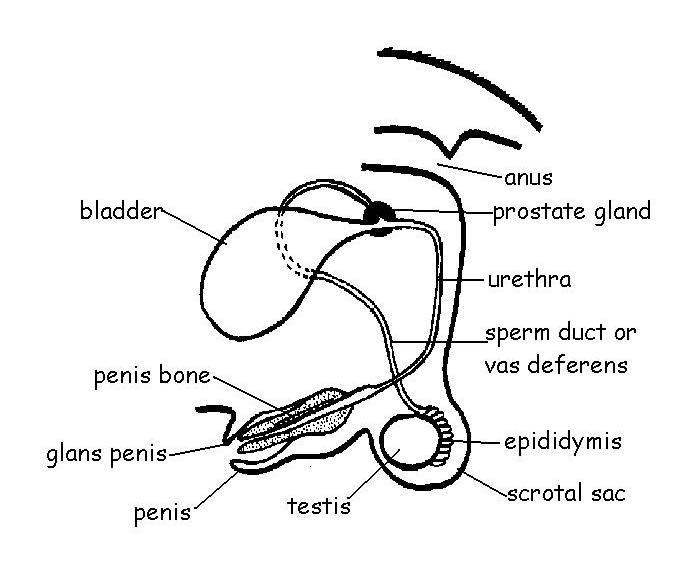
The Diagram below is the diagram of the Male Ruminant Reproductive system.
Study it carefully and use it to answer the following questions:
A
- Mention the functions of the following organs of the male reproductive system. i. Testes ii. Scrotal sac iii. Epididymis iv. Vas Deferens v. Spermatic Cord vi. Urethra
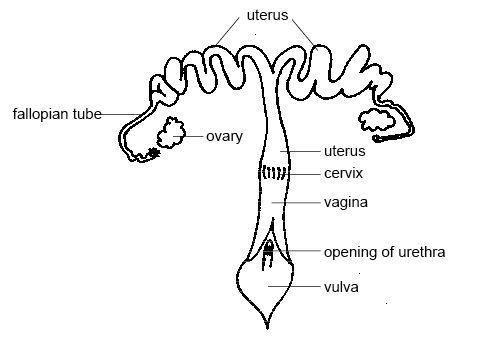
USE THE DIAGRAM OF THE FEMALE RUMINANT REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM TO ANSWER THE QUESTIONS BELOW:
B. Mention the function[s] of the following organs of the female ruminant reproductive system.
i.Ovary
ii.Fallopian tube
iii.Uterus
iv.Vagina
v.Cervix
vi.Cowper’s gland
C.
15th OF JUNE, 2020.
GOOD DAY STUDENTS, HOW WAS YOUR WEEKEND?
PRAY GOD IN HIS INFINITE MERCY WILL PUT AN END TO THIS PANDEMIC CONDITIONS COMPLETELY.
CONTINUE TO PREPARE FOR YOUR EXAMINATIONS. MY PRAYER FOR YOU IS THAT GOD WILL GRANT YOU GOOD SUCCESS DESPITE THE PRESENT WORLD DISTRACTIONS.
Today’s class will start with correction of last class work.
A.
The function/ functions of the following organs of the female monogastric reproductive system.
i. Magnum
1. Albumen is secreted on the yol released or secreted by the ovary. 2. Chalaza is also secreted at the magnum.
Infundibulum
1.It receives the yol released by the ovary. 2.Fertilisation occurs at the infundibulum.
Isthmus
1.it is the organ where the two shell membranes are formed. 2.The shape of the egg is also formed in the isthmus.
Uterus
1.The site where the shell is formed from calcium carbonate by the glands of the uterus. 2.Mineral solutions are added to the eggs.
Vagina
- It accommodates the egg before it moves to the cloaca to be laid.
Cloaca
1.It is the organ through which the egg formed passes to the exterior or passes out.
