10/08/2020
LESSON THIRTEEN
It’s a beautiful day and I say good morning to you all. Hope you’re keeping yourselves warm from the cold weather and keeping safe by adhering to all precautionary measures given by NCDC. The Lord will continue to keep us and our loved ones safe in Jesus name.
Correction to Lesson Twelve’s Objective Test
- a 11.c 21.d 31.c 41.c
2. b 12.b 22.b 32.b 42.d
3. d 13.b 23.d 33.a 43.b
4.b 14.b 24.d 34.c 44.a
5.a 15.a 25.b 35.b 45.b
6.a 16.b 26.b 36.a 46.c
7. a 17.a 27.b 37.c 47.c
8.b 18.c 28.c 38.d 48.c
9.d 19.c 29.b 39.b 49.d
10.a 20.b 30.a 40.b 50.d
Below are Revision Questions that could be of help towards the final examination
- Why is economics referred to as a i. science ii. social science?
- Why is economics referred to as a positive science and not a normative science?
- Differentiate between the following a) wants and needs b) wants and demand c) economic and non economic resources d) wages and salaries e) piece rate and time rate f) opportunity cost and money cost g) consumer goods and capital goods.
- How can we solve the problem of scarcity?
- Name the importance of scale of preference and define it.
- State 5 guidelines used in constructing tables.
- What are the importance of tables in economics?
- Explain the basic economic problems of the society.
- Define production and explain the stages of production.
- State any 5 importance of land to economic development.
03/08/2020
LESSON TWELVE
Good morning to you all. May the month of August be filled with wonderful blessings of good health, love, Peace, happiness and prosperity for us in Jesus name. Happy New Month.
Correction to Lesson eleven’s Objective Test and Assignment
Instruction: kindly mark and score yourself over 50.
1.B 11. C 21.D 31. D 41.A
2.C 12. C 22.D 32. B 42.B
3.B 13. C 23. C 33.B 43.A
4. A 14. B 24. A 34.D 44.C
5.A 15. D 25. A 35. D 45.D
6.B 16.B 26.D 36.B 46.D
7.D 17.B 27. C 37.D 47. C
8.A 18.C 28. D 38.C 48.A
9.C 19.A 29. D 39.C 49.B
10.C 20.D 30. B 40.C 50.D
Differentiate between demand for money and supply of money
Demand for money is the quantity of money that individuals want to hold at a particular time for one reason or the other. This is otherwise called liquidity preference as money is preferred to be kept in liquid form instead of investments whereas supply of money refers to the volume of money in circulation and this is obtained by the addition of paper money, coins and demand deposits.
OBJECTIVE TEST 5
Instruction:
a. Test yourself by answering the questions below. Use 40 minutes for the test.
b. Submit your work using the form below.
Thank you for taking it very serious.
- A tax is defined as [A] a monthly contribution by individuals to the government [B] a sincere attempt by individuals to develop the nation [C] one of the economic duties of the citizens [D] a compulsory levy imposed by the government on citizens.
- A vertical demand curve means that quantity demanded [A] decreases as price rises [B] remains unchanged even though price changes [C] increase while price remains unchanged [D] increases as price as price decreases
- Which of the following would guide a boy in choosing between a book costing $15 and a toy of equivalent value? [A] returns on investment [B] Taste of toys [C] Scarcity and choice [D] Scale of preference
- A perfect competitor is a price- taker because [A] the price is fixed by the marketing board [B] he cannot control the price of his product [C] government fixed the price of his product [D] he can control the price of his product
- Which of the following is an example of a capital good? A [A] tin to milk [B] hammer [C] loaf of bread [D] radio
- The market economic system is also referred to as a [A] capitalist economic system [B] command economic system [C] mixed economic system [D] perfectly competitive system
- If Bala scored 30% in English Language, 61 % in Mathematics, 60% in Economics and 75% in Geography, what is his mean score? [A] 56.5% [B] 62% [C] 63.5% [D] 65%
- A subsidy in economics is [A] a tax on imported goods [B] an incentive in cash or kind [C] a surplus obtained from taxation [D] an ad valorem tax
- Which of the following is not a commodity money? [A] Cowries [B] Salt [C] Beads [D] Coins
- Which of the following will lose during inflation? [A] Creditors [B] Debtors [C] Businessmen [D] Trade
- Functions of commercial banks do not include [A] lending money with interest charges to customers [B] carrying out transactions on behalf of the customers [C] expansion of money supply [D] printing of security documents for customers
- Which of the following is not an example of near money? [A] Fixed deposits [B] Notes and coins [C] Government securities [D] Treasury bills
- A worker’s pay after the deduction of income tax is known as [A] consumer’s income [B] disposable income [C] net income [D] total emolument
- A mining industry is usually located near the [A] market [B] source of raw material supply [C] source of finance [D] reservoir where there is much water
- Which of the following does not affect the mobility of labour? [A] Population size [B] marriage [C] Social unrest [D] Trade Union activities
- An increase in the bank rate by the central bank will [A] make borrowing more attractive [B] reduce the amount of borrowing [C] increase the amount of borrowing [D] increase the money supply
- Which of the following does occur when national income rises? [A] Exports increase [B] imports rise [C] saving fall [D] Tax receipts rise
- The risk in a joint stock company is borne by the [A] general managing [B] managing director [C] shareholders [D] workers of the company
- Interest is the payment made for the use of [A] labour [B] land [C] capital [D] enterprise
- The benefits that occur to a firm due to large scale production are called [A] increasing returns to a factor [B] internal economies of scale [C] external diseconomies of scale [D] decreasing returns to a factor
- Which of the following is not a fixed cost? Cost of [A] land [B] equipment [C] advertisement [D] labour
- The details of the internal affairs of a joint stock company are contained in the company [A] code of conduct [B] articles of association [C] certificate of incorporation [D] trade certificate
- One major set-back in a partnership is [A] access to capital [B] better decision making [C] private business account [D] disagreement among partners
- The type of unemployment commonly found among school leavers seeking jobs is [A] cyclical unemployment [B] residual unemployment [C] seasonal unemployment [D] frictional unemployment
- Tax imposed on goods imported into the country is called [A] income tax [B] tariff [C] poll tax [D] excise duty
- Which of the following is responsible for the low level of productivity by farmers? [A] Inadequate farm labour [B] Poor storage facilities [C] Poor transportation [D] Primitive methods
- If the tax rate is 15% for three individuals on different salary scales, the tax system is said to be [A] progressive [B] proportional [C] specific [D] regressive
- Which of the following is not a direct tax? [A] Company Tax [B] Pay-As-You-Earn [C] Value Added Tax [D] Capital Gains Tax
- When the government desires a large revenue, it should tax commodities for which demand is [A] price elastic [B] price inelastic [C] unitary price elastic [D] perfectly elastic
- The per capita income is the most common index for measuring [A] standard of living [B] population growth rate [C] level o f illiteracy [D] wage rate
- The following are problems in measuring national income except how to [A] measure subsistence production [B] avoid double counting [C] differentiate between Net National Product and Net Domestic Product [D] differentiate between intermediate and final goods
- Investment in an economy is the same as [A] increase in the money supply [B] increase in capital formation [C] purchases of company shares [D] addition to bank deposits
- When a firm is able to buy goods more cheaply because of its large size, it is enjoying [A] marketing economies [B] technical economies [C] welfare economies [D] managerial economies
- Quotas limit the volume of foreign goods as the [A] foreign market [B] transit port [C] exporting country [D] port of entry
- Which of the following is a debit item in a country’s balance of payments? [A] Exports [B] Imports [C] Tourists’ expenditure [D] Residents’ foreign earnings
- In contractionary monetary policy, [A] lending is made more difficult [B] lending is made easy [C] government spending is restricted [D] taxes are reduced
- When the price of commodity X increases and the demand for commodity Y also increase, then commodities X and Y are: [A] normal goods [B] inferior goods [C] substitute goods [D] necessities
- The market period is when [A] demand and supply are perfectly elastic [B] supply in the market is fixed [C] the market demand exceeds supply [D] the market is equilibrium
- A decrease in the demand for a good can be caused by [A] an increase in the price of a substitute [B] an increase in the price of complement [C] a decrease in the price of a complement [D] a fall in the price of the good
- A successful advertising campaign for good X, a closely competing brand of good Y, will move the demand curve for good Y to the [A] equilibrium [B] left [C] right [D] origin
- When government expenditure for a year exceeds the expected revenue, there is [A] balance of payments deficit [B] balance of trade surplus [C] budget deficit [D] budget surplus
- The overall demand for wood for furniture, building and fuel constitute a [A] competitive demand for wood [B] normal demand for wood [C] complementary demand for wood [D] composite demand for wood
- If the price is set above the equilibrium price, market will exhibit [A] an excess demand [B] an excess supply [C] abnormal demand [D] abnormal supply
- A consumer purchasing two commodities X and Y will maximize his satisfaction when [A] the last dollar spent on commodity X gives the same satisfaction as the last dollar spent on commodity Y [B] he spends the same amount on commodities X and Y [C] the ratio of the marginal utility of X its price exceeds the ratio of the marginal utility of Y to its price [D] the marginal utility ratio is greater than their price ratio
- International specialization and trade would increase world output if opportunity cost ratios are [A] the same in various countries [B] different in various countries [C] high in various countries [D] stable in various countries
- Which of the following conditions will not make devaluation useful in improving a country’s balance of payments position? [A] Demand for imports must be elastic [B] The country’s export must have elastic demand in other countries [C] The value of other nations’ currencies must not change [D] There must be increase in wages and other incomes
- Which of the following is not included in measuring national income by the income approach? [A] Wages and salaries [B] Profits of companies [C] Grants to pensioners [D] Rents on landed property
- Which of the following is the main objective of privatization? [A] Creation of additional employment [B] Diversification of the economy [C] Increasing the level of efficiency [D] increasing expenditure
- Which of the following is the major function of the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC)? [A] Exploration [B] Oil transportation [C] Oil refining [D] Regulation of oil price
- The following are functions of the African Development Bank in member countries except [A] aiding economic and social development [B] providing technical assistance for projects [C] promoting both private and public investment project [D] issuing currencies and controlling money supply
27/07/2020
LESSON ELEVEN
Good morning to you once again. We thank God for giving us something to look forward to. September 21st would be a reality and non of us shall be missing in Jesus name. I’m looking forward to having all of you back in school.
