LESSON 13
11th,August 2020.
Topic: Preparation and collection of gases
Good morning everyone ,hope your weekend was good. Today we will look at the above topic, before then ,make sure you check the corrections to previous lessons .God bless you.
In the preparation of gasses, various method are employed and it depends on two major factors.
[i]Vapour density of the gas.
[ii]Solubility of the gas in water.
Gases which are lighter than air[less dense air]are collected by upward delivery of gas also known as
Downward displacement of air .Gases in this category are :Hydrogen[H] and ammonia[NH 3].
On the other hand ,gases which are denser[heavier] than air are collected by downward delivery of gas[upward displacement of air].Examples are HCL,NO2,CO2,SO2,C l2,H2S, SO3.
However ,gases with vapour densites close to that of air[vapour density of air is 14.4],these gases can
Neither displace air upward nor downward. Such gases are collected over water ,if their solubilitiies in
Water are negligible, that is slightly soluble or insoluble in water. Examples of gases in this category
Are O2, N2O, NO, CO, N2 and PH3.
- List gases that can be collected by downward displacement of air.
SS 3 11th,August 2020
CORRECTION TO LESSON 12
1 [a]Zinc blend[ZnS]
[ii]Gypsum [CaSO4.2H2O]
[b][i]Monoclinic sulphur
[ii]Rhombic sulphur
[c]Allotropy is a phenomenon in which an element exist in two or more forms in the same physical
State.
[d]Powdered sulphur is dissolved in carbon [iv] sulphide in a beaker .The solution is warmed
,and filterd into another beaker and allowed to evaporate,when yellow crystals of rhombic sulphur
Are deposited.
2[a][i]SO2
[ii]SO3
[b]When SO2 is passed through water, trioxosulphate[iv] acid is obtained.
SO2 +H2O —–>H2SO4.
[ii]H2SO4 acid is obtained when sulphur[vi] oxide is passed through water.
SO3 +H2O ——>H2SO4
[c]Sulphur [iv] oxide.
3[a][i]S +O2——>SO2
[ii]2SO2 +O2 —–>2SO3
[iii]SO3 +H2SO4 ——>H2S2O7
[iv] H2S2O7 +H2O——->2H2SO4
[b]Concentrated H2SO4 is a strong dehydrating agent. It dehydrates ethanol and sugar as follows:
[i]CH 3CH2OH –>C2H4
[ii] C12H22O11——->12C
LESSON 12
4TH,AUG.2020
TOPIC;Questions based on Sulphur
Goodmorning students,hope your weekend was good.Please do not relent,continue to work hard and success will surely be yours in Jesus name.Today,just want to remind us about SULPHUR.Remenber the occurrence and nature of sulphur,i.e, it occurs free in nature as large yellow deposits, and in combination with other elements viz:Galena[PbS],Zinc blend[ZnS],Iron pyrites[FeS2] and so on.Allotropes,extraction,properties,uses and compounds of sulphur.
Examination questions
1[a]Name two natural ores of sulphur.
[b]Name two allotrotropes of sulohur.
[c]Define allotropy.
[d]How can you prepare a sample of rhombic sulphur.
2[a]Name two oxides of sulphur.
[b]What is obtained when each of them is passed through water?
[c]Name one bleaching agent.
3[a]With equations only describe the preparation of tetraoxosulphate[vi] acid by the contact process.
[b]With examples describe the dehydrating properties of concentrated tetraoxosulphate[vi] acid.
4[a]Describe the behavior of sulphur as it is heated to boiling point.
[b]With equations only show the reactions of sulphur with the following;[i]O2 [ii]H2 [iii]Zn [iv]C [v]H2SO4
5[a][i]State and explain what happens if hydrogen Sulphide gas is bubbled into acidified K2Cr2O7.
[ii]State the equation of the reaction.
[b]How can you obtain a sample of dry hydrogen sulphide in the laboratory?
CORRECTION TO LESSON 11
1.[i]Finely divided iron.