B
Brief explanation of the following parts of a fertile egg.
i. Chalaza
It is a piece of thick protoplasm that extends to both sides of the yolk.It holds the yolk and the embryo in place within the albumen.
ii. Albumen
Albumen is rich in protein.It accounts for over 50% of the total weight of the egg.
iii.Yolk
It is a yellowish jelly-like mass located at the centre of the egg.It supplies nutrients to the embryo.It is rich in proteins,mineral salts,vitamins and other food substances.
iv.Shell
Shell covers the egg externally and protects the egg.It is rich in calcium carbonate.
v.Air space
Air space is located on one of the pointed ends of the egg.It is found in – between the outer and inner membranes. The air space is very important for respiration of the embryo.
vi.Membranes
Membranes are found immediately after the shell.The membranes are given protection to the egg.
vii.Germinal Disc
Germinal Disc is located at the centre of the yolk as a dark spot.It is only found in fertile egg and develops to form chick.Germinal Disc is also called the embryo.
TODAY’S WORK.
REVISION QUESTIONS ON TERMINOLOGIES IN REPRODUCTION OF FARM ANIMALS.
TERMINOLOGIES USED IN REPRODUCTION IN FARM ANIMAL
TERMINOLOGIES refer to specialised words relating to a particular subject.
Terminologies used in Farm animal reproduction include:
i.Oestrus cycle
ii.Heat period
iii.Mating
iv.Gestation period
v.Ovulation
vi.Parturition
vii.Fertilisation
viii.Colostrum
QUESTIONS
A.Define the terminologies listed above.
B.Mention and explain three types of natural mating.
C.Define artificial insemination.
D.Mention three advantages of artificial insemination.
WEEK FOUR. 08 – 06 – 2020
Good day students,how was the weekend? Believe you are making effort to make the good use of this holiday because one of your final examinations may soon start.Do your best to prepare well and I know God will grant you good success.
Today,we ‘ll do correction of last week work and revision questions on reproductive system of a female monogastric animal.
CORRECTION TO WEEK THREE QUESTIONS
A
- Definition of the following routine managementPractices:
i.CULLING: This is the removal of diseased,poorly performing or destructive animals from a flock of farm.
ii. DEBEAKING: It is the process or Operation which involves the partial removal of the beak of fowls.
iii.DEHORNING: It is the process which involves the removal of the horns of farm animals.
iii.CASTRATION:It is the removal of the sex organs especially the tested of the male animal.
v. IDENTIFICATION:This is a method of making marks on farm animals to be recognised by owners.
2.Reasons for culling farm animals.
i.Failure to reproduce.
ii.Low egg production in case of birds.
iii.Pronounced deformation of parts of the body.
iv. Cannibalism among farm animals.
v. Overweight due to excess fat.
vi.Broodiness in case of birds.
viii.Ill-health of farm animals.
3.Reasons for dehorning farm animals.
i.To make handling easier.
ii.To reduce aggressive tendencies in the flock and also reduce injuries to individual animals.
iii.To ease the transportation of farm animals (e.g cattle) from one location to another.
iv.To increase space available to farm animals during feeding.
v.To enhance physical appearance of farm animals (e.g cattle).
3.Three methods of castrating farm animals.
I.Use of Burddizzo.
Burddizzo is a powerful pincers which is applied to the neck of the scrotum to crush the spermatic cords that supplies blood to the testicles.The process destroys the tested which produce the sperm.
ii.Use of rubber rings (Ring method)
The ringmethod involves the application of rubber rings to the neck of the scrotum.The rings squeeze the spermatic cords and prevent blood from reaching the testicles.Thus, destroying the tested that produces the sperm.
iii.Open Method.
This is a method which involves making an incision on the scrotum and the tested are pressed out.
B. Four methods of Farm Identification.
I.Tattooing
ii.Chaining
iii.Branding
iv.Ear notching.
C.Other management practices in animal husbandry.
i.Steaming up
ii.Weaning
iii.Candling etc
REVISION QUESTIONS ON REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OF A FEMALE MONOGASTRIC ANIMAL AND PROCESS OF EGG FORMATION IN POULTRY BIRDS(I.E RUMINANT ANIMAL).
BELOW ARE THE DIAGRAM OF A FEMALE MONOGASTRIC REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM AND A FERTILE EGG OF POULTRY BIRDS (E.G HEN)
USE THE DIAGRAMS TO ANSWER THE QUESTIONS BELOW.