Correction to Lesson Ten’s Objective Test
Instruction: kindly mark and score yourself over 48.
1. D 11. A 21. C 31. B 41. B
2. B 12. A 22. B 32. D 42. B
3. C 13.B 23. B 33. A 43. B
4. B 14. * 24. D 34. C 44. B
5. B 15. C 25. C 35. C 45. B
6. D 16. * 26. B 36. A 46. C
7. C 17. D 27. B 37. D 47. D
8. D 18. C 28. C 38. D 48. D
9. D 19. C 29. C 39. C 49. A
10. A 20. A 30. C 40. C 50. D
THEORY QUESTION
Differentiate between demand for money and supply of money .
OBJECTIVE TEST 4
a. Test yourself by answering the questions below. Thank you for taking this very serious. Use 40 minutes for the test.
b. Submit your work using the form below.
- The opportunity cost to the public for providing health care facilities would be the [A] money spent on building hospitals [B] amount paid as interest on loan to build the facilities [C] goods and services that would have been produced [D] goods and services the health care workers would produce
- Scarcity is the principle problem faced by [A] the poor people in developing countries [B] societies who face the problem of unemployment [C] every individual, firm and government [D] the poor people in the world
- The marks scored by five students in a test in Economics are 0,5,5,3,1. The median mark is [A] 1 [B] 3 [C] 4 [D] 5
- The demand schedule shows how quantity demanded is related to [A] testes of the buyer [B] population of the buyers [C] population of the buyers [D] prices of other commodities
- Which of the following is responsible for the upward slop of a supply curve? [A] The price of the commodity [B] The quantity supplied [C] The law of demand [D] A change in the price of other goods
- Means are s care because [A] they are abundant in supply [B] they are unlimited in supply [C] they have alternative uses [D] wants are limited
- In the long run, the supply of al consumer goods is [A] inelastic [B] constantly elastic [C] perfectly inelastic [D] elastic
- A successful advertisement of eggs will lead to [A] an increase in the demand and price [B] a decrease in the quantity demanded and price [C] an increase in the price and a fall in supply [D] a decrease in the quantity supplied and demanded
- Which of the following will not have its marginal utility equal to zero as more of it is acquired? [A] Cars [B] Food [C] Money [D] Bag
- The law of diminishing returns operates in the [A] foreseeable future only [B] market period [C] long run [D] short run
- The long run average cost curve of a declines over a certain range of output due to [A] increasing cost the firm experiences [B] diminishing returns [C] increasing returns to scale [D] constant returns the firm experience
- State enterprises are business organizations set up mainly to [A] make profit for state [B] complete vigorously with private companies [C] enhance the welfare o f members of the public [D] provide more jobs politicians
- In the short run, profit in a perfect market is maximized when [A] marginal cost exceeds marginal revenue [B] total revenue equals total cost [C] marginal cost equals marginal revenue [D] marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost
- The coefficient of cross elasticity of demand between two goods is positive when the goods are [A] luxury [B] substitutes [C] normal goods [D] complements
- If the percentage change in the pr ice of a commodity is 20% while the percentage change in the quantity demand is 40%, then the coefficient of price elasticity of demand of this commodity will be [A] 0.5 [B] 0.8 [C] 1.0 [D] 2.0
- A direct relationship between two variable in Economics will be shown as a curve with a [A] negative slope [B] positive slope [C] constant slope [D] multiple slope
- A decrease in supply will lead to a [A] rise in quantity bought [B] fall in price and a rise in quantity bought and sold [C] rise in price and a fall in quantity bought and sold [D] rise in price and a rise in quantity and sold
- Entrepreneurship as a factor of production is scarce because [A] not everyone has the time [B] it is difficult to obtain the qualification [C] a lot of people avoid taking risks [D] labour is also scarce
- The demand curve in a perfect market is [A] perfectly elastic [B] fairly elastic [C] fairly inelastic [D] perfectly inelastic
- Which of the following functions is performed by the wholesaler? [A] Breaking of bulk for the consumer [B] Hoarding of goods to hike prices [C] stocks varieties of goods for the consumer [D] Purchasing in bulk from the producer
- A school boy bought a textbook and went home without a cellphone he would have liked to buy. This is a typical case of [A] wrong choice [B] inadequate money cost [C] luxurious lifestyle [D] opportunity cost
- The size of the labour force is likely to be large if the [A] birth rate is low [B] death rate is high [C] rate of emigration is high [D] rate of immigration is high
- The birth rate in a town was 20 births per thousand. If the number of births was 500, the population of the town will be [A] 2,500 [B] 20,500 [C] 25,000 [D] 100,000
- To improve agricultural production, government should [A] be involved in direct production [B] introduce policies to improve agriculture [C] invite foreigners to take over farming [D] import more food
- The national income figures of most west African countries are normally under estimated because of the high incidence of [A] subsistence production [B] non co-operation by foreigners [C] low level of earning [D] illiteracy among citizens
- Any benefit received without contributing to national output is called [A] public good [B] social good [C] free earnings [D] transfer earnings
- Inflation has undesirable effects on the society as a whole because it [A] makes lenders to gain and borrowing to lose [B] make pensioners better off. [C] reduces the purchasing power of money [D] creates a competitive bidding for fixed assets
- A product that can be used as money but which is valuable in its own right is called [A] bank money [B] precious money [C] token money [D] commodity money
- Demand deposits are money because [A] the central bank recognizes them [B] they are medium of exchange [C] cheques are means of payment [D] they represent money
- Medium and long term lending is carried out by [A] retail banking institution [B] development banks [C] central banks [D] commercial banks
- Which of the following debt instruments has the shortest maturity? [A] Bonds [B] Development loan stocks [C] preference stocks [D] Treasury bills
- Proportional taxes are those in which the [A] rich and the poor pay the same amount [B] rich and the poor pay the same percentage [C] poor pays a higher proportion [D] poor pays a lower proportion
- The balance of payment account shows the relationship between [A] the value of visible goods exported and imported [B] the prices of exports and prices of imports [C] a country’s payments on imports and receipts on export [D] payments made on invisible imports and receipts on invisible exports
- At the highest level of total utility, marginal utility is [A] negative [B] positive and falling [C] positive and rising [D] zero
- Which of the following cannot be listed as a natural resource? [A] Factory site [B] Iron ore [C] Gold [D] Cement
- A famer’s capacity to produce on a large in West Africa is limited by [A] absence of buyers [B] inadequate storage facilities [C] development of substitutes [D] absence of industries to patronize them
- Peasant farming is the [A] cultivation of small farm holding [B] use of labour intensive method of agriculture [C] production of food crops [D] production to meet family food requirement
- The type of unemployment associated with a worker who though working, remain virtually unemployed is known as [A] seasonal unemployment [B] structural unemployment [C] disguised unemployment [D] frictional unemployment
- Which of the following describes the elasticity of supply for a linear supply curve drawn from the margin? [A] Perfectly inelastic [B] Perfectly elastic [C] Fairly elastic [D] Unitary
- Price floor is set [A] at the equilibrium [B] below the equilibrium [C] above the equilibrium [D] near the equilibrium
- Which of the following conditions shows that a firm is incurring losses? [A] AR < AC [B] AR=AC [C] AR > AC [D] AR = MC
- For price discrimination to be profitable [A] the elasticities of demand in the two market must be the same [B] there must be different elasticities of demand in the two market [C] there must be many buyers and sellers [D] there must be free entry and exit
- The condition for equilibrium of the consumer demands that a dollar of expenditure on commodity X [A] yields the same marginal utility as commodity Y [B] is proportional to the marginal utility of commodity Y [C] is equal to the utility of the price of commodity Y [D] is equal to the price of commodity Y
- All developing countries exhibit the following features except [A] low standard of living [B] low degree of urbanization [C] high standard of living [D] rapid population growth
- If governments in developing countries want to raise revenue for development, then the major source to rely on is [A] royalties and rent [B] grants and loans [C] sale of government assets [D] taxation
- International specialization and trade would increase world output if opportunity cost rations are [A] stable in various countries [B] the same in various countries [C] high in various countries [D] different in various countries
- The problems of economic development planning include all the following except [A] inadequate statistical data [B] inadequate capital [C] adequate human resource [D] over ambitious plans
- The setting up of cottage industries in the rural areas is aimed at [A] creating employment in the area [B] promoting rural-urban migration [C] reducing the standard of living [D] reducing crimes in the rural areas
- The following are functions performed by an insurance company except [A] mobilization of funds through premium collected [B] promoting rural-urban migration [C] collection of deposits from the public [D] making long term loans available for investment
- Terms of trade is used to describe [A] the volume of exports to other countries [B] the volume of imports vis-à-vis exports [C] expenditure on exports [D] the rate at which exports exchange for imports
20/07/2020
LESSON TEN
It’s another beautiful day and I say good morning to you all. We thank God for the gift of life and wonderful family. Continue to encourage yourself in the Lord like David. This too shall end in praise in Jesus name.