[ii][a]Heat change
[b]Pressure
[iii]Zero
[iv][a]It is a colourless gas.
[b]It is very soluble in water.
[v]3CuO +2NH3 —–à3Cu +H2O +N2
2.[a][i]3H2 +N2 —–à2NH3 Requires high temperature and pressure in the presence of a catalyst of iron impregnated with aluminium.
[ii]N2 +O2 ——-à2NO
[iii]3Mg +N2 —–àMg3N2
[b]Haber process
This is the industrial manufacture of ammonia.Hydrogen and nitrogen in the ratio 3:1 by volume are purified, dried and compressed at a temperature of 600oC and a pressure of 200 atmosphere.The compressed mixture is passed over a catalyst of divided iron mixed with alumina.Ammonia produced is separated by washing with water.
3[a]The manufacture of trioxonitrate[v] acid from ammonia takes place in three stages.They are
[i]The catalytic oxidation of ammonia to nitrogen[ii]oxide[NO]
4NH3 +5O2 —-à4NO +6H2O.It is a reversible reaction and it takes place at about 700oC using a platinium-rhodium catalyst.
[ii]Oxidation of nitrogen[ii]oxide to nitrogen[iv].
2NO +O2 ——à2NO2
[iii]Reaction of nitrogen [iv]oxide with hot water to form trioxonitrate[v] acid.
3NO2 +H2O —–à2HNO3 +NO.The nitrogen[ii] oxide obtained in the third stage reacts with more oxygen to form NO2,which reacts with more oxygen to form NO2,which reacts further with water to form trioxonitrate[v]acid.
[b][i]NaOH +HNO3 —–àNaNO3 +H2O
[ii]CaCO3 +2HNO3 —–àCa[NO3]2 +H2O +CO2
[iii]P +5HNO3 –àH3PO4 +H2O +5NO2
[iv]H2S +2HNO3 —–àS +2H2O +2NO2
[v]4Zn +10HNO3 —–à4Zn[NO3]2 +3H2O +NH4NO3
LESSON 11
28/07/2020
Topic;Questions based on Nitrogen and its compounds.
Good morning students,hope your weekend was fine.Ensure that all necessary corrections are checked.Today we will look at questions that cuts across Nitrogen and its compounds
Past questions based on Nitrogen and its compounds
i.Consider the reaction represented by the following equation;
3H2 +N2 —->2NH3
[1]Name the catalyst used nin the reaction.
[ii]State two measurable quantities which can be used respectively to derive the value of Go for the forward reaction.
[iii]What will be the change in the free energy of the system at equilibrium?
[iv]Give two physical properties of ammonia.
[v]Write an equation to show the reducing property of ammonia.
2.[a]With the aid of balanced chemical equations describe the reaction of Nitrogen with
[i]Hydrogen.
[ii]Oxygen; and
[iii]Magnesium
[b]Describe the Haber process for the production of ammonia.
3.[a] Outline the manufacture of trioxonitrate[v] acid from ammonia.
[b]With equations only,show the reactions of trioxonitrate[v]acid with the following:
[i]NaOH [ii]H2S [iii]CaCO3 [iv]Zn [v]P
4.Describe the laboratory preparation and properties of Nitrogen[iv]oxide.Show the chemical equation of the reaction with all the necessary conditions.
5.[a]How can you obtain a sample of lead from lead[ii]oxide?
[b]Name the gases given out when silver trioxonitrate[v] is heated.
LESSON 10
21/07/2020
Good morning students,hope you are good. I observe that only few of you attempted lesson 9,so lesson 9 is repeated ,meaning attempt it as lesson 10.
LESSON 9
14/07/2020
Hello students,greetings to you all .Pls make sure all corrections are noted before attempting next lesson.
Finailly,we will take the last questions that cuts across question number 3 of WAEC chemistry practical
1[a]Explain briefly the observation in each of the following processes:
[i]When Carbon[iv]oxide is bubbled through lime water,it turns milky but the milkiness disappears when the gas is bubbled for a long time;
[ii]A precipitate of calcium hydroxide is insoluble in excess sodium hydroxide solution whereas that of Lead[ii] hydroxide is soluble.