A.Mention the function or functions of the following organs in egg formation.
i.Magnum
ii.Infundibulum
iii.Isthmus
iv.Uterus
v.Vagina
vi.Cloaca.

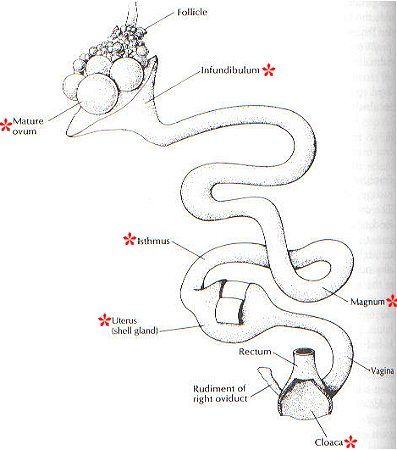

B.
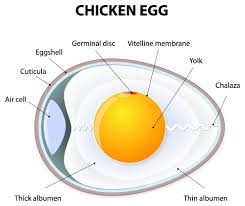
STUDY THE DIAGRAM OF THE FERTILE EGG ABOVE AND USE IT TO ANSWER THE QUESTION BELOW.
Define briefly the following parts of a fertile egg of a domestic fowl:
i.Chalaza
ii.Albumen
iii.Yolk
iv.Shell
v.Air space
vi.Membrane
vii.Germinal disc
01 – 06 – 2020
Hi students,HAPPY NEW MONTH . How are you doing and how was your weekend? Believe you are keeping safe.
Below are corrections to Lesson One and Lesson Two. Go through them and make every necessary correction before answering questions of LESSON THREE.
CORRECTION TO LESSON ONE
(1)a. Diagram A – Maize Weevil
Diagram B – Grasshopper
Diagram C – Cotton stainer
b. Classification based on mode of feeding
Diagram A Boring Insect Pest
Diagram B Biting and chewing Insect Pest
Diagram C Piercing and Sucking Insect Pest
Classification based on location
Diagram A Storage Pest
Diagram B Field Pest
Diagram C Field Pest
c.1. Damage done to crops by Diagram B
i. Destroys the leaves (defoliation)
ii. Destroys succulent parts of the shoot system
iii. Reduces yields of crops
iv. Reduces photosynthetic capacity of crops.
2. Damage done to crops by Diagram C
i. Sucks sap from cotton bolls
ii. Stains lint
iii. Transmits diseases
iv. Creates vents for secondary infection
v. Reduces yield
vi. Destroys bolls of cotton fruit
3. Damage done to crops by Boring Insect Pests
i. Reduces seed quality
ii. Reduces seed viability by destroying the embryo
(2)
| Crops | Mode of Propagation |
| Yam Sugarcane Cassava Garlic | Yam sett, Yam tubers, Yam seed Stem cutting Stem cutting Bulb |
CORRECTION TO LESSON TWO
1.Specimen A Potassium
Specimen B Carbon
Specimen C Calcium
1b.Three uses each of specimens A and B
Specimen A
i. It can be used as fertilizers
ii.It is a component of some fertilizer
iii. It is used in correcting soil acidity
iv. It is used in controlling pests.
v.It is important in the manufacturing of soap.
vi.It is used as a scouring powder
vii.It is sometimes added to compost manure when preparing it.
Specimen B
i. A source of heat for drying/ roasting farm produce
ii. For purification of some produce.
iii. For soil sterilisation when used to produce steam.
iv. Used for driving steam engines.
v. For warming brooder and piglets house.
c. Ways by which specimen C is important in agriculture.
i. It is used to decrease the acidity of fish pond water
ii . It is a component of animal feed.
iii. It Increases activities of soil organisms.
iv. It improves soil structure.
v. For controlling liverfluke by preventing hatching of water snail.
vi. To reduce turbidity in fish pond.
2a. Specimen D Tapeworm
Part of the host found :Intestine of the host
Specimen E – Liverfluke
Part of the host found:Inside the Liver or bile duct
Specimen F – Tick
Part of the host found: Skin or body of host.
b. Ways by which specimen D is adapted to survive in its host .
i.The head or scolex has suckers and hooks for firm attachment to its host.
ii. Has many segments /proglottides which have complete reproductive structures[it increases their survival].
iii. It possesses both male and femalereproductive structures which favor self fertilisation.
iv. They secrete chemicals which ensures their freedom from digestive enzymes of their host’
v. Nutrients are absorbs by all surfaces of the body.
vi.Formation of cyst around the bladderworm ensuring the survival of the bladderworm in the reproductive cycle.
vii.The proglottides contain several eggs which increase probability of survival.