Correction to Lesson Eight’s Assignment
Objective Test 2
Instruction: kindly mark and score yourself over 48.
1. D 11. A 21. C 31. * 41.C
2. C 12. A 22. C 32. A 42.B
3. B 13. A 23. A 33. D 43.B
4. C 14. B 24. C 34. A 44.A
5. A 15. C 25. D 35. C 45.A
6. B 16. D 26. B 36. B 46.B
7. D 17. * 27. B 37.B 47. C
8. B 18. B 28. B 38. D 48.B
9. C 19. B 29. C 39. A 49.C
10. B 20. A 30. A 40. A 50.D
Note:
*Q17. The quantity demanded is greater than the quantity supplied.
*Q31 The options are not related to the question.
THEORY QUESTIONS
Differentiate between;
a. insurance company and the stock exchange market
b. commercial bank and mortgage bank
c. merchant bank and development bank.
OBJECTIVE TEST 3
a. Test yourself by answering the questions below. Thank you for taking this very serious. Use 40 minutes for the test.
b. Submit your work using the form below.
- The relationship between ends and means is [A] choice [B] scale of preference [C] opportunity [D] scarcity
- The problem of choice arises in a firm because [A] workers’ desire are limited [B] there are alternative ways of producing goods [C] supply of resources is adequate [D] firm can always have what they need
- An economic system is best defined as [A] activities that provide the means of live hood in an economy [B] the system of governance adopted by a nation [C] the mode of production and distribution of commodities [D] a series of choice that is available to an individual
- The reward for the effort of an entrepreneur in production is [A] salary [B] profit [C] interest [D] commission
Use the data below to answer question 5
The wages received by five labour are $55, $40, $45, $40 and $900
5. The mean wage in the data is affected by an [A] irregular value [B] unrealistic value [C] abnormal value [D] extreme value
6. The demand for economic recourses is considered a derived demand because it depends on [A] the demand for the final product [B] productivity of the resources [C] the supply of resources [D] the supply of the final product
7. The efficiency of labour depends on the [A] quantity of labour [B] supply of labour [C] quality of labour [D] demand for labour
8. If a rise in the price of one commodity leads to an increase in the demand for another, the two commodities are [A] normal goods [B] complements [C] unrelated good [D] substitutes
9. A product that can be used as money but which is valuable in its own right is called
a. bank note b. precious money c. token money d. commodity money
10. A good with a negative income elasticity of demand is [A] an inferior good [B] a normal good [C] a luxury good [D] a necessity
11. When market demand increases and market supply is unchanged, there is [A] an increase in equilibrium price and quantity [B] a decrease in equilibrium price and quantity [C] an increase in equilibrium price but a fall in quantity [D] a decrease in equilibrium price only
12. If MU is marginal utility and P is price , a consumer of commodities X and Y isin equilibrium, when [A] MUx/Px=MUy/Py [B] MUx/Py=MUy/MUx [C]MUx/Px-MUy [D] MUy-MUx
13. An entrepreneur will continue to employ more units of labour up to a point where the [A] average product equals wages [B] marginal product of lab our is increasing [C] total product of labour is zero [D] wages are equal to marginal product of labour
14. In the short run, the supply of agricultural product is [A] average product equals wages [B] marginal product of labour is increasing [C] total product of labour is zero [D] wages are equal to marginal product of labour
15.Production will take place outside the production possibility boundary,when there is [A] economies of scale [B] economic recession [C] economic growth [D] increasing returns
16. When a market is in equilibrium, an increase in market supply will lead to [A] an increase in price and a decrease in quantity demanded [B] a decrease in price and an increase in quantity demanded [C] an increase in price with quantity demanded unchanged [D] a decrease in price and quantity demanded
17. A farmer spent $700 to produce 5 bags of rice, if the variable cost is $450. The average fixed cost (AFC) is [A] $25 [B] $35 [C] $40 [D] $50
18. In perfect competition, marginal revenue and average revenue are always [A] not equal [B] above the price [C] equal to price [D] below the price
19. Which of the following is not true of a co-operative society? [A] it is a highly democratic form of business organization [B] Profit or dividends are shared according to patronage [C] There is limit to the size of its membership [D] Each member has an equal right in the decision making
20. Transferring ownership of foreign business in a country to the citizen is called [A] indigenization [B] decentralization [C] nationalization [D] commercialization
21. Distribution is an important part of production because it [A] determines what to produce [B] is an economic activity [C] makes commodities available to final consumers [D] is a reward for taking part in production
22. Perishable goods such as tomatoes tend to have [A] elastic supply [B] inelastic supply [C] unitary elastic supply [D] fairly elastic supply
23. A population in which the people above 60 years represent 20% and those below 18 years represent 45% can be described as [A] ageing population [B] population with high dependency ratio [C] population with higher level of manpower [D] optimum population
24. Which of the following will cause a decrease in the quantity supplied of a commodity? [A] Increase in the cost of production [B] Unfavourable weather condition [C] Decrease in the number of producers [D] Decrease in the price of the commodity
25. Infant industries are those industries which [A] product goods used by infants [B] are located in less developed areas [C] are in their early stages of production [D] are located in developed countries
26. The type of unemployment which results from the changes in the pattern of aggregate demand and the techniques of production is [A] seasonal unemployment [B] structural unemployment [C] frictional unemployment [D] residual unemployment
27. Agricultural production in West Africa could be increased through the following ways except [A] improvement of extension service [B] reduction of import duties on agricultural produce [C] effective control of pests and disease of plants an d animals [D] reduction of taxes on farm machinery
28. The charging of different prices to different groups of consumers for the same commodity is [A] price control [B] price system [C] price discrimination [D] price war
29. An industry whose final product is fragile or perishable must be located close to the [A] labour [B] power supply [C] market for the product [D] raw material for the product
30. Which of the following does not form part of money supply? [A] Cash [B] Demand deposit [C] Time deposit [D] Gold
31. Gross National Product (GNP) includes the value of the commodities produced by the [A] residents and citizens abroad [B] citizens plus net income from abroad [C] citizens including contributions of foreigners [D] residents plus net income from abroad
32. The total stock of money available for use in an economy is [A] a function of money [B] a characteristic of money [C] the demand for money [D] the supply of money
33. Using the income approach in the calculation of national income, which of the following items should not be included? [A]students’ grant and scholarship [B] Interests received on capital [C] Income earned by self employed persons [D] Profit of entrepreneurs
34. During inflation, government can effectively control prices by [A] increasing indirect taxes [B] increasing the number of distributors [C] using subsidies to increase supply [D] increasing workers’ income
35. The central bank controls credit activities of bank through [A] the use of bank balance [B] revaluation of currency [C] the use of bank rate [D] the issue of more currencies
36. Mortgage banks specialize in the financing of [A] building of houses [B] building of industries [C] construction of roads [D] small scale business
37. Net property income from abroad is the difference between [A] income and expenditure of a country [B] net national income and gross national expenditure [C] gross national expenditure and income [D] gross national product and gross domestic product
38. Which of the following is a direct tax? [A] Sales tax [B] Custom duties [C] Commodity tax [D] Income tax
39. When government spends less than it collects in revenue in a particular year, the budget is said to the [A] in equilibrium [B] balanced [C] in surplus [D] in deficit
40. Which group contributes more to the total output of a typical less developed country? [A] Teachers [B] Masons [C] Farmers [D] Traders