[b][i]What is primary standard solution ?
[ii]Calculate the mass of sodium trioxocarbonate [iv] required to prepare 250cm3 of 0.15moldm-3solution.[Na=23.0;O=16.0;C=12.0]
[c]Name one gas that can be collected by:
[i]Upward displacdment of air;
[ii]Downward displacement of air.
2[a]Write the electronic configuration of an element with atomic number 15, indicating the distribution of electrons in the energy sub-levels.
CORRECTION TO LESSON 8
1[a][i]Q is copper[ii] trioxocarbonate[iv]/CuCO3.
[ii]Carbon[iv]oxide.
[iii]Excess Q was used to ensure that all ther acid reacted.
[iv]When there is no effervescence.
[v]Filtration.
[vi]To form crystals/to concentrate the filtrate in order to form crystals on cooling or heating to dryness of CuSO4 would not be obtained/anhydrous CuSO4 will not be obtained.
[b][i]White anhydrous copper[ii]tetraoxosulphate[vi]/blue cobalt[ii]chloride paper.
[ii]Alkalin iodine solution/acidified potassium tetraoxomanganese [vii]/acidified potassium heptaoxodichromate[vi].
2[a]-Evaporating dish
-Bunsen burner
-Tripod stand
-Wire gauze
[b][i]Sodium trioxocarbonate[iv],Na2CO3
Potassium trioxocarbonate[iv],K2CO3
Sodium ethanoate,CH3COONa
Potassium ethanoate,CH3COOK
Potassium cyanide,KCN
Sodium Sulphide,Na2S
[ii]The phenimenon is Hydrolysis
[c][i]White precipitate,followed by effervescence and the precipitate dissolves in excess dilute HCL.
[ii]Sulphur[iv]oxide,SO2
Hydrogen Sulphide,H2S
Unsaturated gaseous hydrocarbon[C2H2,C2H4,C3H6,C4H8,C3H4,C4H6etc.][any one]
LESSON 8
07/07/2020
TOPIC;Questions cut across number 3 of both WAEC and NECO practicals
Hello students,how are you today.Please make sure, you check the corrections to previous lessons before attempting lesson 8.
Questions
1[a]In the laboratory preparation of crystals of CuSO4, a green powder Q was added to dilute H2SO4 and stirred.Effervescence occurred and a gas R was given off which turned lime water milky .Excess Q was removed from the mixture. The solution of CuSO4 was concentrated to half its original volume and allowed to stand.[i] What is substance Q?[ii]Name gas R[iii]Why was excess Q used?[iv]How would you know that the reaction is complete[v]What method was used to remove excess Q?[vi]Why was the solution of CuSO4 not heated to dryness?
[b]Name the reagents used for testing each of the following substances in the laboratory:[i] Water [ii]Primary aikanol.
2[a]List tree pieces of apparatus required for the evaporation of sodium chloride solution to dryness.
[b][i] List two normal salts which when dissolved in water turn red litmus blue.
[ii]State the phenomenon that is responsible for the action on the litmus in 2[b][i].
[c][i]State what would be observed on adding BaCl2 solution to a portion of a saturated Na2CO3,followed by dilute HCl in excess.
[ii]A gas Q decolourrized acidified KMnO4 solution.Suggest what Q could be.
CORRECTION TO LESSON 6
1[a]Colourless
[b]Blue
[c]Pink
2.To each of the solution add sodium hydroxide solution in drops then in excess[i]CuSO4 will give a blue precipitate insoluble in excess.[ii]FeSO4 will give a green precipitate insoluble in excess.