2c. Effects of specimen E on its host.
1.Obstructs flow of bile into the intestine.
ii. Destroys liver tissues thus,causing liver rot.
111. Reduces digestion of fats in the host.
1v.It causes mal-absorption of nutrients.
v. Causes emaciation and death of host.
c.Diseases transmitted by specimen F.
i.Heart water disease
ii.Red water disease
iii. Tick fever
iv. Tick paralysis
v.Mange
vi.Scabies
1a. Differentiate between Farm machinery and Farm Implement.
Farm machineries are mechanical devices with parts working together in order to apply power in carrying out farm operations while farm implement are devices which are attached or mounted to a machine to accomplish a specific objectives or operations on the farm.
1b. Examples of farm machineries;
Tractor,Bulldozer,Incubator,Combined harvester,Sheller,Milling machine,Tree puller,Dryer etc
Examples of farm implement:
Harrow,planter,plough,ridger,slasher,seed/fertilizer broadcaster etc.
2.Factors that affect the type of soil formed at a place.
i.Parent material
ii.Climate
iii.Topography
iv.Time
v.Biotic factors[living organisms,vegetation,human influences etc].
01 – 06 – 2020
L E S S O N T H R E E
ROUTINE MANAGEMENT PRACTICES IN FARM ANIMALS.
The following are some of the routine management practices in farm animal husbandry;
i. culling
ii. Debeaking
iii.Dehorning
iv. Castration
v.Identification
ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS
[A] 1.Define the practices mentioned above.
2.mention five reasons for culling farm animals.
3.mention five reasons for dehorning in cattle.
4.Mention three methods of castrating farm animals .
5.Mention five advantages of castrating farm animals.
B. Mention four methods or practices of farm animal identification.
C. Mention four other management practices in farm animals.
No Fields Found.
L E S S O N T W O
NOTE: Please,answer questions in lesson one before answering questions in lesson two. YET TO UPLOAD CORRECTIONS TO LESSON ONE BECAUSE I DID NOT SEE SUBMISSIONS OF LESSON ONE.
A. Use the named specimens below to answer the following questions. SPECIMEN A -Woodash SPECIMEN B – Charcoal SPECIMEN C – Limestone SPECIMEN D -Tapeworm SPECIMEN E – Liverfluke SPECIMEN F -Tick
.1.Statethemajorelement in Specimen A , B and C b.Give three uses of specimens A and B c. Mention three ways by which specimen C is important in agriculture.
2a. Name the part of the host where each of specimens D,E and F can be found. b. Mention two ways by which specimen D is adapted to survive in its host. c. List three effects of specimen E on its host. d. d. List four diseases transmitted by specimen F
B.
1a. Differentiate between Farm Machinery and Farm Implement. b. Mention five Farm machinery and five Farm implement. 2. List four factors that affectthe type of soil formed at a place.
No Fields Found.L E S S O N O N E
Good day students,how are you doing?Believe you are keeping safe and preparing for your Examinations.By the grace of God the holiday will soon be over and we will start proper classsroom revision.Meanwhile, we’ll be using this medium for revision of our topics and to solve past questions.
A


B C
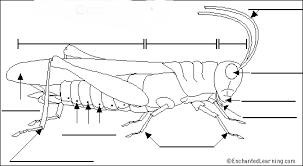

Use the Diagrams above to answer the following questions.
1a Identify specimens A, B and C . b Classify diagrams A,B and C based on their mode of feeding and location. c Mention two economic importance each of specimens A ,B and C.
2. Use the following crops to answer the following questions. Crops:Yam,sugarcane,cassava and garlic. a. Mention the mode of propagation of the crops mentioned above. b. Mention two advantages of staking in yam. c. Name the toxic substance present in cassava and mention two processes of reducing it.
No Fields Found.