41. Economic growth will occur if there is an increase in [A] rural-urban migration [B] substance production [C] the number of entrepreneurs [D] the quantity of underutilized resources
42. International trade exists because of the relative differences in the [A] value of services from country to country [B] cost of production between countries [C] cost of transportation between countries [D] culture of the people of different countries
43. Devaluation means [A] a reduction in the value of the national currency due to rising price [B] a reduction in the value of the domestic currency relative to foreign currencies [C] an increase in the value of the domestic currency relative to foreign currencies [D] a reduction in the purchasing power of a foreign currency
44. Which of the following will help solve balance of payments problem? [A] Massive importation of goods [B] Increased domestic production [C] Reduction in tariff [D] Trade liberalization
45. Terms of trade is measured by [A]index of export prices/index of domestic prices *100[B] index of export prices/index of import prices *100 [C] index of export prices/index of base prices * 100[D] index of import prices/index of export prices * 100
46. Crude oil is usually priced in the international market in [A] Pound sterling [B] Deutschmark [C] US Dollars [D] Euros
47. The African Development Bank (AFDB) performs the following function except [A] promotion of technical development [B] aiding economic development [C] promoting economic integration among member countries [D] breaking the monopoly of foreign oil companies
48. One of the problems facing the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) is [A] the relative inelastic demand for its product [B] that oil prices are stable [C] the new discovery of oil deposits in some countries [D] that substitutes for oil are unavailable
49. Diamond gold and bauxite are examples of [A] mineral resources [B] human resources [C] artificial resources [D] marine resources
50. Economic problems arise mainly as a result of
a. inaccurate statistical data in West Africa b. excessive wastage of available resources c. lack of foresight on the part of resource users d. limitations in availability in availability of resources.
13/07/2020
LESSON NINE
Good day to you all. We thank God for the gift of life and this opportunity once again. This season too shall pass and we will all have a testimony at the end of the day for non of us shall be lost to this pandemic or any other pestilence in Jesus name.
Correction to Lesson Seven’s Objective Test
kindly mark and grade yourself
1. A 11. D 21. A 31. B
2. D 12. A 22. B 32. A
3. C 13. C 23. D 33. B
4. B 14. A 24. D 34. C
5. B 15. D 25. D 35. D
6. A 16. B 26. C 36. B
7. D 17. B 27. C 37. A
8. C 18. A 28. A 38. C
9. B 19. B 29. B 39. C
10. A 20. C 30. D 40. D
Revision Questions on Demand and Supply
Instruction: Answer the following questions using the form below.
1. With the aid of diagrams, explain what is meant by, a change in
a. demand
b. quantities demanded
2. A demand curve slopes downwards but this may not always be so. Explain this statement.
3. Price tends towards the level that equates supply with demand. Explain this statement.
4. Describe each of the following;
a. abnormal demand
b. effective demand
5. With a well labeled diagrams, illustrate the following:
a. perfectly inelastic demand
b. unitary elastic demand
c. fairly elastic demand
d. perfectly elastic demand
06/07/2020
Lesson Eight:Financial Institutions/ Objective test.
Happy New Month. May July cooperate with each and everyone of us for lifting and testimonies in Jesus name. May it please the Lord to continue to uphold us with His right hand of righteousness in Jesus name Amen. We shall not suffer any form of loss in Jesus name.
Instruction: Answer the questions below.
Essay
- Differentiate between money and capital market.
- Explain the measures used by the Central Bank to control the economy.
Objective Test
- Economics is described as a social science because it deals with [A] an aspect of human behavior [B] the distribution of commodities [C] the production of good [D] limited resources which have alternative uses
2. Who bears the risk of production? [A] Production managers [B] Factory workers [C] Entrepreneur [D] Retailers
3. When the means of production are controlled by private individuals, the economic system is called [A] mixed economy [B] capitalism [C] socialism [D] welfarism
4. Which of the following create utility? I. Farmers II Manufacturers III. Consumers IV. Retailers [A] I and II only [B] II and III only [C] I,II and IV only [D] II,III and IV only
5. Optimum population is [A] the population which when combined with available resources yields the maximum output [B] birth rate less death rate [C] increase in standard of living as population increase [D] the minimum number of people that can live in a country
6. The most immobile factor of production is [A] equipment [B] land [C] labour
[D] entrepreneur
7.Total utility increase as more of a commodity is [A] purchased [B] sold [C] produced
[D] consumed
8. Which of the following is considered as a fixed cost of a firm? [A] Wages [B] Interest on debt [C] expenditure on raw materials [D] Fuel and lubricants
9. A firm’s unit fixed cost will fall if the [A] demand for the firm’s product increase [B] demand for the firm’s product falls [C] firm’s output increases [D] firm’s output decrease
10. When marginal product is equal to zero then the [A] average product has reached its highest level [B] total product is at maximum [C] total product is negative [D] average product begins to fall
11. A sewing machine in a clothing factory is a [A] capital good [B] durable consumer good [C] non-durable consumer good [D] product of the factory
12. Diamonds are more expensive than water because the price of the product tends to reflect its [A] total value [B] marginal value [C] revealed preference [D] consumer surplus
13. Steel can be classified as [A] a capital good [B] an intermediate good [C] natural resource [D] an imperishable product
14. The law of demand states that the [A] higher the price, the higher the quantity demand [B] lower the price, the higher the quantity demanded [C] quantity demand remains the same a t any price [D] quantity demanded increases with income
15. Goods for which quantity demanded rises as income rises are [A] complementary goods [B] giffen good [C] normal goods [D] substitutes
16. Which of the following is not constant along a given demand curve for bread? [A] the price of bread [B] The income of consumers [C] The price of substitutes [D] Age distribution
17. A price ceiling established below the equilibrium price will cause [A] quantity demanded to crease [B] quantity supplied to be greater than the quantity demanded [C] demand to be less than supply [D] quantity supplied to decrease
18. A commodity that provides a stable tax revenue has a price elasticity of demand which is [A] elastic [B] inelastic [C] higher than the equilibrium price [D] lower than the equilibrium price
19. Joint ventures are businesses owned by [A] workers and management [B] two or more independent firms [C] professionals [D] traders
20. The condition for perfect market will be violated if [A] the product sold can be substituted for each other [B] there are two many buyers and sellers [C] the product of the industry can be branded [D] the exit or entry of sellers cannot affect the price
21. A profit maximizing monopolist must decide on all the following except [A] output level [B] price level [C] the wage level [D] the combination of inputs
22. Efficient allocation of resources can be attained under [A] a closed shop [B] a monopoly [C] perfect competition [D] subsidized production
23. A rise in interest rate is likely to lead to [A] a fall in the amount of money people want to hold [B] an increase in the desire to buy goods on credit [C] a demand for increase in wages [D] a decrease in the number of bank
24.Which of the following is monetary policy? [A] Control of government expenditure to influence aggregate demand [B] Reduction of tax on capital equipment to increase output [C] The use of interest rate to influence the demand of money [D] Increase in wages to reduce income inequality
25. Inflation can be caused by [A] under population [B] budget surplus [C] excessive price control [D] excessive government expenditure
26. The total stock of goods is fixed in the [A] market period [B] short run [C] long run [D] planning period
27. Double coincidence of wants is associated with [A] opportunity cost [B] trade by barter [C] monopoly [D] commercial policy