3[i]Y
[ii]X
[iii]Z
4 [i][a]Hydrogen sulphide
[b]Sulphur[iv]Oxide
[ii][a]Desicator
[b]Condenser
[c]Sublimation
2[a]Compound[s] which:
[i]has a black colour =MnO2
[ii]Is a basic Oxide=MnO2
[iii]Sublime on heating=NH4Cl
[iv]Dissolves in water to give a solution of pH less than 7=NH4Cl or Pb[NO3]2
[b]The colour of each of the following aqueous solution are:
[i]Caicium hydroxide=Colourless
[ii]Iron[iii]trioxonitrate[v]=Yellow or brownish yellow
[iii]Coppere[ii]tetraoxosulphate[vi]=Blue
[iv]Potassium hepataoxodichromate[vi]=Orange
[c]Neutral oxide which is colourless at room temperature=water
[d]
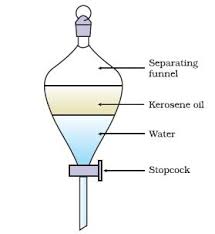
[ii]PhenolphthaleinTitration of strong acid and a weak base.
[b]C1V1[undiluted]
C2V2[diluted]
using dilution law;C1V1=C2V2
V2=C1V1/C2=0.1*50/0.010=500cm3
volume of distilled water to be added to the original solution to make 0.01mol/dm3=500cm3-50cm3=450cm3
[c]Hydrogenchloride/Ammonia/sulphur[iv]Oxide.
DATE;30/6/2020 lesson 7
Hello students,warm greetings to you and hope you are getting ready for resumption.All the best.pls ensure that all lessons are taken and assignments done ,it will do you good.
lesson 6 has not been done,so do that for 30/6/20,tuesday.
CORRECTION TO LESSON 4
[1]a[i]Calorimeter.
[ii]Hoffman voltameter.
b[i]Glucose is soluble in water while Cellulose is not soluble in water.
[ii] Glucose is a strong reducing agent;it reduces Fehlings solution to a red precipitate of copper [i] oxide on boiling.Cellulose does not reduce Fehlings solution.
2[a]i Y is a concentrated teraoxosulphate [iv] acid,while Z is hydrogen chloride gas.
[ii]Acidify a solution of X with dilute HNO3 and silver trioxonitrate [v] solution.White precipitate is formed which is soluble in aqueous ammonia.This confirms the presence of chloride.Alternatively,to the solution of X , add lead two ion solution to get a white precipitate which is soluble when hot and reappears on cooling.This confirms the presence of chloride.
b[1] Calcium chloride is used in the laboratory as drying agent.
[ii]The laboratory technique used is magnetization or dissolution in water and filtration.
3[a]i On bubbling SO3 into acidified KMnO4 solution , becomes decolourised; the purple colour of the solution disappears and it is discharged.
[ii] On mixing zinc dust with CuSO4 solution,the blue colour of the CuSO4 gradually disappears; the solution becomes colourless.A reddish-brown or pink deposit is obtained.
[iii] On adding concentrated HNO3 to freshly prepared FeSO4 solution, the solution changes colour from green to brown.
[b]Substances which ,if added to dilute H2SO4 would give:[i]Hydrogen-Magnesium/Iron/Zinc[ii]ZnSO4-ZnO/ZnCO3/Zn.
Chemistry ss3 23/06/2020 lesson 6
Hello students, how was your weekend? I hope to see you in school very soon as you remain safe .
Please attempt the following questions using the box provided:
1.State the colour observed when distilled water is added to each of the following: :
(a). Silver trioxonitrate( V) solution.
(b). anhydrous copper(I I) tetraoxosulphate(V I)
(c). anhydrous cobalt (I I) chloride
2. Describe one wet chemical test that could be used to distinguish between CuSO4 and FeSO4
3. Use the table below to answer questions (a) to (c)
| Indicator | PH range |
| X | 3.2 – 4.4 |
| Y | 6.0 -7.6 |
| Z | 8.2 -10.0 |
Select from the list the indicators that would be suitable for titrating : ( i ) NaOH solution against HCL.