28. The value of money is determined by the [A] quantity available in the bank [B] quantity of goods and services it can buy [C] quality of the paper used in making it [D] amount of taxes collected
29. The stronger factor which influences the taken of loans is [A] availability of loanable funds [B] the number of creditors [C] the rate of interest [D] government loan policy
30. Saving a substantial part of income will lead to capital [A] accumulation [B] consumption [C] transfer [D] immobility
31. The following are all functions of commercial banks except [A] accepting deposits [B] portfolio of assets an d liabilities [C] articles of incorporation [D] balance of trade account
32. To control the activities of commercial banks, the central bank changes the [A] cash reserve ratio [B] portfolio of assets an d liabilities [C] articles of incorporation [D] balance of trade account
33. Mortgage bank specialize in assisting customers to own [A] business ventures [B] domestic appliance [C] shares [D] house
34. Open market operation is used under monetary policy to [A] expand or contract the amount of money in circulation [B] reduce the inflow of foreign currency [C] control the activities of the capital market [D] make investment more attractive to foreigners
35. A long term loan can be obtained from [A] community bank [B] central banks [C] development banks [D] traditional saving institutions
36. One of the liabilities of a commercial bank is [A] advance [B] deposit [C] cash [D] overdraft
37. Income tax generally tends to be [A] regressive [B] progressive [C] equitable [D] proportional
38. A criticism of a high rate of tax on overtime pay would be that it [A] cab e passed on the consumer [B] leads to inflation [C] makes more goods available [D] can be disincentive to work
39. The allocation of the nation’s wealth to each of the factors of production is the [A] national income [B] government revenue [C] proceed of labour [D] distribution of income
40. Economic growth is the rate of increase in [A] a country’s full employment and real output [B] a nation’s total population [C] the number of commercial bank in the country [D] the general price level
41. Which of these defines correctly the term value added? [A] Difference between cost raw materials and units of labour used [B] Total investment minus depreciation [C] Total revenue from sales minus the cost of production [D] The market value of all the resources employed
42. Gross Domestic Product (GDP) minus Net Domestic (NDP) is equal to [A] foreign factor earnings [B] allowance for depreciation [C] indirect taxes and subsidies [D] value of intermediate products
43. Which of the following is a measure of the standard of living of a country? [A] GDP/(Annual budget ) [B] GNP/(Total Population ) [C] NNP/(Labour Force ) [D] NI/(Dependant Population )
44. In domestic trade, the number of currencies involved is [A] one [B] two [C] four [D] indefinite
45. Invisible trade refers to foreign trade in [A] services [B] commodities [C] capital goods [D] military hardware
46. If a country imports less than its exports, it has [A] a trade deficit [B] a trade surplus [C] unfavourable terms of trade [D] balance of payment deficit
47. When a country devalues its currency, the prices of imports in the domestic currency are excepted to [A] fluctuate [B] fall [C] rise [D] stabilize
48. The decrease in the external value of a country’s currency though market forces is [A] devaluation [B] depreciation [C] deflation [D] decentralization
49. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) assist member countries to deal with [A] shortage of long term loans [B] private sector liquidity problems [C] temporary balance of payment problem [D] government budget deficits
50. Which of the following countries is not a member of the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC)? [A] Nigeria [B] Venezuela [C] Saudi Arabia [D] Egypt
29/06/2020
Lesson Seven: Financial Institutions/ Objective test.
Good day to you all. Believe you are busy doing the needful. You will not be found wanting in Jesus name. I pray the Lord will continue to bless and keep us under the shadow of His wings in Jesus name. Stay safe and connected to your maker. Do have a great day.
Correction to Lesson Six’s Assignment (22/ 06/2020)
Study the answers carefully and effect corrections where necessary.
1a. Population can be defined as the total number of people living in a particular geographical area or country at a point in time whereas population census is the national or official headcount of the entire people living in a particular geographical area at a point in time usually one year.
i. Birth Rate: This is the number of births per thousand of the population in a given period of time.
ii. Death Rate: This is the number of deaths per thousand of the population in a given period of time.
iii. Natural Growth Rate: this is the rate of increase experienced in a country due to natural factors i.e. births and deaths.
2. Find the appropriate angle that represent each age group:

3a. Values of X, Y and Z
X = 2,275 + 2,725 = 5,000
Y = 7,500 – 4,265 = 3,235
Z = 6,000 – 3,250 = 2,750
b. Total Population of the town:
10 and below + 11-14 + 15-35 + 36-64 + 65 and above
4,000 + 5,000 + 2,500 + 7,500 + 6,000
= 25,000
c. Difference between population of Male and Female aged 14 and below:
Male aged 14 and below:
10 and below + 11-14
1,350 + 2,275 = 3,625
Female aged 14 and below:
10 and below + 11-14
2,650 + 2,725 = 5,375
(Female aged 14 and below- Male aged 14 and below)
5,375 – 3,625 = 1,750
d. The percentage of the population aged 14 and below:
Population aged 14 and below * 100%
Total Population
1,750 * 100
25,000 = 7%
e. The dependency ratio of the town = Dependents : Independents
Dependent Population:
10 and below + 11 & 14 + 65 & above
4,000 + 5,000 + 6, 000 = 15,000
Independent Population:
15 – 35 + 36 – 64
2,500 +7,500 = 10,000
Dependency Ratio = Dependents : Independents
15,000 : 10,000
= 3 : 2
4.Treasury bill is a short term government financial security that matures within three months whereas Treasury Certificate is also a government financial security which matures after a year. They are both issued through the Central Bank and made available to individuals and corporate organisations through the Commercial Banks to either borrow or lend money in the Capital Market.
5a. Savings Account: This is a popular type of account operated by low income earners. It is operated with the use of passbook. It attracts interest. Withdrawals can only be made by the owner of the account and frequent withdrawals are discouraged. Withdrawals are limited to twice in a month.
b. Current/Demand Account: This is operated by high income earners/ businesses. It is operated with the use of cheques. It does not attract interest. Owners enjoy privileges like overdrafts and loans. There is no limit to the amount of withdrawals.
c. Time/ Fixed Deposit Account: Here, money is deposited for a specific period of time and before a withdrawal is made a 7-14 days notice is given. It yields a high rate of interest.
d. Government Bond:This is a long term financial security issued to source for funds. They are generally regarded as very safe.
6a. Credit Creation: This refers to the process by which commercial banks make it possible to make more money from deposits through the issuance of loans or overdrafts. This is made possible by the interest they charge on loans or overdrafts and interest they pay to customers.
b. Factors that affect credit creation abilities of commercial banks;
i. Collateral security available: If collateral security is not available, banks will be scared of lending, hence the lower the volume of money created.
ii. Central Bank restriction: Central bank may sometimes restrict them from lending e.g. Open Market Operation, Special Directive e.t.c.
iii. Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) : The higher the CRR, the lower the ability of commercial banks to create money.
iv. Interest Rate Charged: The higher the rate of interest charged, the lower the interest of customers to obtain loans as they are discouraged, hence the lower the ability of commercial banks to create money and vice versa.
v. Willingness of the public to take bank loans: Commercial banks are able to create money when the public are willing to take bank loans and overdraft. Without these, there won’t be interest to be charged.
vi. Desire of people to save: When people save, deposits are created and it is from these deposits that banks give out loans. So, the more people save, the more the banks are able to create credit or money and vice versa.
Instruction: Answer all the following questions using the form below.