( i i ) NaOH Solution against CH3COOH (aq) . ( iii ) HCL(aq) against NH3 (aq)
4. ( I ) State one gas that can be tested for using each of the following reagents : (a) Lead (I I ) ethanoate solution . (b) acidified potassium tetraoxomanganate (I v ) solution
(I I ). Name one laboratory apparatus used for : (a) Keeping solids dry (b) Changing vapour to liquid (c) . Name a suitable method for obtaining iodine from a mixture of iodine and sand.
2. (a) C onsider the following compounds MnO2 , NaHCO2 , NH2CL and Pb(NO3)2. Select the compound(s) which ( I ) has black colour (i i ) is a basic oxide ( ii i ) sublime on heating ( i v ) on heating (I v ) dissolves in water to water to give a solution of PH less than 7 .
(b) State the colour of each of the following aqueous solutions ; (i) Calcium hydroxixe ( i i ) iron ( i i i ) trioxosulphate ( v ) ;( i i i ) Copper (I I ) tetraoxosulphate (i v) . ( I v ) Potassium heptaoxodiochromate ( v i )
(c ) Give one example of a neutral oxidewhich is a colouless liquid at room temperature.
(d ) Draw and label a diagram for a set-up that can be used for the separation of two immiscible liquids.
3. (a) State an indicator suitable for the titration of (i) dilute HCL and NaOH(aq) ; ( i i ) dilute CH3COOH and KOH(aq) ; ( I I I ) dilute HCL and NH3(aq). Give a reason for your answer in each case.
(b) Calculate the volume of water that would be added to 50cm3 of 0.10mol dm3 of HCL to dilute it to 0.010mol dm3.
(c ) Name one gas that could be used to demonstrate the fountain experiment.
LESSON 5
DATE;16/06/20
Hello students,hope you are doing great .By Gods grace keep preparing hard for your exams and success will be yours in JESUS name.AMEN.
Lesson 4 will be repeated this week because ,I did not see any submission.Ensure that the corrections for lessons 1,2,&3 is properly checked, so that you will be able to note your mistakes. Pls participate in all the lessons,do not assume anything.God bless You all..
CORRECTION TO LESSON 3 SS3
1.Chlorine
2.Irritating smell
3.Does not burn in air or support combustion
4.Colourless but misty in damp air .
5.Turns red from blue
6Nitrogen [iv] oxide
7.Does not burn or support combustion
8.Irritating
9.Splint burns
10.White fumes
11.Turns red from blue
12.Burning sulphur or burning match
13.Does not burn or support combustion
14.Colourless
15.Burns with blue flame depositing yellow sulphur on cold surface
16.Turns faint red.
17.Colourless
18.Does not burn or support combustion
19. Turns red.
20.Colourless
21.Burns with blue flame,explodes if mixed with air
22.Odourless.
23.Rekindles glowing splint
24.Colourless
25.Does not burn or support combustion
26.Turns faint red
27.Colourless
28.Odourless
29.Does not burn or suooprt combustion
30.Colourless.
LESSON 4
DATE:09-06-20
Hello my students, I hope you are doing great. I have checked your submissions, most of you are still on lesson 1. Please make sure you attempt lessons 2&3 and the corrections will be sent. Today,we will be looking at questions that cut across no.3 for chemistry practicals.
1(a). Name one laboratory apparatus/set-up for
i. Determine the heat of neutralization
ii. Decomposing water into hydrogen and oxygen.
b. Outline a suitable procedure for distinguishing between glucose and cellulose using
i. One physical test a part from tasting
ii. One chemical test.
ci. Mention one salt which produces brown fumes on being heated strongly.
ii. What is the action of the brown fumes mentioned in ci above on litmus above?
iii. Give one reasons why it is not advisable to collect nitrogen by displacement of air.
2. A soluble chloride X reacted with a liquid Y on heating, to give gas Z which turned moist blue litmus paper red and fumed in moist air
i. Identify Y&Z
ii. Give one chemical test to confirm that X is a chloride
bi. State one laboratory use of calcium chloride
ii. Name one laboratory technique suitably for separating a mixture of iron filings and ammonium chloride without applying heat.