Objective Test
1. The money payment made to owners of land and labour are
a. rent and wages b. interest and profit c. wages and profit d. dividend and salary
2. The price elasticity co efficient indicates
a. how far business can reduce cost b. the degree of competition c. the extent to which demand curve shifts d. consumers responsiveness to price changes
3. Every society strives to pursue all the following economic objectives except
a. increased production b. price stability c. an inequitable distribution of income d. sustainable growth and development
4. Which of the following best describes capital as a factor of production?
a. a natural resource found everywhere b. a stock of physical asset used for production c. the organization of human and material resources for production d. resources used in training labour
5. The system whereby goods are exchanged for goods is known as
a. stock exchange b. barter exchange c. banking d. co operative system
6. The graph of the function x = a + by is
a. linear b. quadratic c. cubical d.. exponential
7. Productivity per worker is best measured by
a. total output less number of workers b. total output multiplied by number of workers c. number of workers less total output d. total output divided by number of workers
8. In determining cost, economists consist of
a. implicit cost b. explicit cost c. implicit and explicit cost d. explicit cost less implicit cost
9. The precautionary motive of holding money is to enable the holder to
a. buy stocks when interests are high b. overcome unforeseen circumstances c. buy goods and services on a daily basis d. buy fixed assets
10. In the long run, all factor inputs are
a. variable b. diminishing c. constant d. fixed
11. The benefits that results from concentrating similar firms in an area is referred to as
a. external diseconomies of scale b. internal diseconomies of scale c. internal economies of scale d. external economies of scale
12. Per Capital Income in any West African country is measured by
a. dividing the GNP by total population b. adding the total savings to the GNP c. multiplying the GNP by the total population d. subtracting the GNP from the GDP
13. A priority rating of aggregate individual wants is called
a. scarcity b. choice c. scale of preference d. opportunity cost
14. Profit can be calculated by
a. subtracting total cost from total revenue b. subtracting average revenue from total cost dividing total revenue by total output d. dividing marginal revenue by marginal cost
15. The marginal revenue curve of a of a monopolist is
a. upward sloping from right to left b. downward sloping from right to left c. parallel to the quantity axis
d. downward sloping from left to right
16. When all factor input are doubled, the production possibility curve will
a. left to right and return to its original position b. shift from left to right c. shift from right to left d. remain in its former position
17. Income elasticity of demand is the measurement of the responsiveness of
a. price to changes in income b. quantity demanded to changes in income c. changes in expenditure to changes in income d. changes in expenditure to changes in price of the commodity
18. The establishment of industries in rural areas will help to reduce
a. rural-urban migration b. urban-urban migration c. urban-rural migration d. rural-rural migration
19. Government impose taxes mainly to
a. punish the citizens b. provide social amenities c. donate to poorer countries d. execute white elephant projects
20. In a perfect market, price and quantity to be bought are determined by the
a. consumers and retailers b. producers and wholesalers c. forces of demand and supply d. interest of government and producers
21. When the price elasticity of supply is equal to 0.4, supply is said to be
a. inelastic b. elastic c. unitary elastic d. perfectly elastic
22. In the money market, money can only be borrowed for
a. long term b. short term c. capital projects d. public utilities
23. Deflation can be controlled by increase in
a. the bank rate b. income tax c. the price level d. the budget deficit
24. Mortgage banks give loans to investors on long term basis to
a. finance agriculture b. establish banks c. acquire machinery d. build houses
25. The situation whereby a government spends more than its budget for a fiscal year is known as
a. extra budget b. surplus budget c. mid-year budget d. deficit budget
26. In a socialist economy, factors of production are owned and controlled by the
a. citizens b. businessmen c. government d. foreigners
27. One quality of money which makes it possible to be easily carried is its
a. scarcity b. durability c. portability d. acceptability
28. A form of tax in which the poor pays a higher rate than the rich is known as
a. regressive tax b. proportional tax c. oppressive tax d. progressive tax
29. The reduction in the value of a country’s currency in relation to the value of currencies of other nations is known as
a. deflation b. devaluation c. inflation d. revaluation
30. The creation of utility can be referred to as
a. value added b. profit maximization c. entrepreneurship d. production
31. Government revenue will increase if tax is imposed on a good whose demand is
a. elastic b. inelastic c. unitary elastic d. perfectly elastic
32. Occupational distribution of population is mainly influenced by
a. economic factors b. religious factors c. geographical factors d. social factors
33. Proportional tax refers to
a. taxation of the rich only b. equal tax for all people c. unequal tax for all people d. taxation of civil servants only
34. Which of the following is not an item of capital expenditure?
a. construction of highways b. building of dams c. payment of salaries and wages d. building of new universities
35. The population which yields the highest income per head is known as
a. over population b. under population c. extreme population d. optimum population
36. Price discrimination can only occur when there is
a. perfect competition b. imperfect competition c. merger d. partnership
37. Commodity market can best be described as a market in which
a. goods are sold b. labour is sold and bought c. short term loans are obtained d. quoted stocks are bought
38. Provision of services is classified under
a. primary production b. secondary production c. tertiary production d. production possibilities
39. In ordinary partnership, the risks are
a. borne by the workers b. borne by the creditors c. shared among the partners d. undertaken by the active partners
40. Balance of trade is defined as the relationship between
a. invisible imports and export b. visible and invisible exports c. imports and exports services
d. visible exports and visible imports
Theory Questions
- Define the following terms:
a. Overdraft
b. Standing order
c. Bill of exchange
d. Passbook
e. Cheque
2. State 4 types of cheque.
22/06/2020
LESSON SIX: POPULATION/FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS
Good day to you all. We thank God for the gift of life and that we are well. Please continue to take advantage of this period and opportunity to groom yourself to become a better person. We pray that all this will soon be over and we will have our lives back. You will not be a victim of circumstance in Jesus name. You will fulfill your purpose and destiny in Jesus name. Stay connected to your maker.
Correction To Lesson Five’s Assignment – Market Structures (16/6/2020)
Study this carefully and do your corrections.
1a. A market can be described as any form of arrangement where buyers and sellers come in contact for the purpose of buying and selling.
b. Features of a Perfect Market
i. Large number of buyers and sellers: There are a large number of buyers and sellers because there are no restrictions to entry.
ii. Free entry and exit: Here, nobody is deprived of being a buyer or seller because there are no restrictions to entry. There are no legal formalities that restricts an interested member from buying or selling.
iii. Homogenous Goods: Goods sold in this market are identical, so buyers cannot give preference to one product over another.
iv. No preferential treatment: Equal treatment is given to all categories of buyers in this market. Everybody is treated alike. If anyone is treated poorly, the next seller will be readily available to attend to such a customer.
v. No government intervention: IN a perfect market, the government do not control the prices at which commodities are sold. Prices are determined through price system.
c. Similarities between monopolistic competition and perfect competition.
– They both maximise profit when MC=MR
– Both have large number of buyers and sellers
– There is free entry and exit in both
– Both can make abnormal profit in the short run
Differences between monopolistic competition and perfect competition.
| Monopolistic competition | Perfect competition | |
| 1 | Differentiated products are sold here | Identical goods are sold here |
| 2 | There is high degree of control over price (price variation exists) | Price is constant and determined by price system |
| 3 | When in equilibrium, Price is higher than both MC and MR | At equilibrium, MC=MR=P |
| 4 | It is a reality i.e. can exist in real life | It does not exist in real life situation |
2.

3ai. To make profit.
ii. When losses are made.
b. Consumers benefit from perfect competition in the following ways;
i. Competition allows consumers to benefit from lower prices.
ii. It promotes production of good quality goods.
iii. Efficient allocation of resources enables producers to produce what the consumers want.
c. Profit is maximised for a perfect competitor when;
i. MC=MR
ii. AC curve falls below the AR curve.
iii. MC curve cuts MR curve from below.
4.

Today, we shall be reviewing the topic POPULATION and questions on FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS.
Population can be described as the total number of people living within a country or a particular geographical area at a point in time. Population is said to be dynamic and not static because it changes from time to time. It is affected by the following factors;
a. Birth/Fertility rate
b. Death/Mortality rate
c. Migration which is divided into emigration and immigration.
The population of a place can be grouped or classified using the following criteria;
a. Sex distribution
b. Age distribution
c. Geographical distribution
d. Occupational distribution
Types of Population
a. Optimum population: This is the population which when combined with the available resources and the given level of technology brings about the maximum output per head. It is the population that is neither too small nor large.
b. Over population: This can be defined as the population where we have more people than the available resources that can support the living standard of the people.
c. Under population:In this type of population, the population of people is less than the available resources.

Revision Questions on Population
Instruction: kindly submit your homework using the form below. To attach your DIAGRAMS USE THE UPLOAD FILES AT THE BEGINNING OF THE PAGE. THANK YOU.
1a. Differentiate between population and population census.
b. What is;
i. birth rate
ii. death rate
iii. natural growth rate?
c. Give two reasons why people migrate.
2. The table below shows the age distribution of a hypothetical population:
| Age | Number of People(million) |
| Under 20 | 20.90 |
| 20-29 | 13.75 |
| 30-59 | 12.10 |
| 60 and above | 8.25 |
| Total | 55.00 |
Present the information in the form of a pie chart. Show your workings clearly.
3. The data here shows an hypothetical age distribution of the population of a town in Nigeria.
Sex Age in Years
| 10 &Below | 11-14 | 15-35 | 36-64 | 65&above | |
| Male | 1350 | 2275 | 1135 | Y | 3250 |
| Female | 2650 | 2725 | 1365 | 4265 | Z |
| Total | 4000 | X | 2500 | 7500 | 6000 |
From the data, calculate
a. X, Y, Z
b. The total population of the town.
c. The difference between the population of male and female aged 14 and below.
d. The percentage of the population aged 14 and below.
e. The dependency ratio of the town.