3a. State what you would see on
i. bubbling SO2 into acidified KMnO4 solution
ii. Mixing zinc dust with CuSO4 solution
iii. Adding concentrated HNO3 to freshly prepared FeSO4 solution
b. List two substances in which, if added to dilute H2SO4, would give you
i. H2(g)
ii. ZnSO4(AQ).
CORRECTION TO LESSON ONE
1 (a) (I) Blue- black
(11) Black
(111) Pink or Purple
(1v) Yellow
(b) Pass each gas separately through ammoniacal copper (1) chloride. Reddish-brown precipitate indicates ethyne. No precipitate indicate ethene.
2 (a) 1 Ammonia gives dense white fumes with concentrated HCL.
11 Test for the-COOH functional group add saturated NaHCO3 / Na2CO3 solution, effervescent or gas is evolved, or add alcohol and warm with a few drops of concentrated H2SO4. Sweet smell of ester occurs.
SS3 REVISION LESSON 3
02/06/2020
Hello students, warm greetings to you and hope you are doing great.
TOPIC: QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS CONTINUES
When little of a given substances is heated in an ignition tube or in a small hard test-tube until no further change is observed ,gases usually evolved from such substances .These gases are being identified by:
[1]Noting their colours .
[11]Noting their odours
[111]Inserting in the gas ,a burning splint.
[iv]Testing the gas with a moist red and moist blue litmus paper to know if the gas is acidic or basic.
With the knowledge of identification of gasnues,fill in the spaces[1-30] in the table below as an assignment using the form provided under the table,after suppling your name,class and Email.
| GAS | COLOUR | ODOUR | ACTION WITH SPLINT | ACTION WITH LITMUS PAPER |
| 1 | Greenish yellow | 2 | 3 | Turns red then bleashes |
| Hydrogen Chloride[HCL] | 4 | Irritating smell | Does not burn or support combustion | 5 |
| 6 | Reddish brown | Iritating ssmell | 7 | Turns red litmus blue |
| Trioxonitrate iv] acid vapour | Pale yellow Fumes | 8 | 9 | Turns red from blue |
| Tetraoxosulphate [vi] acid | 10 | Irritating | Does not burn or support combustion | 11 |
| Sulpuhur [vi] oxide | Colourless | 12 | 13 | Turns red |
| Hydrogen Sulphide | 14 | Rotten egg | 15 | 16 |
| Ammonia | 17 | Chocking | 18 | 19 |
| Hydrogen | 20 | Odourless | 21 | Not applicable |
| oxygen | Colourless | 22 | 23 | Not applicable |
| Carbon [iv] oxide | 24 | Faint and not easily detected | 25 | 26 |
| Water vapour | 27 | 28 | 29 | Not applicable |
| Nitrogen | 30 | Odourless | Does not support combustion | Not applicable |
CORRECTION TO LESSON TWO
1 (a) (1) Only two of the metals, Zn and Fe will liberate a gas, H2 from one of the aqueous solutions, dilute hydrochloric acid. Of these metals , only Fe will form a green solution. Therefore, R is Fe .
Zinc will form a colourless solution because zinc Ione is colourless. Therefore, S is Zn . A!long the metals, only Cu will have no reaction with three of the aqueous solutions, FeSO4, CuSO4 and HCl, since copper is less active than Fe and H and will not displace its own ion. But Cooper will displace silver ion from AgNO3 forming a greyish- white deposit of silver. The light blue solution is CuSO4. Therefore, Q is Cu.The only other metal T is Pb.
(11) Only dilute HCl will give off a gas,hydrogen ,by reacting with the active metals Zn (S) and iron (R).That is B is dilute HCl.Of the four aqueous solutions only AgNO3 will form a greyish deposit of solid silver with Cu, Fe,Zn and Pb because all four metals displace silver ion in AgNO3 ,since all are more active than silver.Therefore D is AgNO3.