4.Differentiate between treasury bill and treasury certificate.
5. Define the following terms:
a. savings account
b. current account
c. fixed deposit account
d. government bond
6a. What is credit creation?
b. Mention any 4 factors that affect the credit creation abilities of commercial banks.
NOTE: kindly submit your homework using the form below. To attach your DIAGRAMS USE THE UPLOAD FILES AT THE BEGINNING OF THE PAGE. THANK YOU.
15/06/2020
LESSON FIVE: MARKET STRUCTURES
Good day to you all. Believe you’re staying safe and responsible. Please continue to adhere strictly to the guidelines provided by the government.The Lord will continue to protect and keep us safe in Jesus name. Continue to put in the beautiful effort, you will see that it would pay off at the end of the day. Stay blessed.
Correction to Lesson Four’s Assignment (Cost and Revenue Concepts) 08/06/2020
2a. Profit can be defined as the difference between the total revenue and total cost. It is expressed as
TR-TC.
bi. Total Revenue (TR): This is the total amount of income generated from the sale of a firm’s products. It is expressed as
Price×Quantity Sold or AR × Quantity Sold.
ii. Average Revenue (AR): This is revenue per unit of product sold. i.e. the amount of money realised/gotten from the sale of on product. It is the price per unit of a firm’s product. It is expressed as
AR = TR
Q.
iii. Marginal Revenue (MR): This is the addition to total revenue as a result of selling an additional unit of the product . It is expressed as
MR = Change in TR
Change in Units Sold
iv. Average Fixed Cost (AFC): This is the fixed cost of producing one unit of output in a production process. It is expressed as
AFC = TFC
Unit of Output

MARKET STRUCTURES
A market can be described as any form of arrangement where buyers and sellers come in contact for the purpose of buying and selling. Market has two broad divisions, i.e.
1. Market according to goods and services sold in them. Examples are Labour Market, Commodity Market, Foreign Exchange Market, Stock Exchange Market, Money Market e.t.c.
2. Market according to prices. This is divided into
a. Perfect Market
b. Imperfect Market
REVISION QUESTIONS ON MARKET STRUCTURES
INSTRUCTION: Answer the questions using the form below. To attach your DIAGRAMS USE THE UPLOAD FILE AT THE BEGINNING OF THE PAGE. THANK YOU.
1a. Define a market.
b. Explain 4 features of a perfect market.
c. State any 2 ways by which monopolistic competition and perfect competition are the same and any 3 ways in which they are different.
2. With the aid of a diagram, explain the supernormal profit of a monopolist.
3a. Why would a producer
i. enter a competitive market?
ii. leave a competitive market?
b. In what 2 ways do consumers benefit from perfect competition?
c. Give 2 conditions necessary for profit maximization for a perfectly competitive firm.
4. Explain with diagram(s) the “short run” and “long run” equilibrium position of a firm in a perfectly competitive market.
NOTE: kindly submit your homework using the form below. To attach your DIAGRAMS USE THE UPLOAD LINK AT THE TOP OF THE PAGE. THANK YOU.
08/06/2020
LESSON FOUR: COST AND REVENUE CONCEPTS
Good day students, hope you had a great night. I want to appreciate all of you. Those who have been doing and submitting their assignment promptly, i say weldone and for those who have not been doing the revision exercises, please do so. The questions will help to refresh your memories and keep you on your toes. The Lord will continue to increase you in knowledge,wisdom and understanding in Jesus name. However, your last assignment were all muddled up because there were no names on them. Kindly ensure you include your name when using the upload file for easy identification. Thank you.
Correction to Lesson Three 01/06/2020( Theory of Cost and Revenue)
3b. Implicit costs are the costs which the owner of the firm directly incurs on factors of production or supplied by him e.g. owners managerial skills, owner’s-occupied buildings e.t.c.
Explicit costs are the payments made for resources that are from outside i.e. it comprises all direct payment made for materials used for production gotten from outside e.g. cash paid for transportation of raw materials, advertisement e.t.c.
LESSON FOUR: COST AND REVENUE CONCEPTS
INSTRUCTION: Kindly submit your answers using the form below.
1. The table below represents the output level of a particular firm producing soft drinks. Use the information in the table to answer the questions that follow;
Output(units)
0
24
46
72
96
116
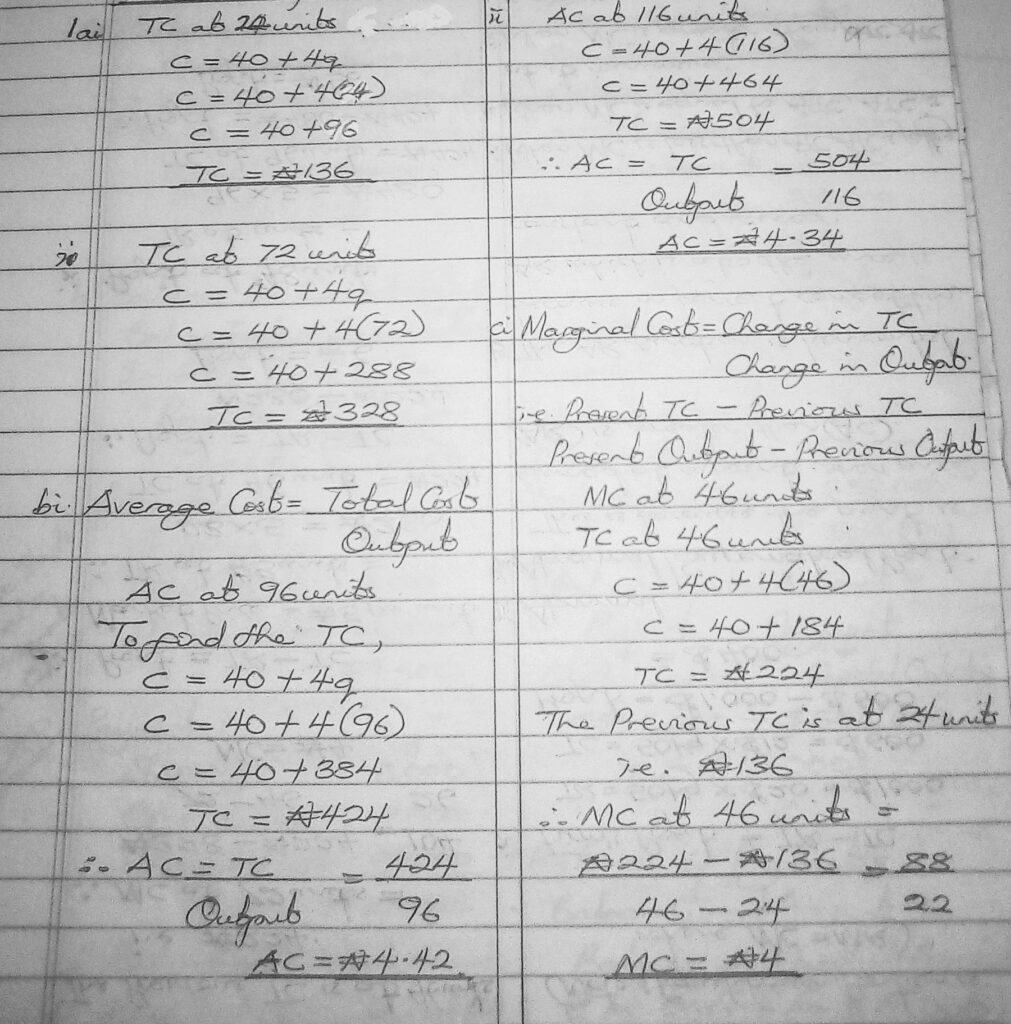
Given the cost equation of the firm in Naira as C=40+4q, where C is the total cost and Q is quantity produced. Calculate;
a. The total cost of producing;
i. 24 units
ii. 72 units of output.
b. The average cost when
i. 96 units
ii. 116 units were produced.
c. The marginal cost when
i.46 units
ii. 72 units were produced.
d. If the firm is operating in a perfectly competitive market and the market price is #5 per unit, determine the profit when;
i. 46 units are produced.
ii. 96 units are produced.
2a. Define profit of a firm.
b. With appropriate formulae, explain the following;
i. total revenue (TR)
ii. average revenue (AR)
iii. marginal revenue (MR)
iv. average fixed cost (AFC)
3. The diagram below represents the equilibrium position of a firm in a perfectly competitive industry. study it carefully and answer the questions that follow.
ai. At what level of output and price is the firm in equilibrium?
ii. Calculate the firm’s profit in equilibrium.
iii. What type of profit is it? Explain your answer.
b. Why is the average revenue (AR) function horizontal?
c. State any two ways in which marginal cost (MC) and average total cost (ATC) are related.
01-06-2020
LESSON THREE: COST AND REVENUE CONCEPTS
Good morning to you all and happy new month. I pray that this month will be a month of good tidings for each and everyone of us in Jesus name. The Lord will continue to keep us safe in Jesus name.
kindly find below the CORRECTION TO QUESTIONS THREE & FOUR, LESSON TWO. Take time to look at the note after the answers, it will definitely shed more light on the answers provided. Stay Blessed.
Study it carefully and make necessary corrections.
NOTE:
Capital account items have returns on them. Investment is an item in the capital account. It can either be an inflow i.e. imports(receipts) or outflow i.e. exports(payment). All things being equal, there would normally be returns on investment.
Unrequited transfers are voluntary transfer of money by a government in which little or nothing is expected in return. Examples are foreign aid, debt forgiveness, membership dues to an international organisation e.t.c. It is a unilateral transfer i.e. it is one sided and have no returns. It is treated in the current account along with other visible and invisible items of trade.
Today, we are going to review COST AND REVENUE CONCEPTS
Production can only take place when the factors of production are readily available in the right proportion. To get the factors of production money must be spent. The entire money put together to get, buy or spent on the factors of production is referred to as COST.
INSTRUCTION: Kindly submit your answers using the form below. To attach PICTURES/DIAGRAMS use the UPLOAD FILES AT THE BEGINNING OF THE PAGE. THANK YOU.
REVISION QUESTIONS
1a. In your own words, differentiate between cost and price.
b. Distinguish between the following;
i. Fixed cost and variable cost
ii. Marginal cost and marginal revenue
iii. Total cost and total revenue
iv. Average cost and average revenue
2. From the table below, answer the following questions;
| Output of Beans(kg) | Total Revenue(N) | Marginal Revenue(N) | Total Cost(N) | Marginal Cost(N) |
| 10 | 150 | – | 250 | – |
| 20 | 200 | 5 | 300 | 5 |
| 30 | 350 | 15 | 450 | 13 |
| 40 | 450 | F | 500 | 7 |
| 50 | 550 | 5 | 550 | M |
| 60 | 600 | 5 | 580 | 3 |
| 70 | 630 | X | 700 | 12 |
a. Complete the table by calculating the values of F,M and X.
b. What would be the profit-maximizing output of this firm?
c. If this firm were operating under perfect competition, what would be the price of its product
3a. Under which conditions will a firm continue to operate at a loss in the short-run? (Use figures or a diagram to explain your answer).
b. Distinguish between implicit and explicit cost.
No Fields Found.CORRECTION TO QUESTIONS ONE AND TWO, LESSON ONE
Study it carefully and make necessary corrections. Thank you.
Date: 25-05-2020
Good morning to you all. Believe your weekend was great. This week, we are still going to look at more questions on the topic INTERNATIONAL TRADE. The answers from our first lesson would be posted later today. This is to enable those who couldn’t submit last week to do so and those who submitted to do it again.
Remain blessed and continue to stay safe.
Note : If you have any difficulty in tackling the questions, kindly private chat me on WhatsApp 08030725755.
Thank you.
Revision Class Two
Topic: International Trade
Instruction: Kindly submit your answers using the form below.
1a. Define the term Balance of Payment.
b. What are the main components of balance of payment?
c. Explain each of the following terms;
i. Export promotion ii. Depreciation
iii. Devaluation iv. Terms of trade
v. Balance of trade.
d. What is economic integration?
e. Highlight any 3 problems of economic integration in West Africa.
2a. What is balance of payment disequilibrium?
b. Explain the two types of balance of payment disequilibrium.
c. Highlight any 4 reasons most West African countries are experiencing balance of payment problem.
d. Discuss the measures that can be taken by a country seeking to correct its balance of payment deficit.
e. How is balance of payment financed?
3. The table below shows the extract from the balance of payments for Country A. Use the table to answer the questions that follow:
| Items of Transaction | Receipts($) | Payment($) | |
| 1. | Merchandise(visible trade) | 52,000.00 | 40,000.00 |
| 2. | Shipping, other transport and travel | 4,000.00 | 8,000.00 |
| 3. | Investment Income | 20,000.00 | 5,000.00 |
| 4. | Other services | 2,500.00 | 7,500.00 |
| 5. | Unrequited transfers | 22,800.00 | 7,000.00 |
| 6. | Direct Investment | 50,000.00 | 26,000.00 |
| 7. | Other long-term capital | 254,000.00 | 289,000.00 |
| 8. | Short-term capital | 221,000.00 | 238,000.00 |
Calculate the; a. Balance of trade
b. Balance on current account
c. Balance on capital account
d. Balance of payment.
4. The table below shows the composition of exports and imports of a hypothetical country. Use the information to answer the question that follow.
| Exports | Amount $ | Imports | Amount $ |
| Crude Oil | 120,000,000 | Rice and Flour | 140,000,000 |
| Groundnuts | 40,000,000 | Petroleum Product | 80,000,000 |
| Tourism | 45,000,000 | Vehicles & Accessories | 50,000,000 |
| Shipping and Insurance | 60,000,000 | Banking Services | 60,000,000 |
| Bauxite | 80,000,000 | Freight and Insurance | 40,000,000 |
a. Calculate the value of visible exports.
b. Calculate the balance of trade for the country.
c. List the items of invisible exports and imports.
d. Calculate the current account balance of the country.
e. Is the country developed or developing? Give one reason for your answer.
No Fields Found.Date: 18-05-2020
Hello dear students, I believe you’re all doing great and staying safe. I can only imagine how tired you are waiting for the exam that is taking forever to start. The bible says the coming of the Lord will be like a thief in the night. For those that are prepared, it will be a day of rejoicing and opposite for those that are not prepared.
Please don’t get tired of waiting, see this time as an opportunity given to you by God to equip you and get strength in your weak areas for that outstanding result.
My prayer for you is that you will be battle ready, you will not be weary and thou it tarries the Lord will grant you grace to wait in Jesus name. It will be worth the wait by the grace of God and you will have a testimony.
Best wishes and lots of love.
Pending the time classroom revision will start, we would be using this forum for our revision. Kindly take advantage of this platform to groom yourself to be self confident.
Revision Class One: International Trade
Instruction: Go through the topic to refresh your memory and try to answer the questions without checking your note.
International Trade: This is the trade between two or more countries. It is divided into two;
a. Bi-lateral b. multi- lateral
It takes two forms;
a. Home/Domestic/Internal trade
b. International/Foreign/External trade
Basic Concepts of Foreign Trade
- Principle of Comparative Cost Advantage( propounded by David Ricardo)
- Terms of Trade
- Balance of Trade/Visible Balance
- Balance of Payment
- Principle of Absolute Advantage( propounded by Adam Smith)
Instruction: Answer the following questions and submit before the next class using the form below.
- The extract from a country’s balance of payments account is shown below.
| Items | Import($million) | Export($million) |
| Agricultural products | ——— | 200 |
| Mineral products | ——— | 300 |
| Consumer goods | 250 | ——– |
| Capital goods | 400 | ——– |
| Insurance | 50 | 25 |
| Banking | 75 | 30 |
| Transportation | 85 | 25 |
| Loans | 150 | 60 |
Using the table above, calculate the;
a. balance of trade
b. invisible trade balance
c. balance on current account
3. The table below represents an extraction from the balance of payments account of Country X in West Africa. Use the information in the table below to answer the questions that follow:
| Items | Receipts(in million$) | Payments(in million$) |
| Invisible import | ——- | 30 |
| Visible import | ——- | 40 |
| Invisible export | 20 | ——- |
| Visible export | 15 | ——- |
| Interest/Profit/Dividend | 4 | 25 |
- a. Calculate the balance of trade and comment on your answer.
b. If the price index for both import and export for country X are 400 000 and 300 000 respectively, determine the terms of trade.
c.Determine
i.the invisible trade balance
ii. the current account balance
d.Give an example each of visible import and an invisible export in any West African country. - Do have a rewarding day. Looking forward to hearing from you. God bless you.