The brownish deposit of R,S,And(I.e.Fe,Zn,andPb)in C is due to Cu deposited from CuSO4 because both Fe,Zn and Pb are more active than Cu.Therefore C is CuSO4.The remaining aqueous solution A must be. FeSO4.
(111)The gas evolved is Hydrogen. It can be tested by bringing a lighted splint near the mouth of the test-tube.A pop sound due to explosive burning of hydrogen in the air, indicates hydrogen.
(b)Other anions such as trioxosulphate(iv) and triocarbonate(iv) also form white precipitates with bariumchloride solution. But these white precipitates are dissolved by dilute HCl acid.Therefore,acidifying the unknown solution with dilute HCl acid eliminates trioxosulphate(iv)ion and triocarbonate(iv) ion when a white precipitate is formed on addition of bariumchloride solution, leaving tetraoxosulphate (vi) ion.
(2) Note that since both are trioxonitrate(v) salts the selected should be to distinguish between ammonium ion sodium ions.
Put about 2g of each in a separate test-tube. Add NaOH(AQ) to each and warm. Where a gas is given off with irritating smell and turns wet red litmus paper blue. The gas is NH3 and salt is NH4NO3 . where no gas is given off the salt is NaNO3.
(b) Note that the basic difference between the is that why cyclohexene is an unsaturated cyclic hydrocarbon, ethanoic acid is a saturated alchanoic acid. They are both liquids hence,the test chosen is either
(I) test for unsaturation or
(I) test for acidity.
To 2cm3 of each liquid in a test-tube add bromine water. The one that decolourises is cyclohexene while the one that does not dicolourise bromine water is ethanoic acid OR to 2cm3 of each liquid in a test-tube add saturated NaHCO3 solution. Where effervescence occurs and gas evolved turn Lime water milky, the liquid is ethanoic acid, where no gas evolved the liquid is cyclohexene.
(C) Note that since both are salts of calcium, the test chosen will be to distinguish between Cl– and CO32-. Put about 2g of each I’m separate dry test-tubes. Add dilute HCL to each. Where there is effervescence with evolution of a colourless gas that turns lime water milky, the reagent is CaCO3. Where there is no visible reaction, the reagent is CaCl2.
(d) Note that both are salts of sodium. Test should distinguish SO32- from SO42-. Make a solution of each. To 2cm3 of each in a test tube add dilute HCL. Then add BaCl2 solution to each. The one that forms a white precipitate insoluble in excess dilute HLC is Na2SO4.while the one whose precipitate dissolves in excess dilute HCL is Na2SO3.
(3) To the unknown solutions add few drops of NH3 solution dropwise and later in excess. White gelatinous precipitate soluble in excess confirms Zn2+ while white gelatinous precipitate insoluble in excess confirms Al3+.
(bi) dilute H2SO4
(bii) ammonia solution
(biii) concentrated tetraoxosulphate (vi) acid or concentrated tetraoxophosphate(v)acid.
(c) effervescence occurs with the evolution of a colourless gas.
LESSON TWO DATE;20/05/20
Hello students,how are you doing and your studies?do stay safe.
Topic;QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS [continuation]
Qualitative analysis can also be used to test for gases like O2 ,co2, NH3,SO2 H2S, etc.
CLASS WORK/REVISION QUESTION
[1a]A,B,C and D represent dilute aquesous solutions of FeSO4,AgNO3,HCL,CuSO4, but not necessary in that order.Q,R,S, and T represents stripes of the metal Zn,Cu,Fe and Pb but necessarily in that order.Each of the metal were added to each of the solutions in separate test-tubes.
The following observations were made:
| Q | R | S | T | |
| A | No visible reaction | No visible reaction | Grey deposit and colourless solution formed | No visible reaction |
| B | No visible reaction | Gas evolved light-green solution formed | Gas evolved and colourless solution formed | Hardly any reaction.strip became slightly whitish |
| C | No visible reaction | Brownish -red deposit and light green solution formed | Brownish -red deposit and colourless solution formed | Brownish-red deposit and colourless solution formed |
| D | Greyish white deposit and light -blue solution formed | Greyish-white deposit and light -green solution formed . | Greyish-white deposit and light -green solution formed | Greyisy-white deposit and colourless solution formed |
[1]Identify the metal Q,R,S and T stating your reasons.
[11]Identify the aqueous solutions A,B,C, and D stating your reasons.
[111]Name the gas evolved and state how you would test for it.
[b]Explain why,in testing for tetraoxosulphate[vi] ions in an unknown solution is with barium chloride solution ,the unknown solution is first acidified with dilute hydrochloric acid.
[2]Describe one chemical test only that could be used to distinguish the compounds in pair below;
[a]Ammonium trioxonitrate [v] and sodium trioxonitrate [v].
[b]cychlohexane and ethanoic acid.
[c]calcium trioxocarbonate [vi] and calcium chloride.
[d]sodium trioxosulphate [iv] and sodium tetraoxosulpate [vi].
[3][a]Describe briefly one chemical test you would perform to distinguish between zinc and aluminium ions in solution.
[b]Mention one laboratory reagent you would use to
[1]produce ammonia from [NH4]2SO4 .
[11]Diffrenciate beteew precipitate of AgCl and AgI.
[111]Dehydrate ethanol.
[c]State what you would observe on adding dilute H2SO4 to a portion of the Na2CO3.
LESSON ONE
Hello students,hope your day is fine and you are coping with the present situation in the world ,ensure you stay safe.
We shall have more of revision and past questions from different topics on this platform.
Topic Date delivered:14/05/20
QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS
This process is used to identify the type of particles(not the amount of substances) present in a chemical sample. It can be used to identify the type of cations ,anions, gases or functional group (s) present in a given sample.
The method involves physical appearance (colour), observation (flame test), heating (identification of gases) and the use of some chemical reagents.
For identification of cations,(basic radicals), NaOH and ammonium hydroxide are the most common reagents used, the solubility or insolubility of the cations in these reagents during the analysis, deep on the particular cations present, which eventually will be confirmed., other reagents are sometimes added.
For anions (acidic radicals), the most common reagents are dilute trioxonitrate ( iv) acid,silvertrioxonitrate (iv)and ammonium hydroxide (for chloride test),Iron(11) tetraoxosulphate(vi), conc.tetraoxosulphate (vi) acid(for trioxonitrate(v)( ion test), dilute trioxonitrate(v) acid, or dilute HCl,lime water(for triocarbonate (v) iron and carbon (iv) oxide)bariumchloride, bariumtrioxonitrate(v), dilute HCl and potassiumtetroxomanganate (vii) or potassiumheptaoxodichromate(vi) (for tetraoxosulphate (vi) ion, trioxosulphate(v) ion and sulphor (iv)oxide gas test). The different anions give different observations, leading to the confirmation of the actual one (s) present.
For organic compounds, the following reagents are used for testing, water, saturated, sodiumhydrogentrioxocarbonate(iv) ,NaOH, HCl(dilute), brome water, alkaline potassium tetraoxomanganate (vii), ethanoic acid, conc.tetraoxosulphate (vi) acid ,ethanol, Fehling’s reagents, iodine solution.
Revision Questions
1 (a) State the colour of
(I) starch on reacting with iodine;
(ii) manganese (IV) oxide powder;
(iii) phenolphthalein indicator in a solution of pH 10; and
(iv) the colloidal suspension formed when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to sodiumtrioxothiosulphate(vi)solution.
(b) Give one chemical test to distinguish between ethene and ethyne.
2. (a) I. State what is observed when ammonium is tested with conc.HCl.
ii Give one chemical test for – COOH functional group.
Fill the following below; Your name in the appropriate box,Email address,subject and answers[both in the message box].
No Fields Found.